Sunlight Reflects off a Fish in Water
£0.00
This diagram is a new addition to the site! More information will be added ASAP 🙂
Description
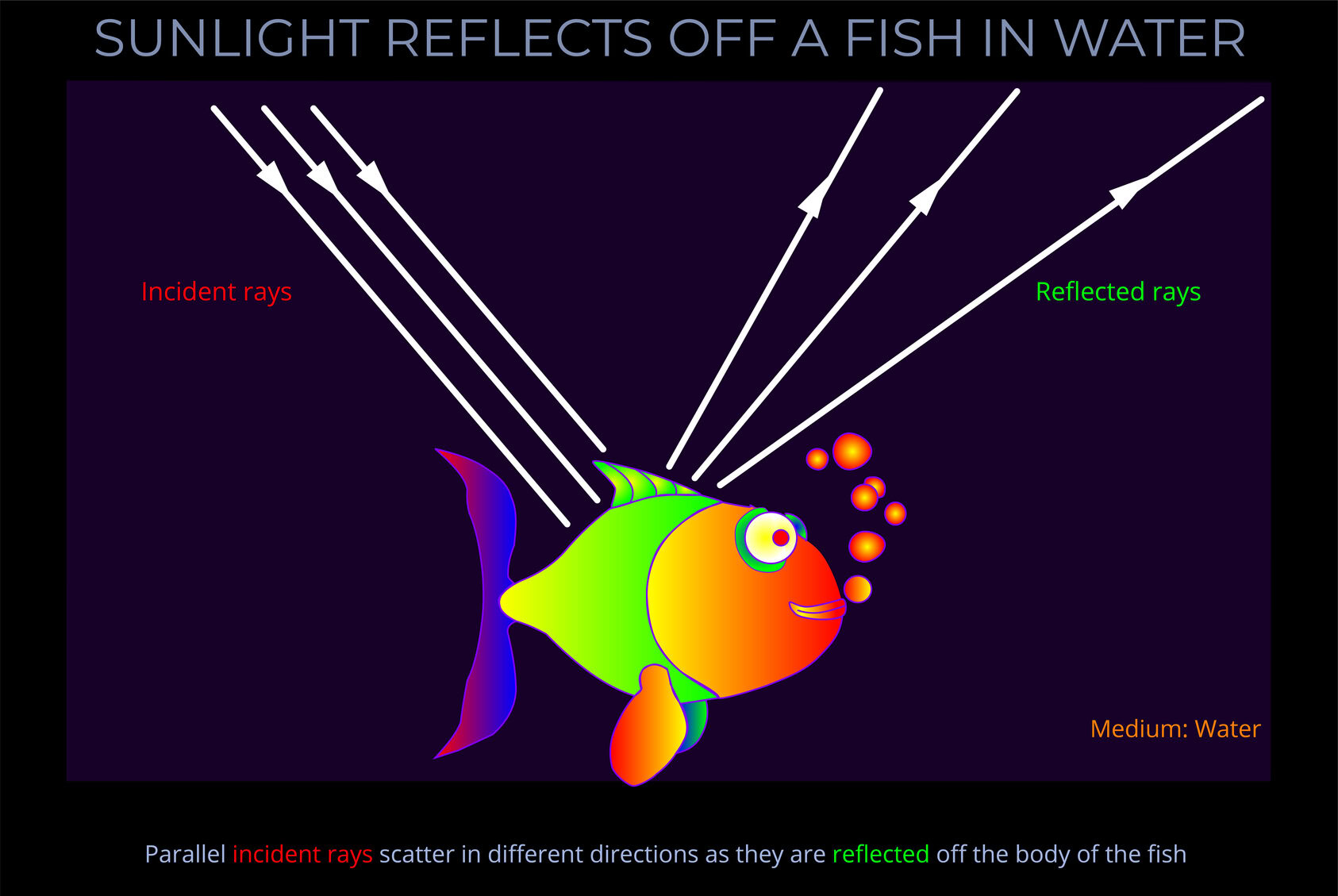
Sunlight Reflects off a Fish in Water
TRY SOME QUICK QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS TO GET STARTED
About the diagram
Have you already checked out An Introduction to Reflection, Refraction and Dispersion?
It is the opening page of our Reflection, Refraction and Dispersion Series and contains masses of useful information. This is the table of contents:
Overview
Everything we see in the world is a product of reflection. As light travels through the air it is invisible, but when light that has been reflected off the surface of an object enters our eyes it forms an image that light-sensitive cells react to. Let’s take a close look at the basics of reflection.
When you have reviewed this page, find out more on the following pages:
- Refraction, Reflection and Total Internal Reflection
- Actual and Observed Position of an Object in Water
The diagram
This diagram shows sunlight being reflected off a fish in water and provides a close-up view of what is happening in another of our diagrams: Refraction, Reflection and Total Internal Reflection.
- The source for the incident rays is sunlight. It this situation the Sun can be considered to transmit parallel rays of light.
- If each scale on the fishes skin has an uneven surface and causes the rays to scatter as they are reflected this causes diffuse reflection.
- Diffuse reflection takes place when light is scattered as it reflects off a rough surface. When reflected light scatters randomly it doesn’t produce a mirror-image.
- Some kinds of fish scales can appear iridescent. Iridescence is the phenomenon produced by certain surfaces that appear to gradually change colour as the angle of view or the angle of illumination changes. Other examples of iridescence include soap bubbles, feathers, butterfly wings and seashells. Iridescence is often created by microstructures that interfere with the path of light rays.
Some key terms
Reflection is the process where light rebounds from a surface into the medium it came from, instead of being absorbed by an opaque material or transmitted through a transparent one.
- The three laws of reflection are as follows:
- When light hits a reflective surface, the incoming light, the reflected light, and an imaginary line perpendicular to the surface (called the “normal line”) are all in the same flat area.
- The angle between the incoming light and the normal line is the same as the angle between the reflected light and the normal line. In other words, light bounces off the surface at the same angle as it came in.
- The incoming and reflected light are mirror images of each other when looking along the normal line. If you were to fold the flat area along the normal line, the incoming light would line up with the reflected light.
In physics and optics, a medium refers to any material through which light or other electromagnetic waves can travel. It’s essentially a substance that acts as a carrier for these waves.
- Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation, which travels in the form of waves. These waves consist of oscillating electric and magnetic fields.
- The properties of the medium, such as its density and composition, influence how light propagates through it.
- Different mediums can affect the speed, direction, and behaviour of light waves. For instance, light travels slower in water compared to a vacuum.
- Examples of Mediums:
- Transparent: Materials like air, glass, and water allow most light to pass through, with minimal absorption or scattering. These are good examples of mediums for light propagation.
- Translucent: Some materials, like frosted glass or thin paper, partially transmit light. They allow some light to pass through while diffusing or scattering the rest.
- Opaque: Materials like wood or metal block light completely. They don’t allow any light to travel through them.
Incident light refers to light that is travelling towards an object or medium.
- Incident light refers to light that is travelling towards an object or medium.
- Incident light may come from the Sun, an artificial source or may have already been reflected off another surface, such as a mirror.
- When incident light strikes a surface or object, it may be absorbed, reflected, refracted, transmitted or undergo any combination of these optical effects.
- Incident light is typically represented on a ray diagram as a straight line with an arrow to indicate its direction of propagation.
A light source is a natural or man-made object that emits one or more wavelengths of light.
- The Sun is the most important light source in our lives and emits every wavelength of light in the visible spectrum.
- Celestial sources of light include other stars, comets and meteors.
- Other natural sources of light include lightning, volcanoes and forest fires.
- There are also bio-luminescent light sources including some species of fish and insects as well as types of bacteria and algae.
- Man-made light sources of the most simple type include natural tars and resins, wax candles, lamps that burn oil, fats or paraffin and gas lamps.
- Modern man-made light sources include tungsten light sources. These are a type of incandescent source which means they radiate light when electricity is used to heat a filament inside a glass bulb.
- Halogen bulbs are more efficient and long-lasting versions of incandescent tungsten lamps and produce a very uniform bright light throughout the bulb’s lifetime.
- Fluorescent lights are non-incandescent sources of light. They generally work by passing electricity through a glass tube of gas such as mercury, neon, argon or xenon instead of a filament. These lamps are very efficient at emitting visible light, produce less waste heat, and typically last much longer than incandescent lamps.
- An LED (Light Emitting Diode) is an electroluminescent light source. It produces light by passing an electrical charge across the junction of a semiconductor.
- Made-made lights can emit a single wavelength, bands of wavelengths or combinations of wavelengths.
- An LED light typically emits a single colour of light which is composed of a very narrow range of wavelengths.
Scattering occurs when light waves interact with particles or irregularities within a medium, causing the light to change direction. This can happen when light encounters obstacles such as atmospheric molecules, dust particles, or surface imperfections.
- Scattering happens when individual photons or light waves are deflected in different directions, depending on the medium’s composition, particle size, and surface properties.
- Scattering contributes to various natural phenomena, such as the sky’s blue colour, the whiteness of clouds, and the shimmering of water surfaces.
- Scattering differs from other optical phenomena:
- Reflection: Light bounces back, as in a mirror.
- Refraction: Light is bent as it passes through different materials.
- Diffraction: Light spreads out after encountering an obstacle.
- Absorption: Light is absorbed by the material and not re-emitted.Scattering differs from other optical phenomena.
- Scattering can be effectively subdivided into regular scattering and random scattering, each characterized by distinct mechanisms and patterns of light interaction.