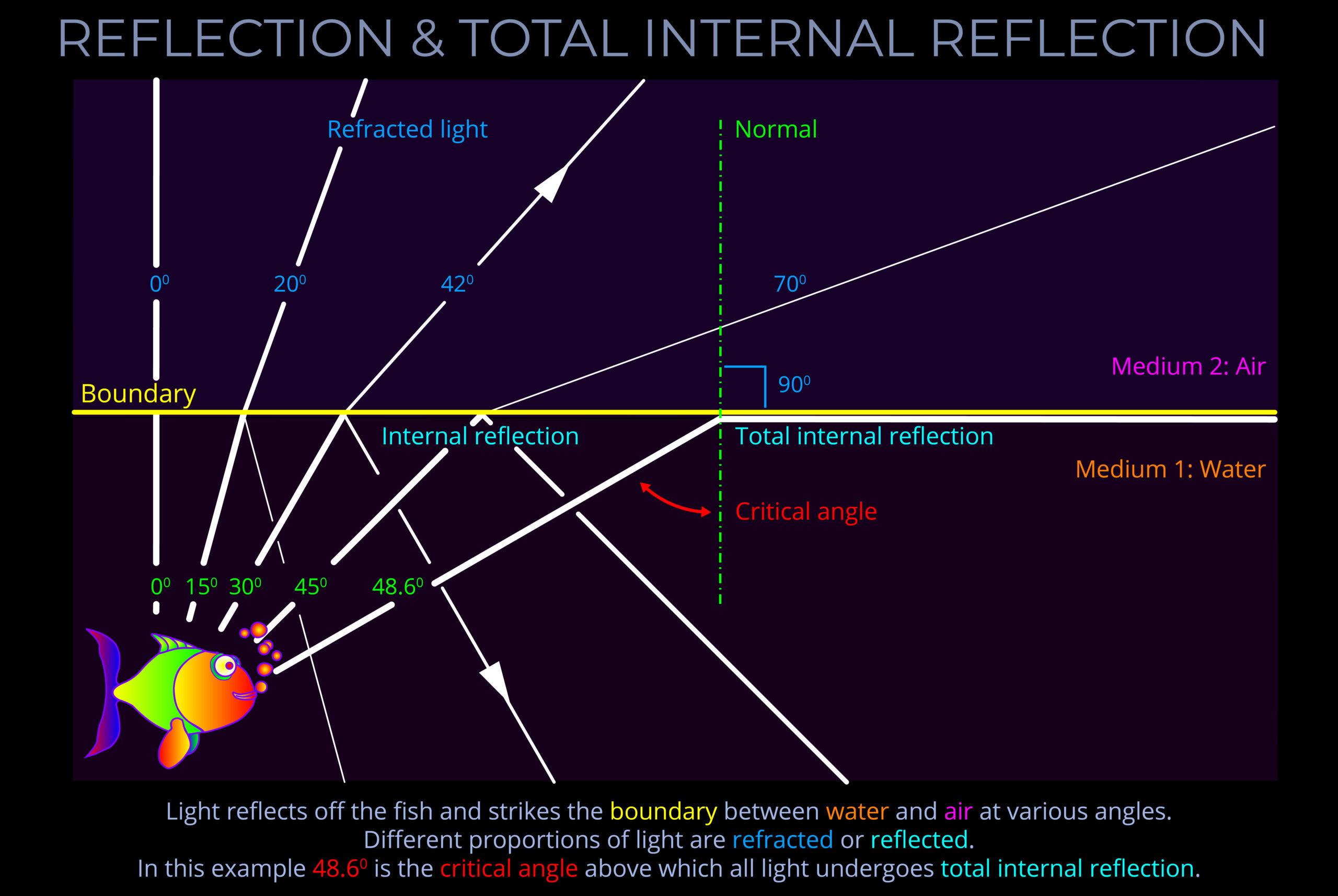
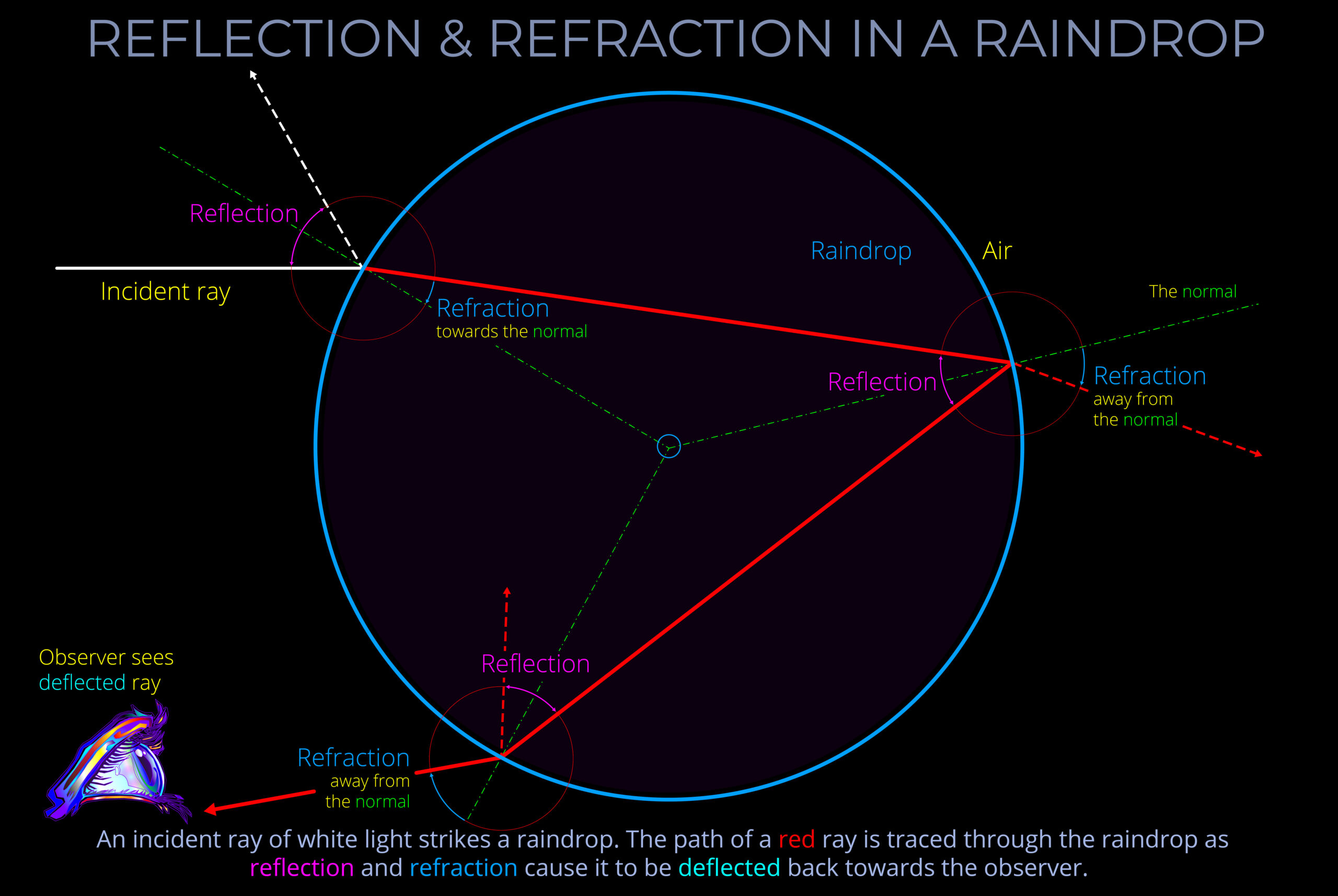
Reflection is the process where light rebounds from a surface into the medium it came from, instead of being absorbed by an opaque material or transmitted through a transparent one.
- The three laws of reflection are as follows:
- When light hits a reflective surface, the incoming light, the reflected light, and an imaginary line perpendicular to the surface (called the “normal line”) are all in the same flat area.
- The angle between the incoming light and the normal line is the same as the angle between the reflected light and the normal line. In other words, light bounces off the surface at the same angle as it came in.
- The incoming and reflected light are mirror images of each other when looking along the normal line. If you were to fold the flat area along the normal line, the incoming light would line up with the reflected light.
- The laws of reflection apply to both specular reflection, where light reflects off a smooth surface in a single direction, and to diffuse reflection, where light reflects off a rough surface in multiple directions.
- Specular reflection occurs when light waves reflect off a smooth surface, such as a mirror. The arrangement of the waves remains the same and forms an image of objects that the light has already encountered, which becomes visible to an observer.
- Diffuse reflection occurs when light reflects off a rough surface, such as a painted wall. In this case, scattering takes place, and waves are reflected randomly in many different directions, so no image is formed.
- Reflection occurs irrespective of the optical density of a medium through which the incident light is propagating or of the medium off which it bounces.
- Reflection is the process where light rebounds from a surface into the medium it came from, instead of being absorbed by an opaque material or transmitted through a transparent one.
- The three laws of reflection are as follows:
- When light hits a reflective surface, the incoming light, the reflected light, and an imaginary line perpendicular to the surface (called the “normal line”) are all in the same flat area.
- The angle between the incoming light and the normal line is the same as the angle between the reflected light and the normal line. In other words, light bounces off the surface at the same angle as it came in.
- The incoming and reflected light are mirror images of each other when looking along the normal line. If you were to fold the flat area along the normal line, the incoming light would line up with the reflected light.