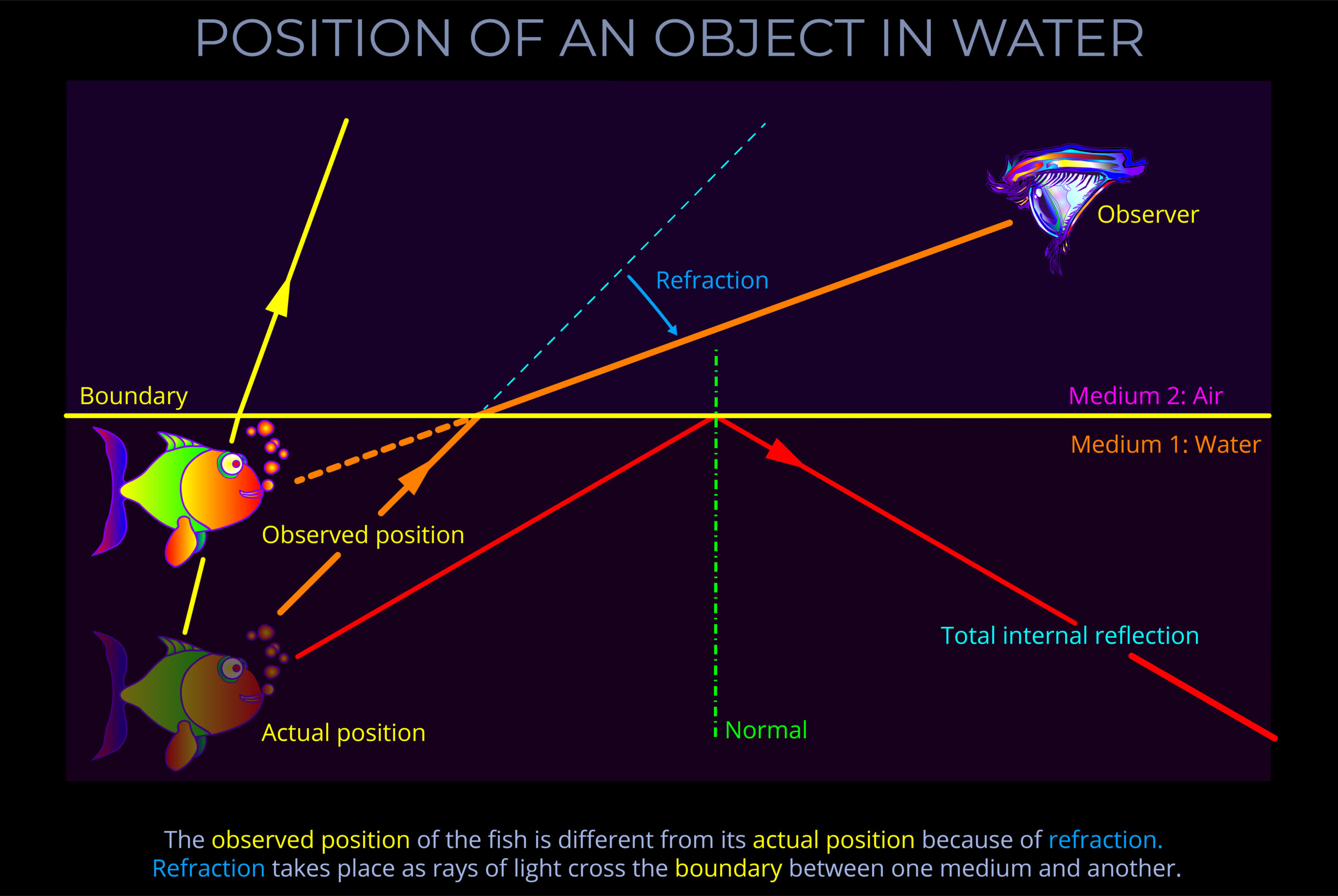
- Diffuse reflections occur when light scatters off rough or irregular surfaces.
- When microscopic features on a surface are significantly larger than the individual wavelengths of light within the visible spectrum, each wavelength of light encounters bumps and ridges exceeding their size.
- Instead of reflecting neatly in one direction, the light scatters in different directions.
- In this case, scattering doesn’t happen completely randomly. The surface features influence the direction of the scattered light, depending on the angle of incidence and the specific bumps and ridges it encounters.
- This scattering creates diffuse reflections, responsible for the soft, uniform illumination seen on textured surfaces like matte paint or unpolished wood.
- In the case of a matte phone screen, for example, the light doesn’t form a clear reflection of your face but rather creates a soft, hazy glow due to the scattered light.
- Even microscopic features smaller than wavelengths of visible light can contribute to diffuse reflection, especially for rough surfaces with complex geometries. These features can cause multiple reflections and scattering within the material, leading to a softer appearance.
- It is interesting to note that both diffuse and specular reflections involve all wavelengths of visible light (unless the surface specifically absorbs certain wavelengths). This explains why even diffuse reflections still appear colourful despite the scattering.
References
- In the field of optics, diffusion refers to situations that cause parallel rays of light to spread out more widely. When light undergoes diffusion it becomes less concentrated.Diffuse reflections occur when light scatters off rough or irregular surfaces.
- When microscopic features on a surface are significantly larger than the individual wavelengths of light within the visible spectrum, each wavelength of light encounters bumps and ridges exceeding their size.
- Instead of reflecting neatly in one direction, the light scatters in different directions.
- In this case, scattering doesn’t happen completely randomly. The surface features influence the direction of the scattered light, depending on the angle of incidence and the specific bumps and ridges it encounters.
- This scattering creates diffuse reflections, responsible for the soft, uniform illumination seen on textured surfaces like matte paint or unpolished wood.
- In the case of a matte phone screen, for example, the light doesn’t form a clear reflection of your face but rather creates a soft, hazy glow due to the diffused light.