Wave propagation refers to any of the ways in which waves travel.
- Electromagnetic radiation propagates through space, carrying electromagnetic energy in the form of electromagnetic waves.
- The propagation of electromagnetic radiation through space is sometimes described in terms of photons rather than waves.
- Photons are particles that are sometimes used to explain the behaviour of electromagnetic waves.
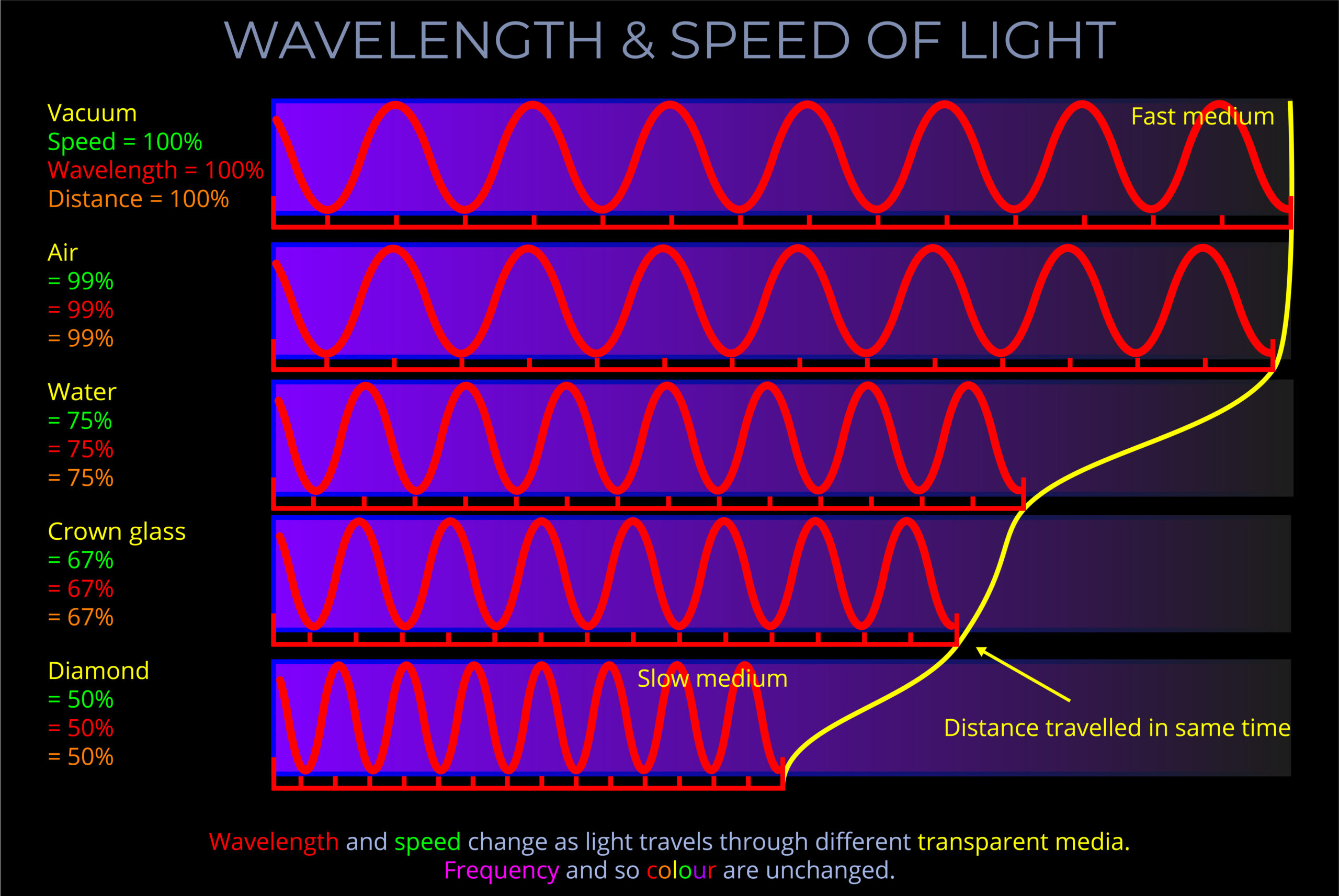
- Propagation of electromagnetic waves can occur in a vacuum as well as through different media. Other wave types such as sound waves cannot propagate through a vacuum and require a transmission medium.
- All forms of electromagnetic radiation propagate in similar ways whether they are radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visible) light, ultraviolet, X-rays or gamma rays.
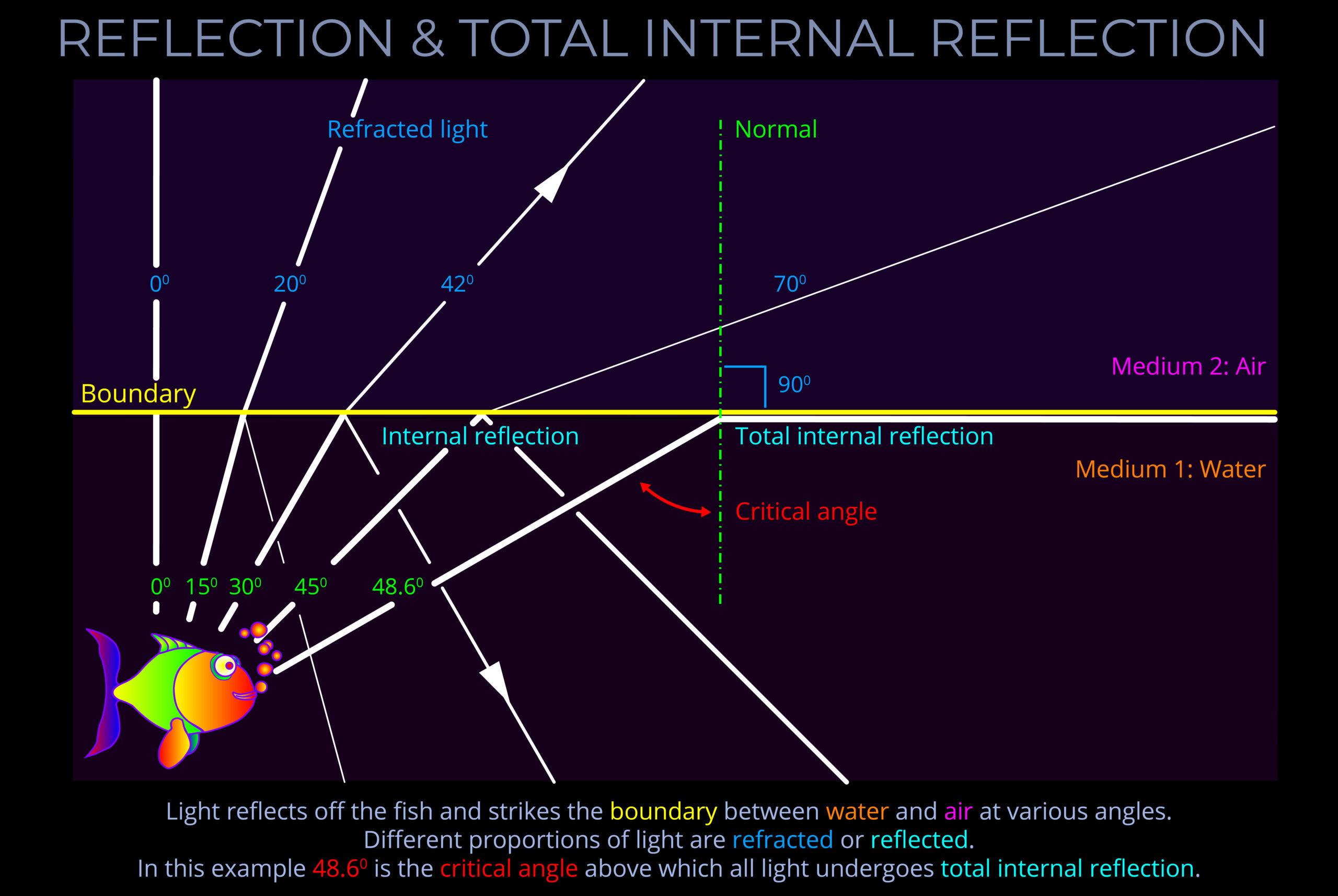
- When a light wave encounters an object, it may be transmitted, reflected, absorbed, refracted, polarized, diffracted, or scattered depending on the composition of the object and the wavelength of the light.
- The speed of electromagnetic waves as they propagate through a vacuum is a constant ie. 299,792,458 meters per second. This constant speed is a fundamental principle of physics.