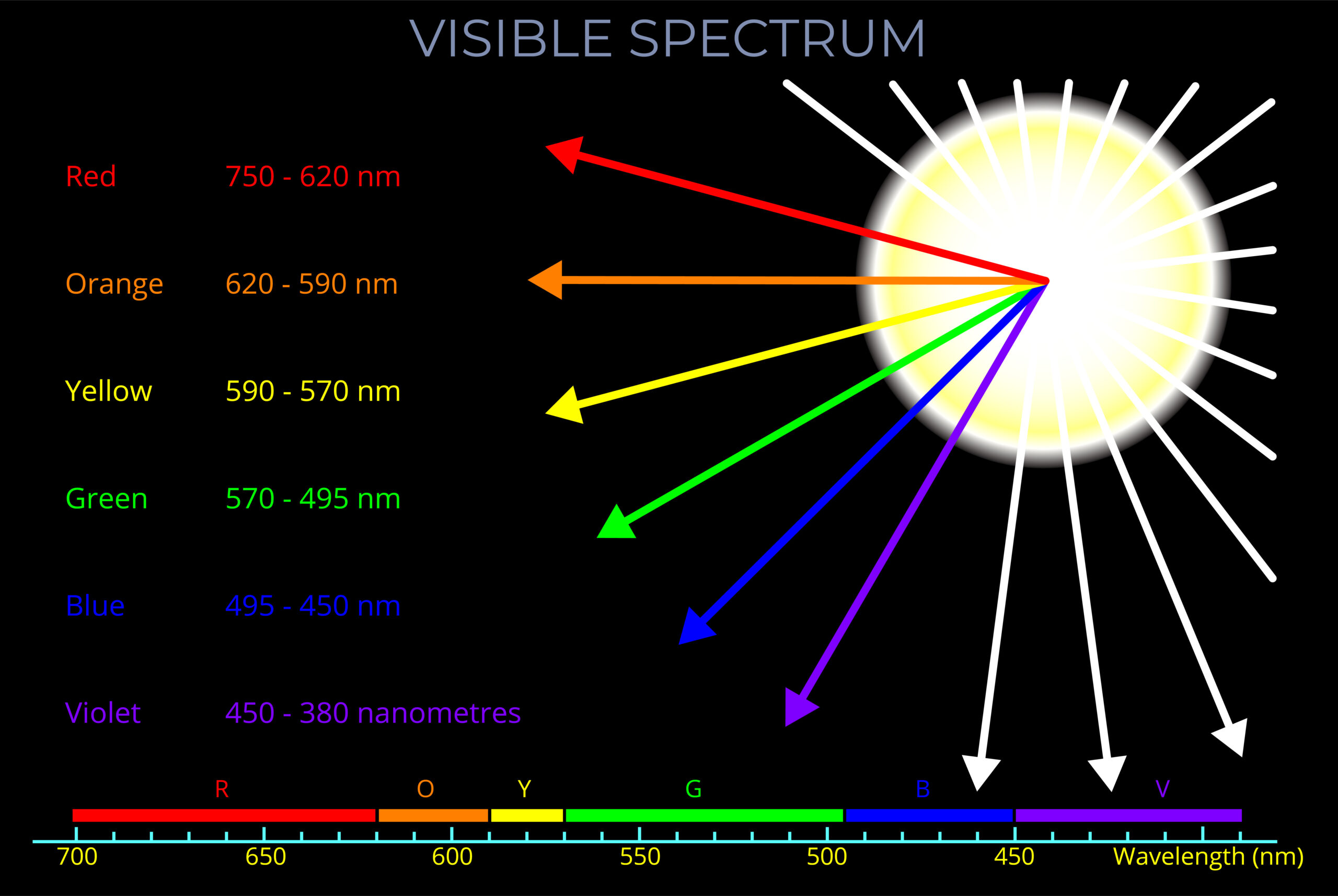
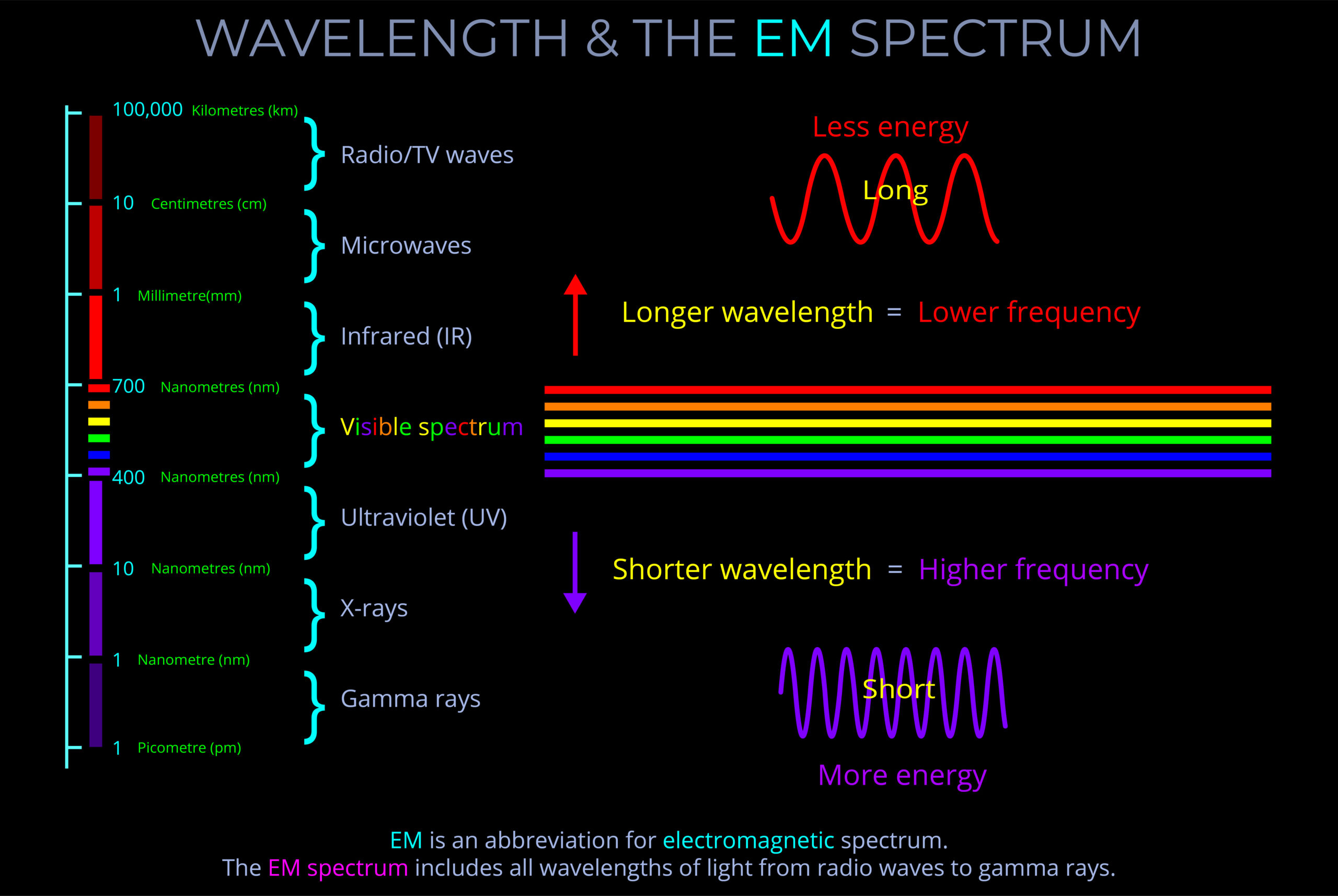
Electromagnetic radiation refers to the transfer of all forms of radiation through space by electromagnetic waves (or their quanta, photons) . This includes gamma rays, ultraviolet (UV), infrared (IR), X-rays, and radio waves, as well as visible light.
- Detached from its source, electromagnetic radiation (EM radiation or EMR), is transported by electromagnetic waves and propagates through space at the speed of light.
- Man-made technologies that produce electromagnetic radiation include radio and TV transmitters, radar, MRI scanners, microwave ovens, computer screens, mobile phones, all types of lights and lamps, electric blankets, electric bar heaters, lasers and x-ray machines.
- At the quantum scale of electromagnetism, electromagnetic radiation is described in terms of photons rather than waves. Photons are elementary particles responsible for all electromagnetic phenomena.
- The term quantum refers to the smallest quantity into which something can be divided. A quantum of a thing is indivisible into smaller units so they have no sub-structure. A photon is a quantum of electromagnetic radiation.
- A single photon with a wavelength corresponding with gamma rays might carry 100,000 times the energy of a single photon of visible light.
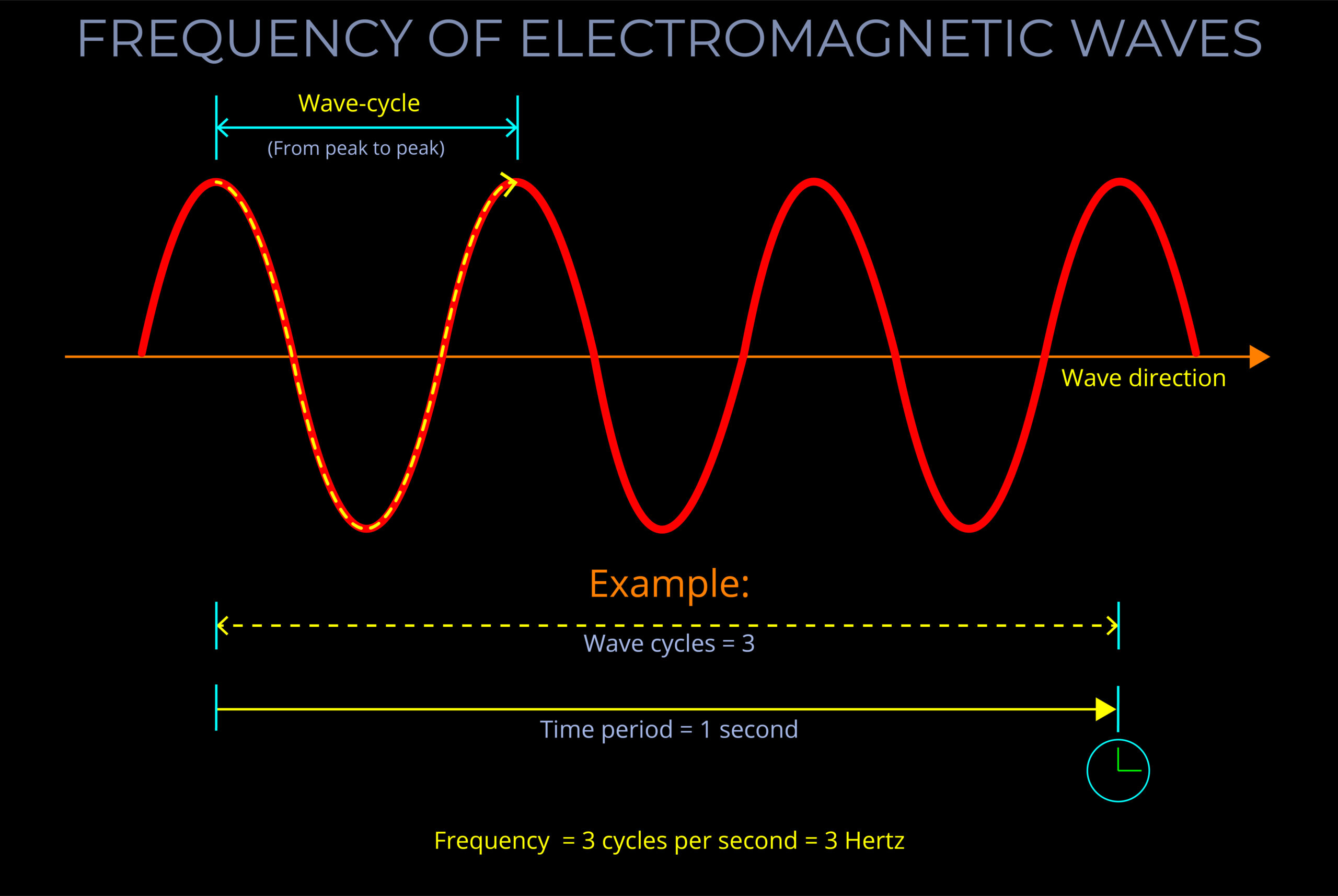
- Electromagnetic radiation has both energy and momentum. The energy of electromagnetic radiation is proportional to its frequency, while the momentum of electromagnetic radiation is proportional to its wavelength.
- In the context of electromagnetic radiation, proportional means that the energy and momentum of the radiation are directly related to its frequency and wavelength.
- As a result, if the frequency of the radiation increases, the energy and momentum of the radiation also increase. Similarly, if the wavelength of the radiation decreases, the energy and momentum of the radiation also increase.
Particle-wave duality
- The particle concepts, energy and momentum, and the wave concepts, frequency and wavelength, are all connected with particle-wave duality.
- Particle-wave duality is the concept that all objects have both particle-like and wave-like properties. This means that objects can behave like particles in some situations and like waves in other situations.
- Particle-wave duality can be seen in many different experiments. For example, if we shine a beam of light at a double slit, we will see an interference pattern on the screen behind the slits. This interference pattern is characteristic of waves. However, if we reduce the intensity of the light beam until only one photon is passing through the slits at a time, we will still see the interference pattern. This shows that the photon, which is a particle, is also behaving like a wave
Equations
- The energy and momentum of an object are related to its frequency and wavelength by the following equations:
E = hf
p = h/λ
where:
- E is the energy of the object
- p is the momentum of the object
- h is Planck’s constant
- f is the frequency of the object’s associated wave
- λ is the wavelength of the object’s associated wave
- These equations show that the energy and momentum of an object are directly related to the frequency and wavelength of its associated wave. This means that if an object has a higher energy or momentum, it will also have a higher frequency and wavelength.
Electromagnetic radiation is a type of energy more commonly simply called light. Detached from its source, it is transported by electromagnetic waves (or their quanta, photons) and propagates through space at the speed of light.
- Electromagnetic radiation (EM radiation or EMR) includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visible) light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays.
- Man-made technologies that produce electromagnetic radiation include radio and TV transmitters, radar, MRI scanners, microwave ovens, computer screens, mobile phones, all types of lights and lamps, electric blankets, electric bar heaters, lasers and x-ray machines.
- At the quantum scale of electromagnetism, electromagnetic radiation is described in terms of photons rather than waves. Photons are elementary particles responsible for all electromagnetic phenomena.
- The term quantum refers to the smallest quantity into which something can be divided. A quantum of a thing is indivisible into smaller units so they have no sub-structure. A photon is a quantum of electromagnetic radiation.
- A single photon with a wavelength corresponding with gamma rays might carry 100,000 times the energy of a single photon of visible light.