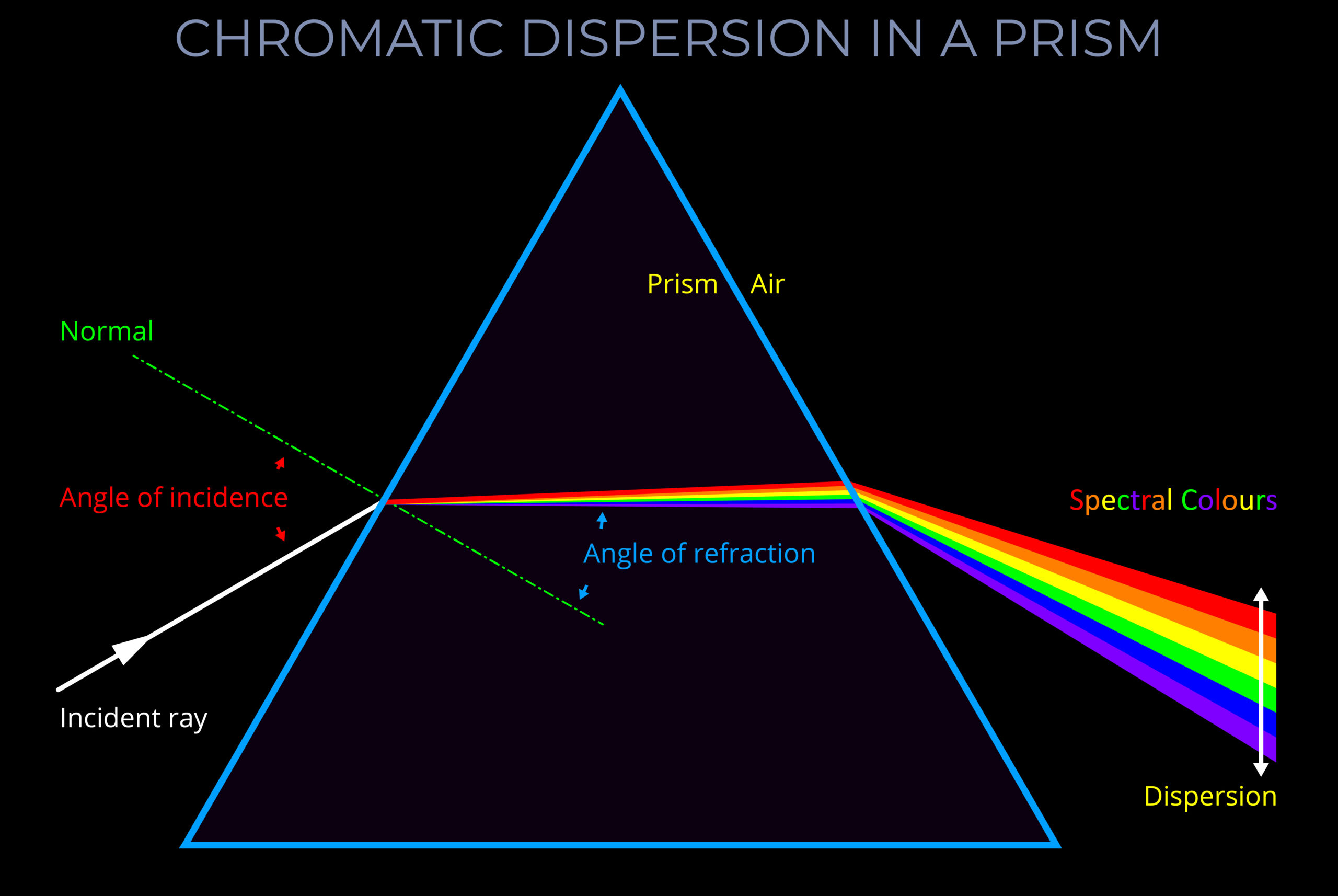
Chromatic dispersion is the process where light, under specific conditions, splits into its constituent wavelengths, and the colours linked with each wavelength become visible to a human observer.
- Chromatic dispersion denotes the process of separation according to colour.
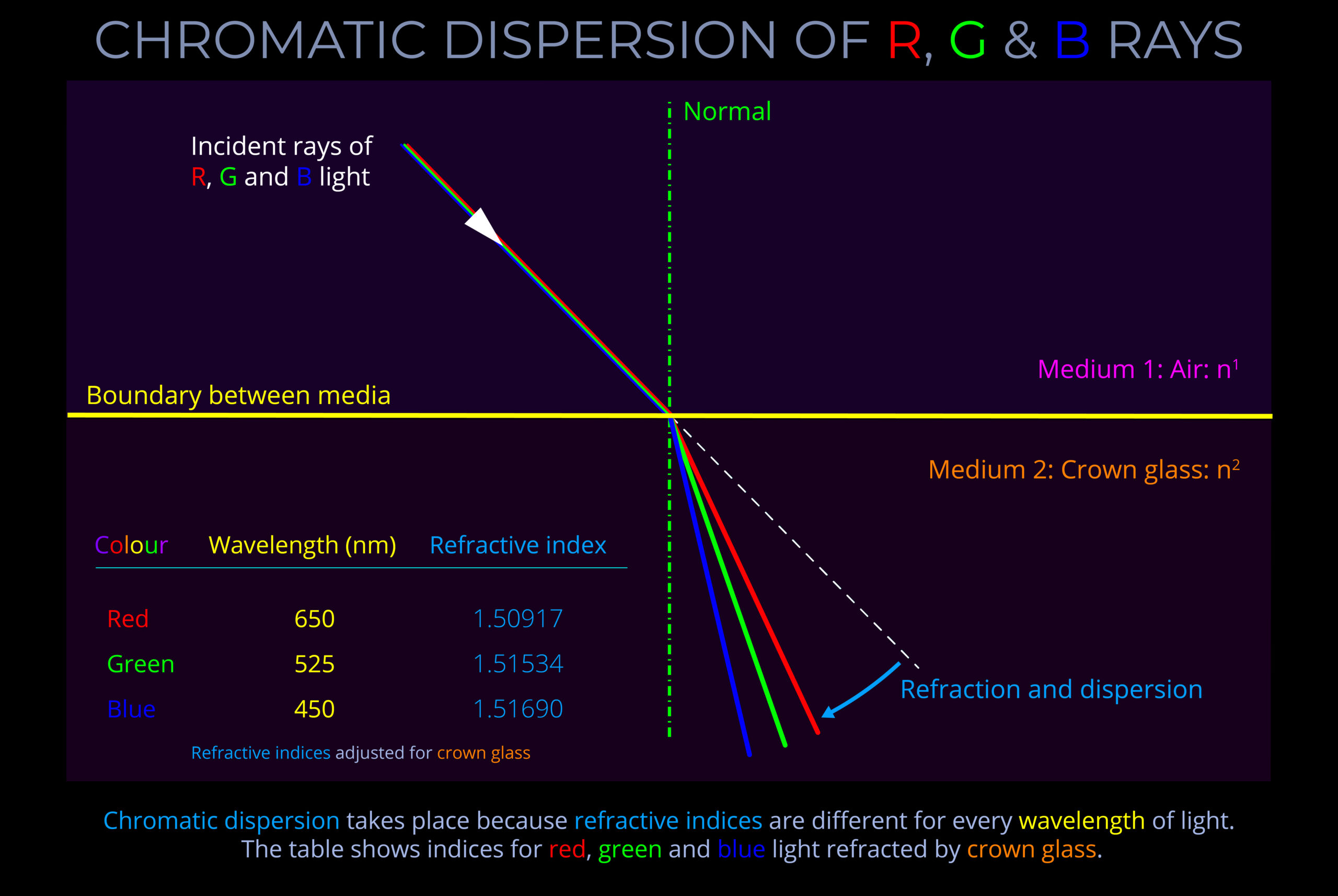
- Chromatic dispersion is the result of the connection between wavelength and refractive index..
- When light moves from one medium (like air) to another (like water or glass), each wavelength is influenced to a varying extent based on the refractive index of the involved media. The outcome is that every wavelength changes its direction and speed. If the light source emits white light, the individual wavelengths spread out, with red at one end and violet at the other.
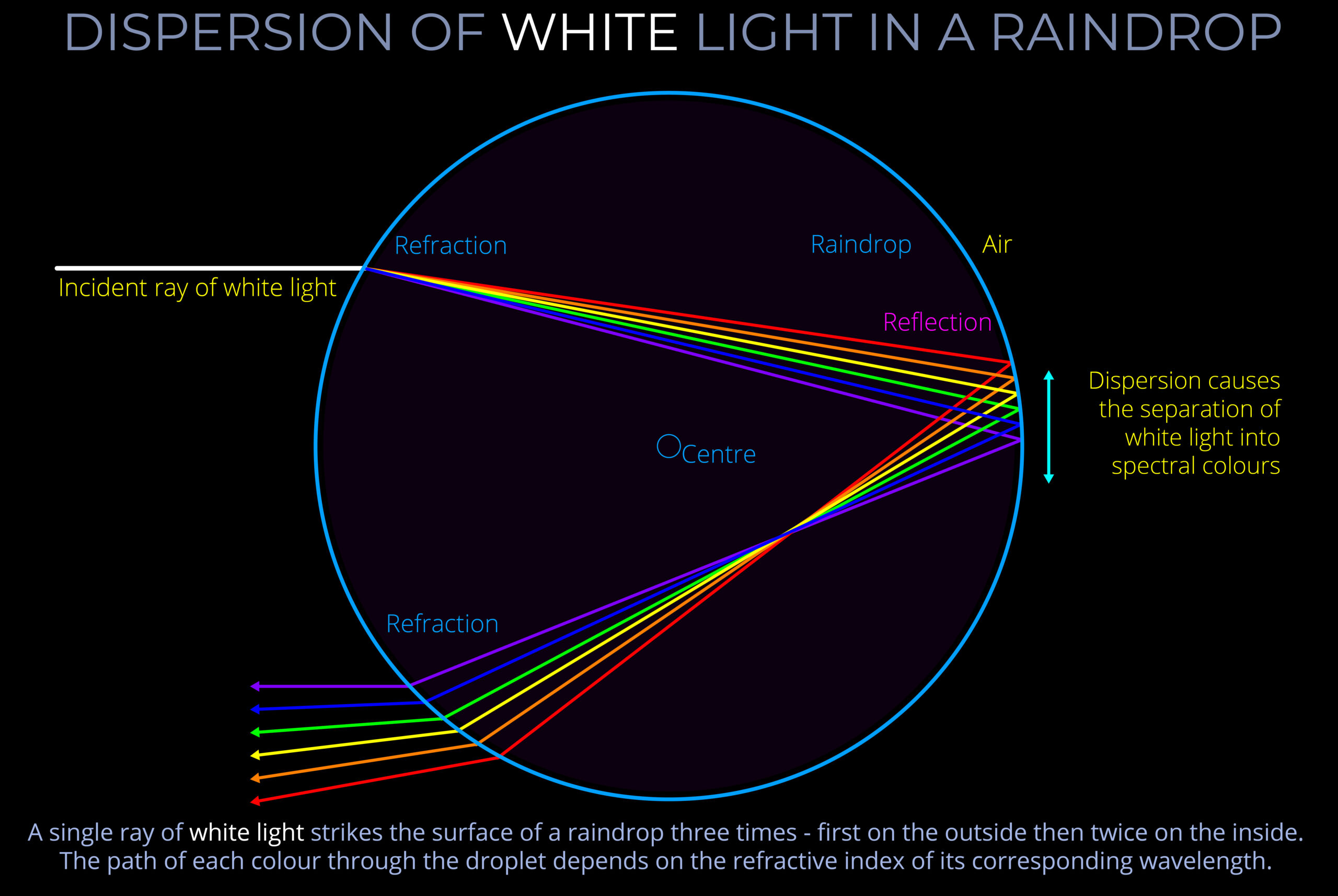
- A familiar example of chromatic dispersion is when white light strikes raindrops and a rainbow becomes visible to an observer.
- Keep in mind that wavelength is a characteristic of electromagnetic radiation, whilst colour is an aspect of visual perception.
- Chromatic dispersion is the process where light, under specific conditions, splits into its constituent wavelengths, and the colours linked with each wavelength become visible to a human observer.
- Chromatic dispersion is the result of the connection between wavelength and refractive index..
- When light moves from one medium (like air) to another (like water or glass), each wavelength is influenced to a varying extent based on the refractive index of the involved media. The outcome is that every wavelength changes its direction and speed.
- If the light source emits white light, the individual wavelengths spread out, with red at one end and violet at the other.
- A familiar example of chromatic dispersion is when white light strikes raindrops and a rainbow becomes visible to an observer.