In the field of optics, dispersion is shorthand for chromatic dispersion which refers to the way that light, under certain conditions, separates into its component wavelengths, enabling the colours corresponding with each wavelength to become visible to a human observer.
- Chromatic dispersion refers to dispersion of light according to its wavelength or colour.
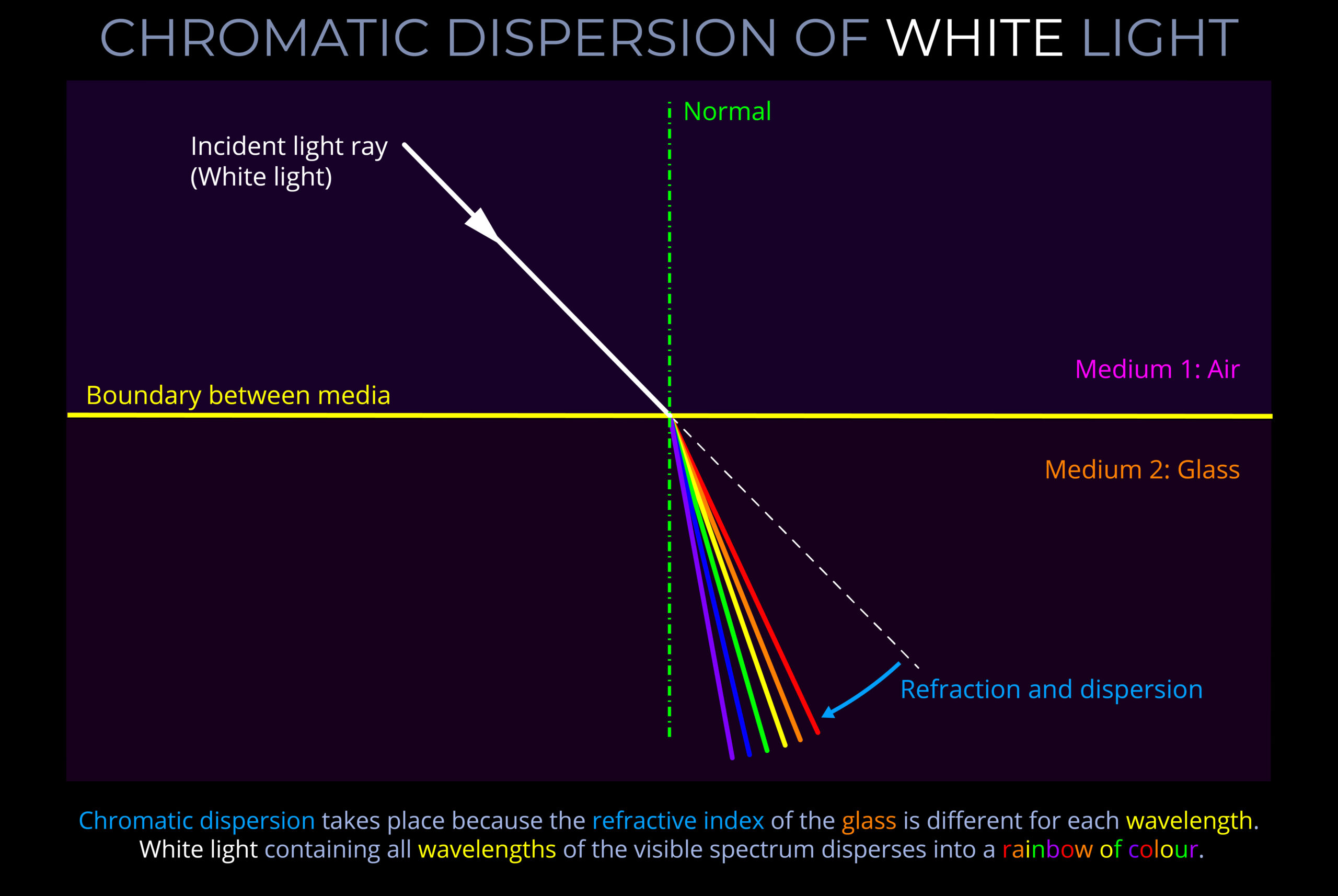
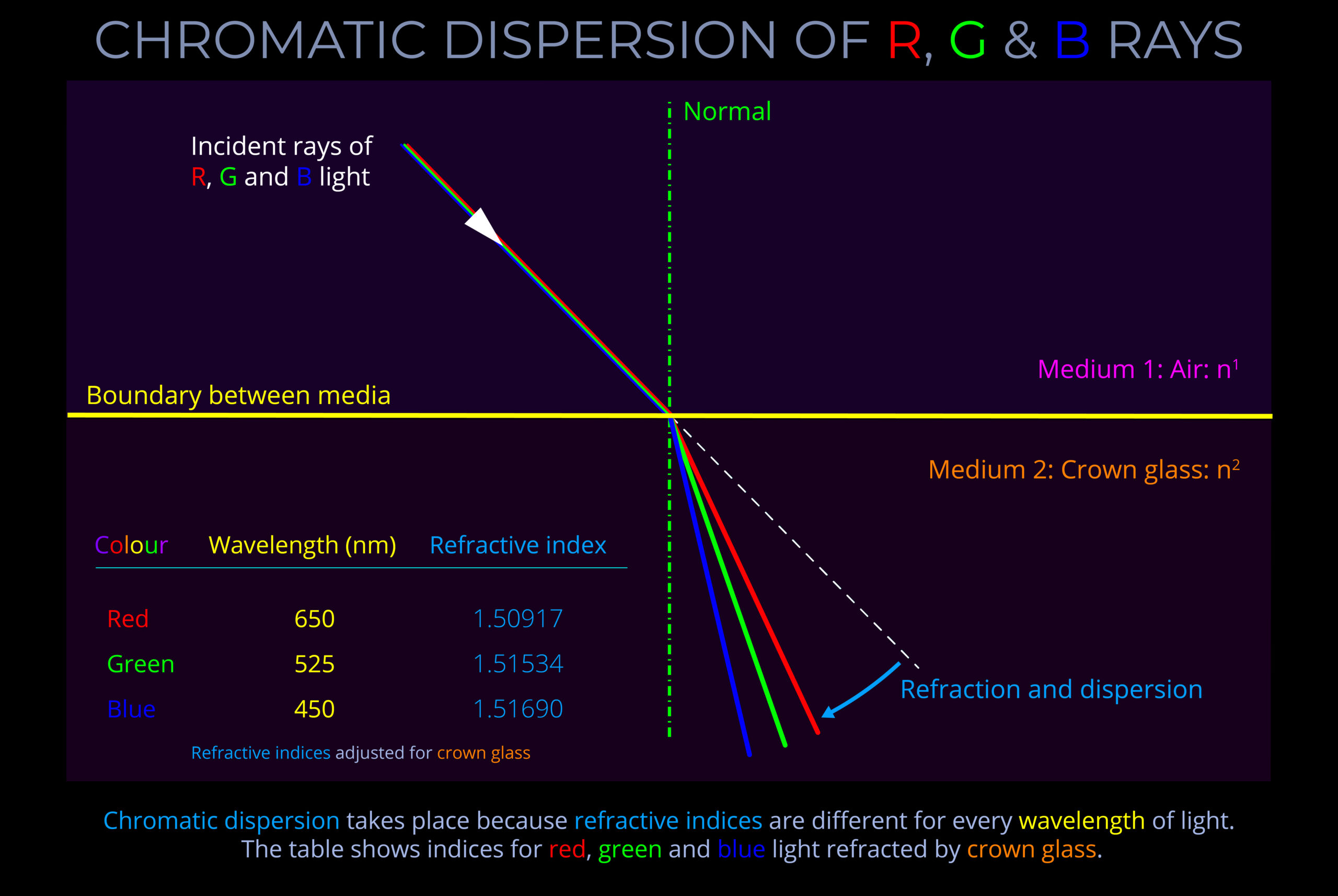
- Chromatic dispersion is the result of the relationship between wavelength and refractive index.
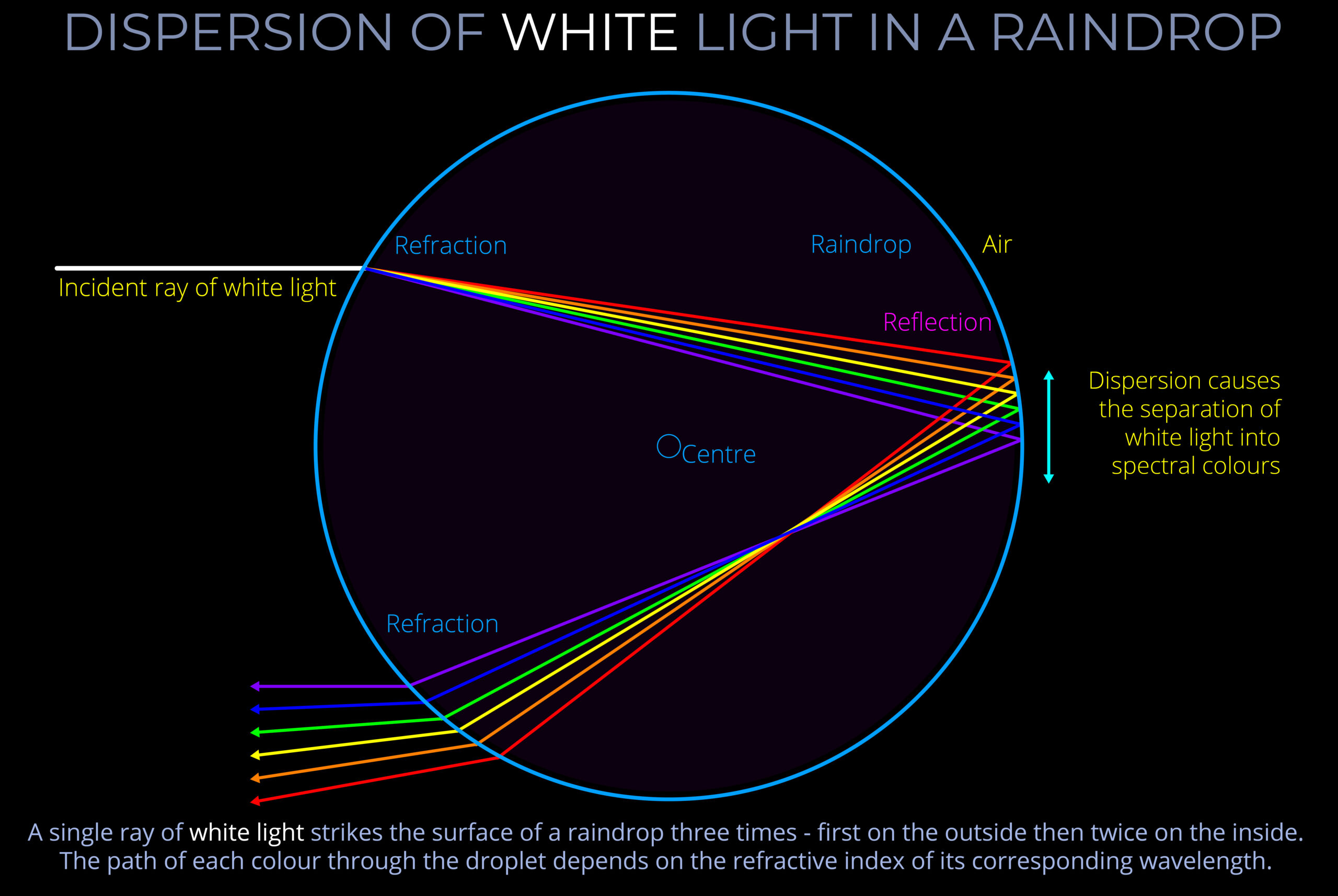
- When light travels from one medium (such as air) to another (such as glass or water) each wavelength is refracted differently, causing the separation of white light into its constituent colours.
- When light undergoes refraction each wavelength changes direction by a different amount. In the case of white light, the separate wavelengths fan out into distinct bands of colour with red on one side and violet on the other.
- Familiar examples of chromatic dispersion are when white light strikes a prism or raindrops and a rainbow of colours become visible to an observer.
- Remember that wavelength is a property of electromagnetic radiation, whilst colour is a feature of visual perception.