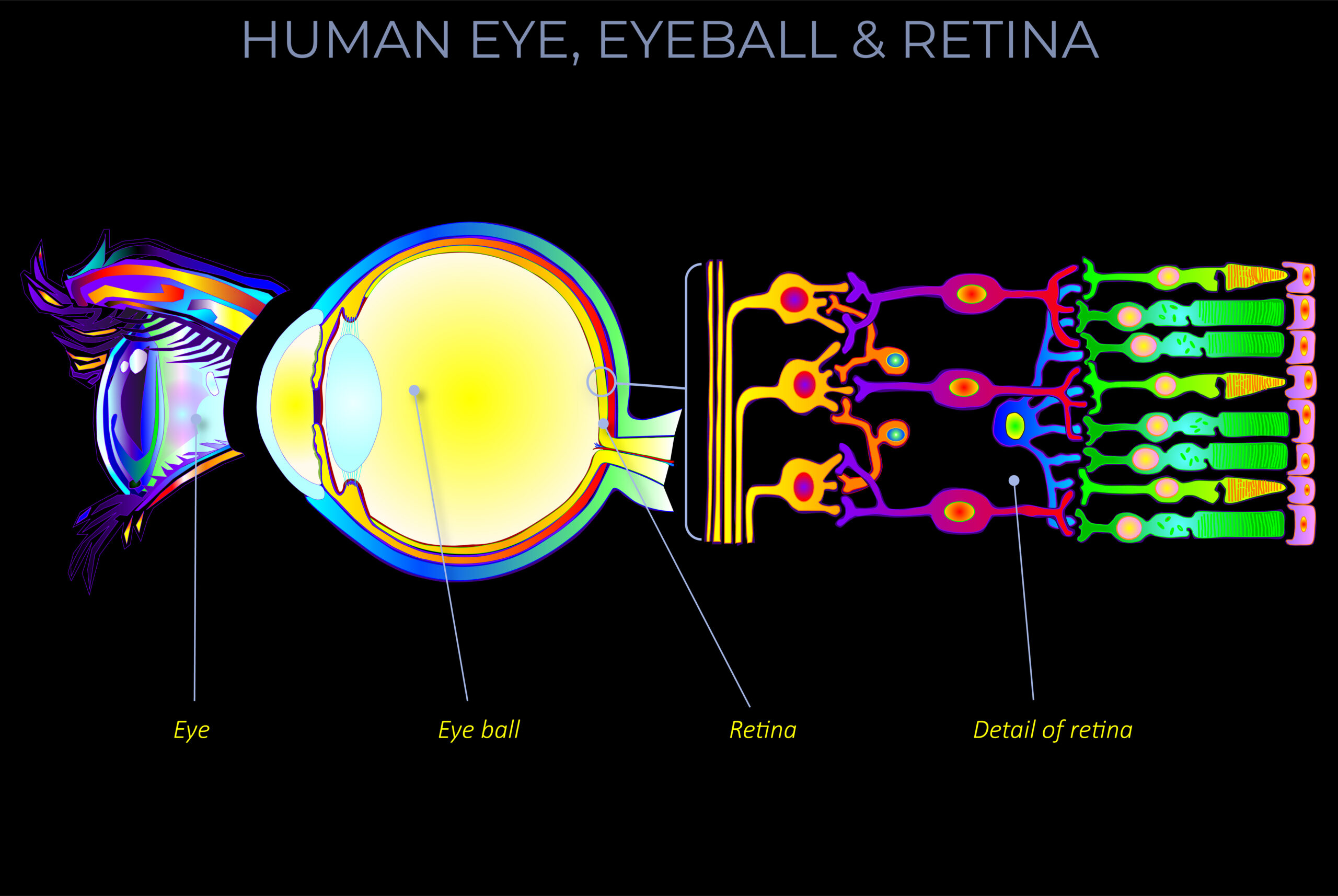
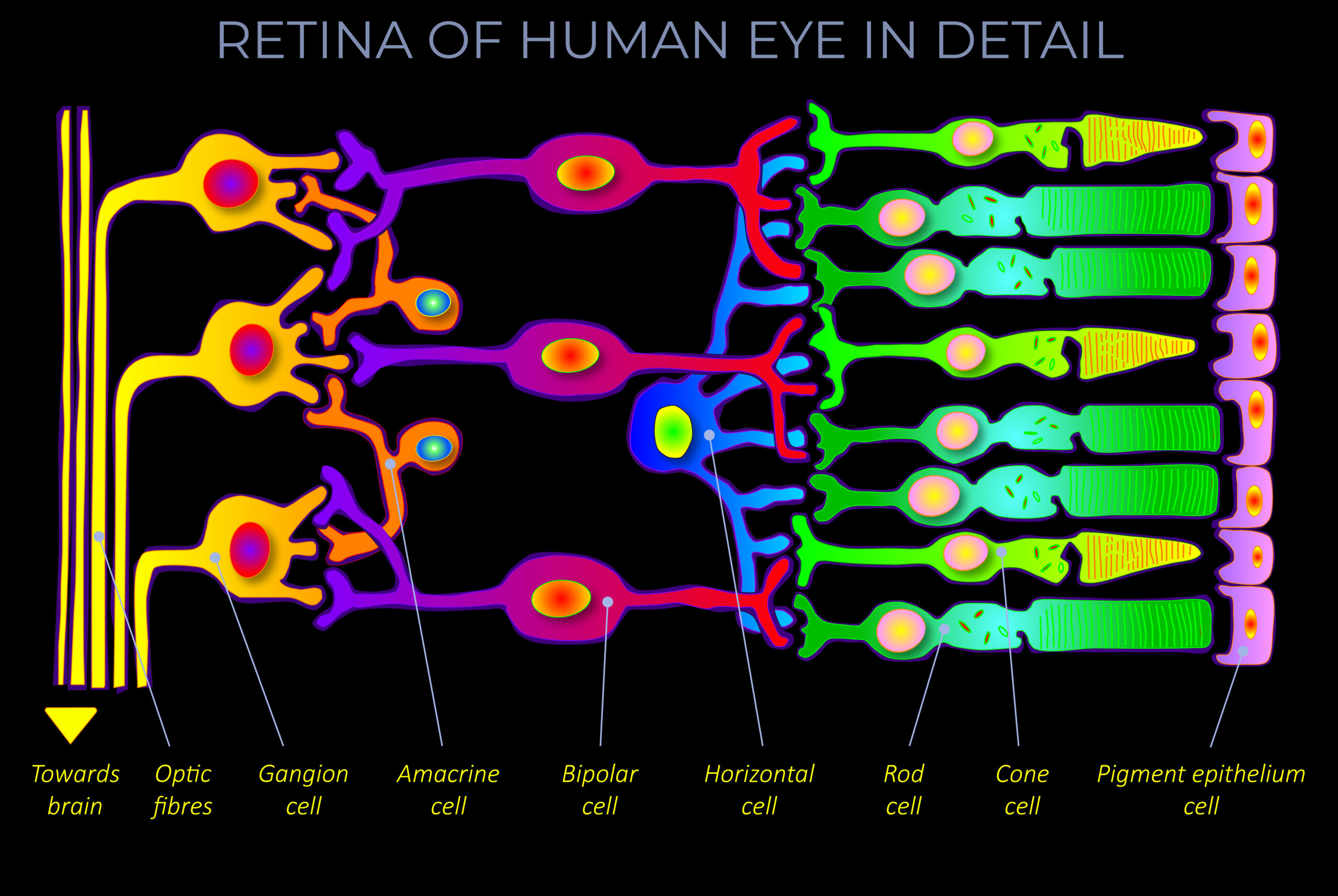
Amacrine cells are interneurons in the human retina that interact with retinal ganglion cells and/or bipolar cells.
- Amacrine cells are a type of interneuron within the human retina.
- Amacrine cells are embedded in the retinal circuitry.
- Amacrine cells are activated by and provide feedback to bipolar cells. They also form junctions with ganglion cells and communicate with each other.
- Amacrine cells send complex spatial and temporal information about the visual world to ganglion cells.
- Amacrine cells contribute additional information to the flow of data transmitted through bipolar cells and control and refine the response of ganglion cells (including their subtypes) to stimuli.
- Most amacrine cells do not have long, tail-like axons. However, they do possess multiple connections to other neurons in their vicinity.
- Axons are the part of neurons that transmit electrical impulses to other neurons.
- Neurons, of which amacrine cells are an example, are the nerve cells that comprise the human central nervous system.
About amacrine cell functions
Amacrine cells are a type of neuron found in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue lining the back of the human eye. They play a critical role in the processing of visual signals before these signals are sent to the brain.
Amacrine cells are known to contribute to narrowly task-specific visual functions such as:
- Spatial Contrast Enhancement: Amacrine cells contribute to a process called lateral inhibition, which helps to enhance the contrast between light and dark areas in a visual scene, thereby improving our ability to see edges and borders.
- Temporal Contrast Enhancement: Amacrine cells play a role in detecting changes in light intensity over time, which helps us to perceive motion and changes in a visual scene.
- Direction Selectivity: Certain types of amacrine cells are involved in detecting the direction of moving objects. These are known as starburst amacrine cells.
- Centre-surround antagonism: Amacrine cells interact with both bipolar cells and retinal ganglion cells to contribute to the centre-surround antagonistic structure of ganglion cell receptive fields.
- Complex Visual Processing: Amacrine cells form connections with multiple types of retinal cells, including bipolar cells and ganglion cells. This allows them to participate in complex processing and integration of visual information.
- Inhibitory Signalling: Many amacrine cells arstae inhibitory interneurons, which means they can inhibit the activity of other neurons. This inhibitory function plays a role in shaping the output of retinal ganglion cells, which send visual information to the brain.
- Regulation of Circadian Rhythm: Some amacrine cells release a pigment called melanopsin and are involved in non-image-forming visual functions, such as the regulation of circadian rhythms and the pupillary light reflex.
- Neurotransmitter Release: Amacrine cells can release a variety of neurotransmitters, including GABA, glycine, dopamine, and others, allowing them to modulate the activity of various neural circuits in the retina.
About centre-surround antagonism
Centre-surround antagonism refers to the way retinal neurons organize their receptive fields.
- Centre-surround antagonism refers to the way that light striking the human retina is processed by groups of light-sensitive cone cells.
- The centre component is primed to measure the sum-total of signals received from a small number of cone cells directly connected to a bipolar cell.
- The surround component is primed to measure the sum of signals received from a much larger number of cones around the centre point.
- The two signals are then compared to find the degree to which they disagree.
References
- Amacrine cells are interneurons in the human retina within the eyeball that interact with retinal ganglion cells and/or bipolar cells.
- Amacrine cells are an example of neurons which are the nerve cells that comprise the human central nervous system.
- Amacrine cells are activated by and provide feedback to bipolar cells. They also form junctions with ganglion cells and communicate with each other.
- Amacrine cells send complex spatial and temporal information about the visual world to ganglion cells.