Retina of the Human Eye in Detail
£0.00
This diagram is a new addition to the site! More information will be added ASAP 🙂
Description
Retina of the Human Eye in Detail
TRY SOME QUICK QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS TO GET STARTED
About the diagram
Some key terms
The rainbow axis is an imaginary straight line that connects the light source, observer and anti-solar point.
- The centre of a rainbow is always on its axis.
- The centre of a rainbow always corresponds with the anti-solar point.
- When drawing a diagram showing the axis of a rainbow, the Sun and anti-solar point, are at opposite ends with the observer between them.
- From an observer’s point of view, the rainbow axis is an imaginary line that they look along towards the centre of a rainbow.
A virtual photon is a theoretical concept in particle physics. Virtual photons are thought to be particles that exist for an incredibly brief time and cannot be directly observed. Their existence is inferred through their role in mediating interactions between other particles.
- Virtual photons are created when two charged particles interact with each other. For example, when two electrons interact with each other, they can exchange a virtual photon. This exchange of a virtual photon causes the electrons to repel each other. The electric force that we observe is thought to be due to the exchange of virtual photons between charged particles.
- Virtual photons are thought to play a role in many different physical phenomena, including the electromagnetic force, the weak force, and the strong force.
- More generally, a photon is a particle that carries electromagnetic radiation. It is the fundamental unit of light.
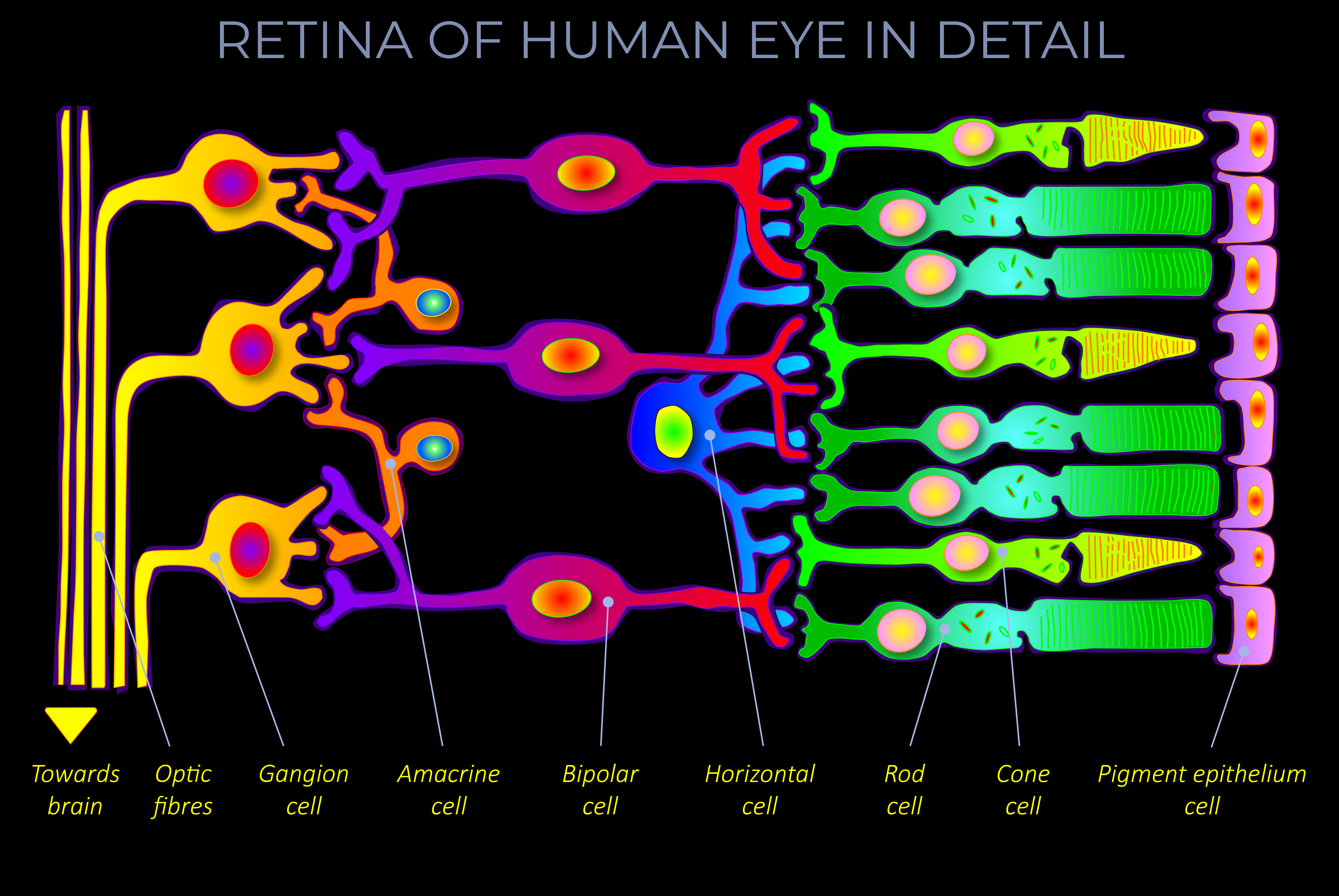
Vision, the human visual system, is a complex interplay between various components of the eye, including the cornea, pupil, lens, iris, retina, and optic nerve. It collaborates to capture, focus, and convert light into electrical signals that are transmitted to the brain for visual processing and interpretation.
- Vision begins when light emitted or reflected by an object or scene enters our eyes through the cornea, pupil, and lens.
- The cornea and the lens work together to concentrate and focus light onto the retina, which is the photosensitive layer of cells at the back of the eyeball.
- The iris, located between the cornea and the lens, regulates the amount of light reaching the retina. It also determines eye colour and controls the size of the pupil.
- The retina plays a vital role in converting differences in the wavelength and brightness of incoming light into electrical signals.
- The optic nerve, which exits at the back of the eye, carries these signals to the visual processing areas of the brain.
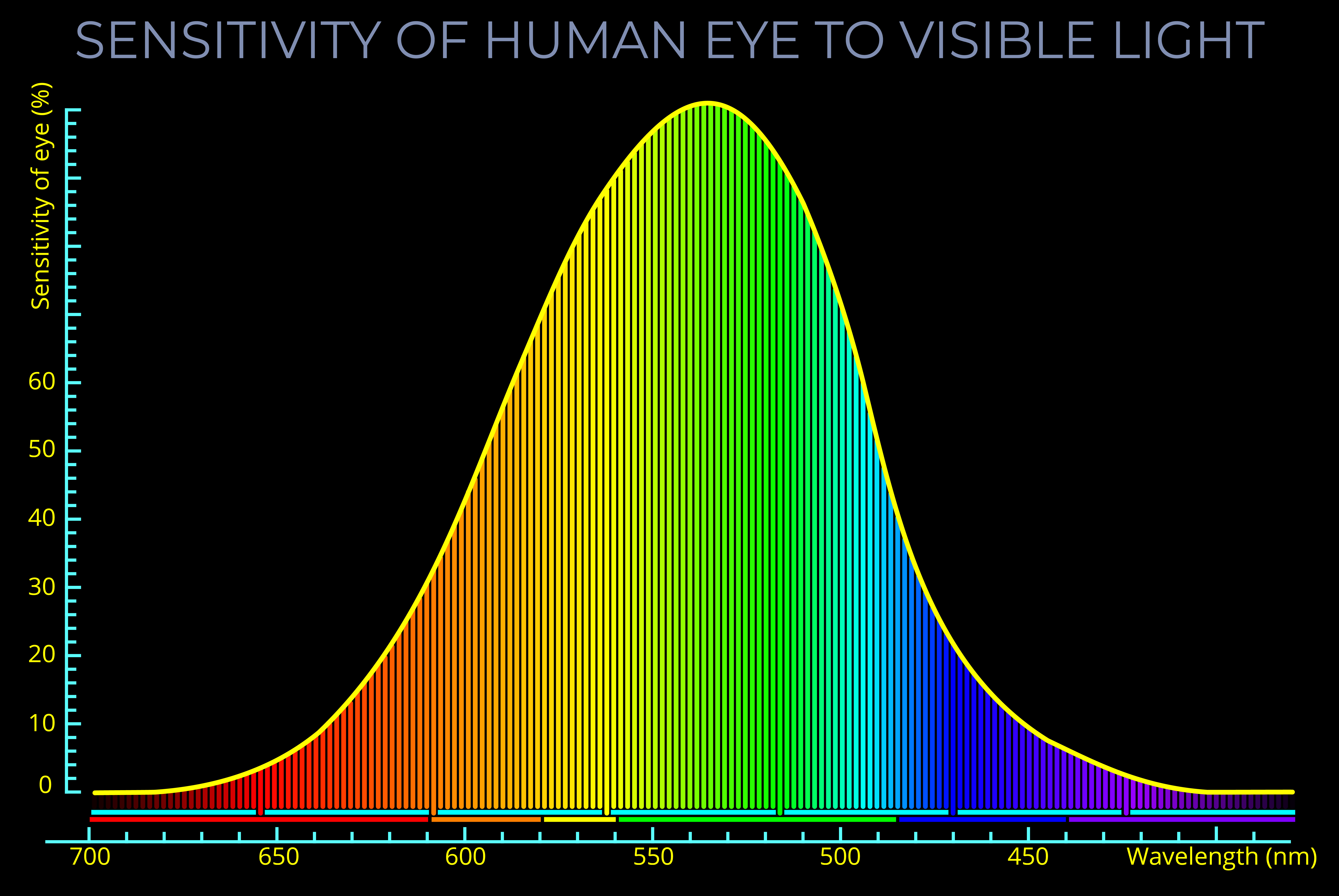
Visual perception is the human ability to see and understand our surroundings by virtue of the sensitivity of our eyes to wavelengths of light across the entire visible spectrum, from red to violet.
- Visual perception is a complex process that relies on the intricate interaction between our eyes, the brain, and the interpretation of light signals. It enables us to perceive various visual attributes such as shapes, sizes, textures, depths, motions, and spatial relationships, all of which contribute to our comprehensive understanding and interpretation of the visual world around us.
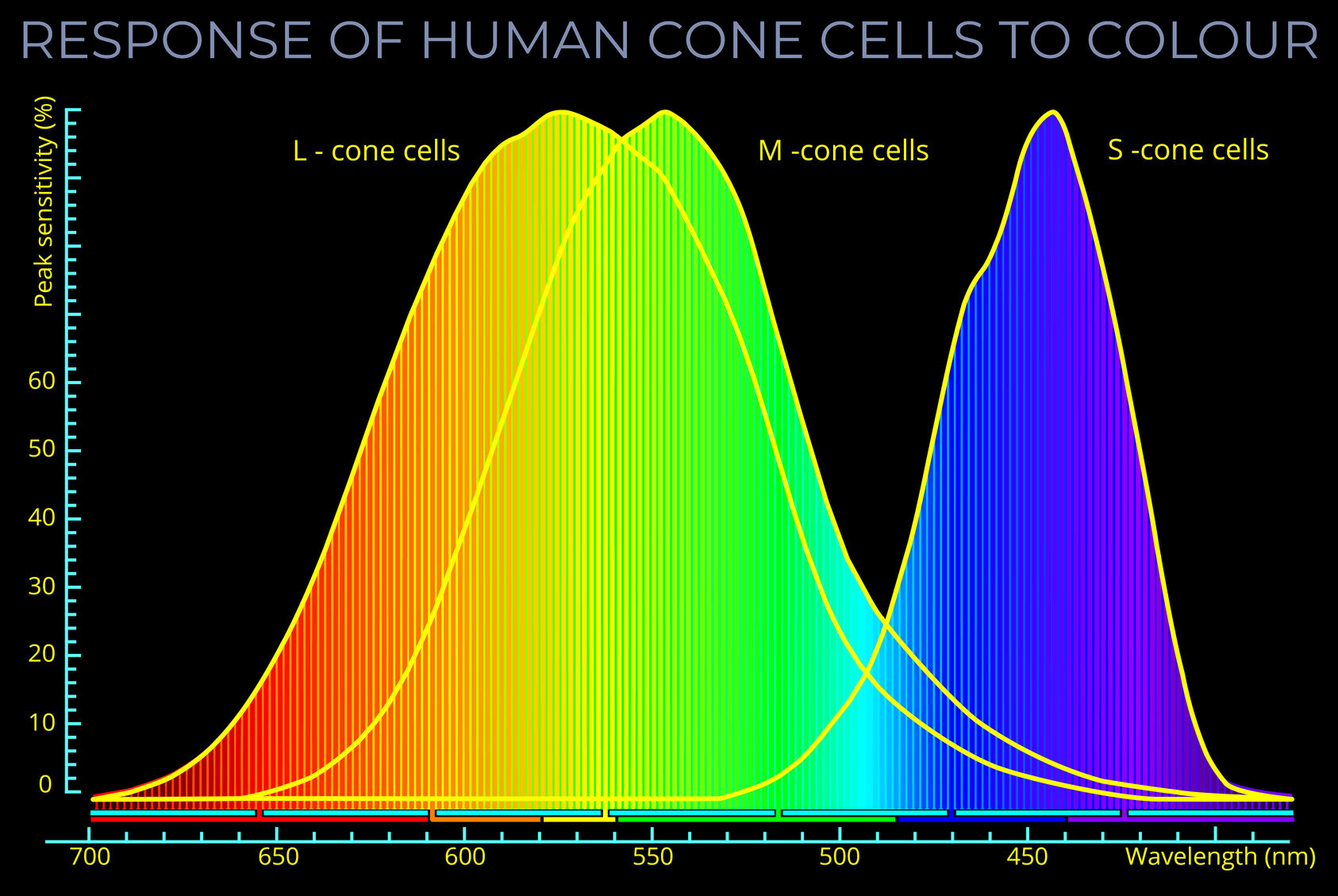
Trichromacy is the form of colour vision (trichromatic colour vision) possessed by human beings and other trichromats. It involves three different types of cone cells and one type of rod cell within the retina of the eye. Three independent channels convey colour information to subsequent visual processing centres and towards the visual cortex of the brain.
- Trichromatic colour theory of human vision explores various aspects of trichromacy, including:
- The functions, differences, and connections between the three types of cone cells (and the one type of rod cell) and other types of neurons within the human retina.
- The sensitivity of the three types of cones to three overlapping ranges of wavelengths of light that make up the visible spectrum and enable trichromatic colour vision.
- The sensitivity and function of rod cells in low levels of lighting.
- The role of rods and cones in encoding colour information in anticipation of subsequent stages of visual processing.
- The details of how colour information is produced across the entire surface of the retina of both eyes is encoded onto separate channels.
- Colour vision is the human ability to distinguish between objects based on the wavelengths of the light they emit, reflect or transmit. The human eye and brain together translate light into colour.
- Colour is not a property of electromagnetic radiation, but a feature of visual perception.
- The human eye, and so human perception, is tuned to the range of wavelengths of light that make up the visible spectrum and so to the corresponding spectral colours between red and violet.
- Light, however, is rarely of a single wavelength, so an observer will usually be exposed to a spread of different wavelengths of light or a mixture of wavelengths from different areas of the spectrum.
- An observer’s perception of colour is a subjective process as the eyes and brain respond together to stimuli produced when incoming light reacts with light-sensitive cells within the retina at the back of the eye.
- The perception of colour can be influenced by various factors, such as lighting conditions, surrounding colours, and individual differences in colour perception.
A photon is a particle that carries electromagnetic radiation. It is the fundamental unit of light.
- Thinking of photons as particles is useful for understanding the quantum nature of light.
- In the world of quantum physics, photons are the fundamental constituents of all forms of electromagnetic radiation, including light. They serve as the carriers of the electromagnetic force.
- Photons are elementary particles that have no mass and no electric charge. They are the quanta of the electromagnetic field, which is the fundamental field that describes electromagnetic interactions. Electromagnetic radiation, including light, is a manifestation of the electromagnetic field.
- Photons are the carriers of electromagnetic force because they are the only particles that can mediate electromagnetic interactions. When two charged particles interact electromagnetically, they exchange photons. The exchange of photons gives rise to the electromagnetic force.<
- Photons have no rest mass and always travel at the speed of light in a vacuum.
- Photons exhibit both wave-like and particle-like properties, a characteristic referred to as wave-particle duality. This duality is inherent to quantum particles, causing light to behave as a wave under certain conditions, as both waves and photons in others, and strictly as particles in yet others.
Colour is not a property of electromagnetic radiation, but a feature of visual perception by an observer.
- The human eye and so human visual perception are tuned to the visible spectrum and so to spectral colours between red and violet.
- There are no properties of electromagnetic radiation that distinguish visible light from other parts of the electromagnetic spectrum.
- Objects appear to be different colours to an observer depending on the wavelengths, frequencies and amplitude of visible light at the moment it strikes the retina at the back of the eye.