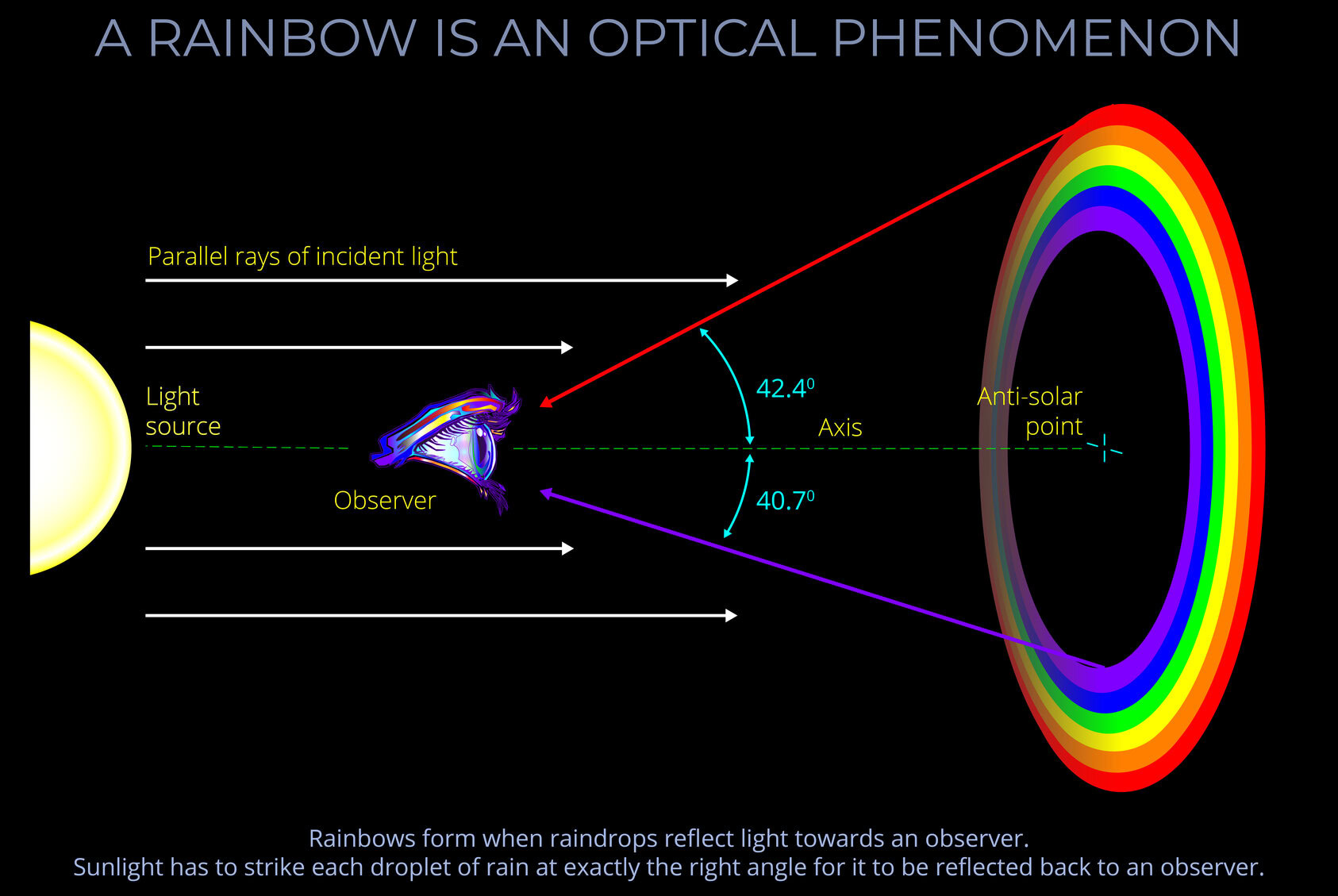
A Rainbow is an Optical Phenomenon
£0.00
This is one of a set of almost 40 diagrams exploring Rainbows.
Each diagram appears on a separate page and is supported by a full explanation.
- Follow the links embedded in the text for definitions of all the key terms.
- For quick reference don’t miss the summaries of key terms further down each page.
Description
A Rainbow is an Optical Phenomenon
TRY SOME QUICK QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS TO GET STARTED
About the Diagram
An overview of rainbows
About the diagram
Atmospheric rainbow summary
Visual processing
Visual processing is a complex and dynamic process that involves interactions between various retinal cells, neural pathways, and brain regions, ultimately leading to conscious visual perception.
Visual processing begins the moment light enters the human eye. It then progresses through multiple stages as signals travel towards the visual cortex, where the neural activity is integrated, resulting in conscious visual experience.
As visual processing begins the retina starts to process information about colors, as well as basic information about the shape and movement associated with those colors. By the end of this stage, multiple forms of information about a visual scene are ready to be conveyed to higher brain regions.
Let’s examine two major forms of processing, trichromatic and opponent-processing, which occur within the eyeball as visual information is gathered from light entering our eyes.
Trichromacy, also known as the trichromatic theory of colour vision, explains how three types of cone receptors in the retina work together with bipolar cells to perform their role in the initial stage of colour processing. Rod cells also play a significant role in this form of processing visual information, particularly in low-light conditions.
Opponent-processing, also known as the opponent-process theory of colour vision, explains the second form of processing. Opponent-processing involves ganglion cells that process the data received from trichromatic processing and combine it with other intercellular activities.
It is interesting to note that as both trichromatic and opponent-process theories developed over the last century, researchers and authors have often pitted one theory against the other. However, both processes are crucial for understanding how colour vision occurs.
Trichromatic theory explains the encoding of visual information when light hits the retina, while opponent-processing explains a subsequent stage of information convergence, assembly, and coding before the data leaves the retina via the optic nerve.
Note that:
- Both trichromatic and opponent-processing occur independently within each retina, without comparing with the other.
- Each eye gathers information from a specific viewpoint, approximately 50 mm to the left or right of the nose.
- The two impressions are later compared and combined to provide us with a single three-dimensional, stereoscopic view of the world, rather than two flattened images.
We can consider the layers of retinal cells involved in trichromatic and opponent-processing as examining, interpreting, and transmitting visually relevant information. However, it would be incorrect to view this as a straightforward linear process due to the intricate neural networking, cross-referencing, and feedback loops within the retina.
Some key terms
The visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum is called the visible spectrum.
- The visible spectrum is the range of wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum that correspond with all the different colours we see in the world.
- As light travels through the air it is invisible to our eyes.
- Human beings don’t see wavelengths of light, but they do see the spectral colours that correspond with each wavelength and colours produced when different wavelengths are combined.
- The visible spectrum includes all the spectral colours between red and violet and each is produced by a single wavelength.
- The visible spectrum is often divided into named colours, though any division of this kind is somewhat arbitrary.
- Traditional colours referred to in English include red, orange, yellow, green, blue, and violet.
Visible light is the range of wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation perceived as colour by human observers.
- Visible light is a form of electromagnetic radiation.
- Other forms of electromagnetic radiation include radio waves, microwaves, infrared, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays.
- Visible light is perceived by a human observer as all the spectral colours between red and violet plus all other colours that result from combining wavelengths together in different proportions.
- A spectral colour is produced by a single wavelength of light.
- The complete range of colours that can be perceived by a human observer is called the visible spectrum.
- The range of wavelengths that produce visible light is a very small part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Refraction refers to the way that electromagnetic radiation (light) changes speed and direction as it travels across the boundary between one transparent medium and another.
- Light bends towards the normal and slows down when it moves from a fast medium (like air) to a slower medium (like water).
- Light bends away from the normal and speeds up when it moves from a slow medium (like diamond) to a faster medium (like glass).
- These phenomena are governed by Snell’s law, which describes the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction.
- The refractive index (index of refraction) of a medium indicates how much the speed and direction of light are altered when travelling in or out of a medium.
- It is calculated by dividing the speed of light in a vacuum by the speed of light in the material.
- Snell’s law relates the angles of incidence and refraction to the refractive indices of the two media involved.
- Snell’s law states that the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is equal to the ratio of the refractive indices.
Visible light refers to the range of wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation that is perceived as colour by human observers. While the range of visible light is generally considered to be 400-700 nm, the exact range of colours perceptible can vary slightly between individuals.
- Visible light is one form of electromagnetic radiation. Other forms of electromagnetic radiation include radio waves, microwaves, infrared, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. Visible light ranges from approximately 400 nanometres (nm) for violet to 700 nm for red.
- A human observer perceives visible light as a combination of all the spectral colours between red and violet, as well as a vast range of other colours produced from the blending of different wavelengths in varying proportions.
The visible spectrum is the range of wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum that correspond with all the different colours we see in the world.
- As light travels through the air it is invisible to our eyes.
- Human beings don’t see wavelengths of light, but they do see the spectral colours that correspond with each wavelength and colours produced when different wavelengths are combined.
- The visible spectrum includes all the spectral colours between red and violet and each is produced by a single wavelength.
- The visible spectrum is often divided into named colours, though any division of this kind is somewhat arbitrary.
- Traditional colours referred to in English include red, orange, yellow, green, blue, and violet.
Incident light refers to light that is travelling towards an object or medium.
- Incident light refers to light that is travelling towards an object or medium.
- Incident light may come from the Sun, an artificial source or may have already been reflected off another surface, such as a mirror.
- When incident light strikes a surface or object, it may be absorbed, reflected, refracted, transmitted or undergo any combination of these optical effects.
- Incident light is typically represented on a ray diagram as a straight line with an arrow to indicate its direction of propagation.
Total internal reflection occurs when light travelling through a denser medium strikes a boundary with a less dense medium at an angle exceeding a specific critical angle. As a result, all the light is reflected back into the denser medium, and no light transmits into the second medium.
- Total Internal reflection only takes place when the first medium (where the light originates) is denser than the second medium.
- The critical angle is the angle of incidence above which total internal reflection occurs.
- The critical angle is measured with respect to the normal.
- The normal is an imaginary line drawn in a ray diagram perpendicular to, so at a right angle to (900), to the boundary between two media.
Reflection is the process where light rebounds from a surface into the medium it came from, instead of being absorbed by an opaque material or transmitted through a transparent one.
- The three laws of reflection are as follows:
- When light hits a reflective surface, the incoming light, the reflected light, and an imaginary line perpendicular to the surface (called the “normal line”) are all in the same flat area.
- The angle between the incoming light and the normal line is the same as the angle between the reflected light and the normal line. In other words, light bounces off the surface at the same angle as it came in.
- The incoming and reflected light are mirror images of each other when looking along the normal line. If you were to fold the flat area along the normal line, the incoming light would line up with the reflected light.
- The observer effect is a principle of physics and states that any interaction between a particle and a measuring device will inevitably change the state of the particle. This is because the act of measurement itself imposes a disturbance on the particle’s wave function, which is the mathematical description of its state.
- The concept of observation refers to the act of engaging with an electron or other particle, achieved through measuring its position or momentum.
- In the context of quantum mechanics, observation isn’t a passive undertaking, observation actively alters a particle’s state.
- This means that any kind of interaction with an atom, or with one of its constituent particles, that provides insight into its state results in a change to that state. The act of observation is always intrusive and will always change the state of the object being observed.
- It can be challenging to reconcile this with our daily experience, where we believe we can observe things without inducing any change in them.
A human observer is a person who engages in observation by watching things.
- In the presence of visible light, an observer perceives colour because the retina at the back of the human eye is sensitive to wavelengths of light that fall within the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
- The visual experience of colour is associated with words such as red, blue, yellow, etc.
- The retina’s response to visible light can be described in terms of wavelength, frequency and brightness.
- Other properties of the world around us must be inferred from light patterns.
- An observation can take many forms such as:
- Watching an ocean sunset or the sky at night.
- Studying a baby’s face.
- Exploring something that can’t be seen by collecting data from an instrument or machine.
- Experimenting in a laboratory setting.