- Light travels through a vacuum at 299,792 kilometres per second.
- Light travels at slower speeds through other media compared to a vacuum. The exact speed of light in a medium depends on its optical properties, particularly its refractive index.
- While a vacuum is devoid of matter, in the context of optics, a vacuum is considered a reference point for comparing the speeds of light in other media. It’s not contradictory to refer to a vacuum as a “medium” in this context; rather, it’s a baseline for comparison.
- Within the Earth’s atmosphere, light can travel at speeds near the speed of light. However, when the air is full of water droplets or dust, light travels at significantly lower speeds.
- Understanding whether a medium is considered “fast” or “slow” is valuable in predicting the behaviour of light when it crosses the boundary between different media. As such:
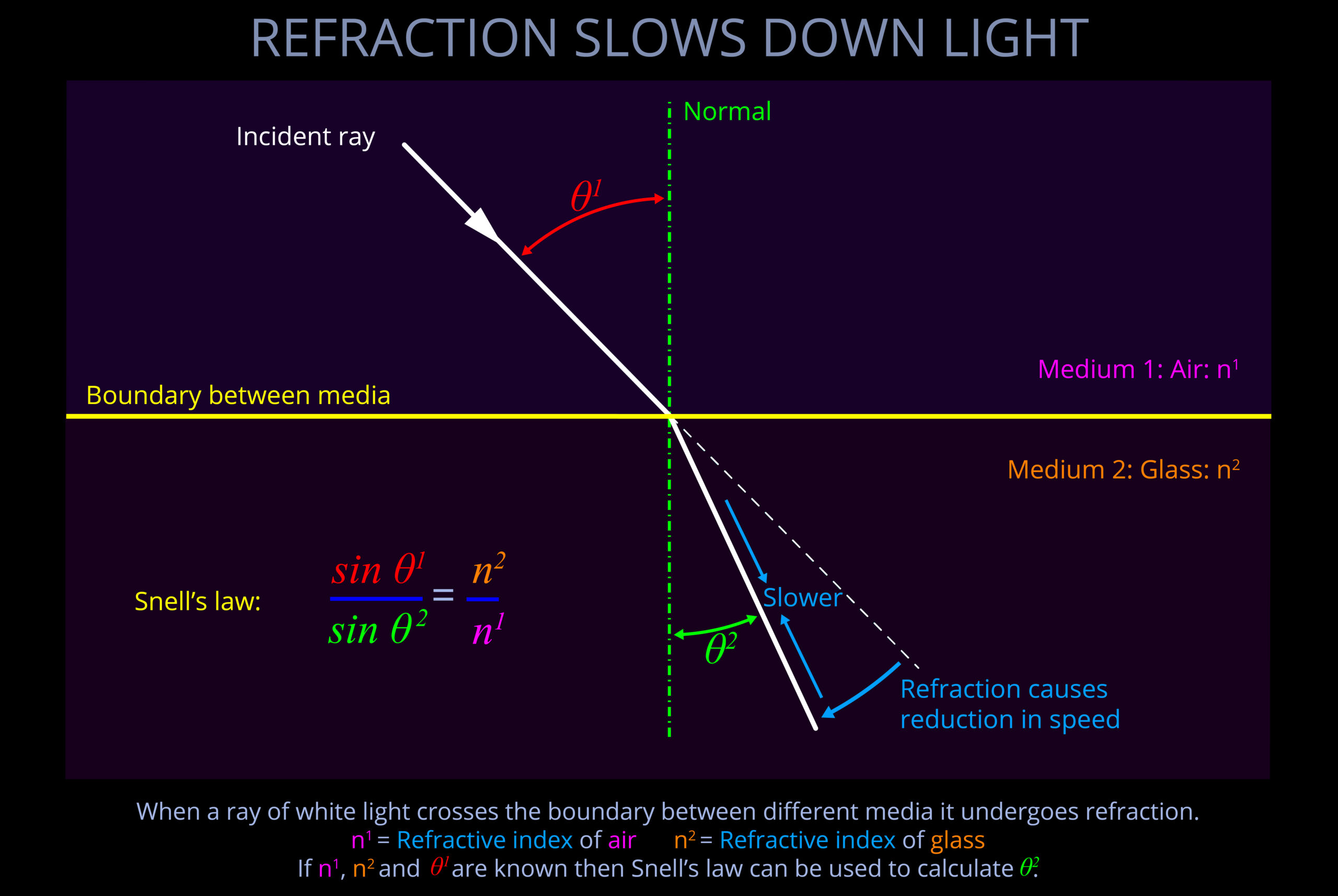
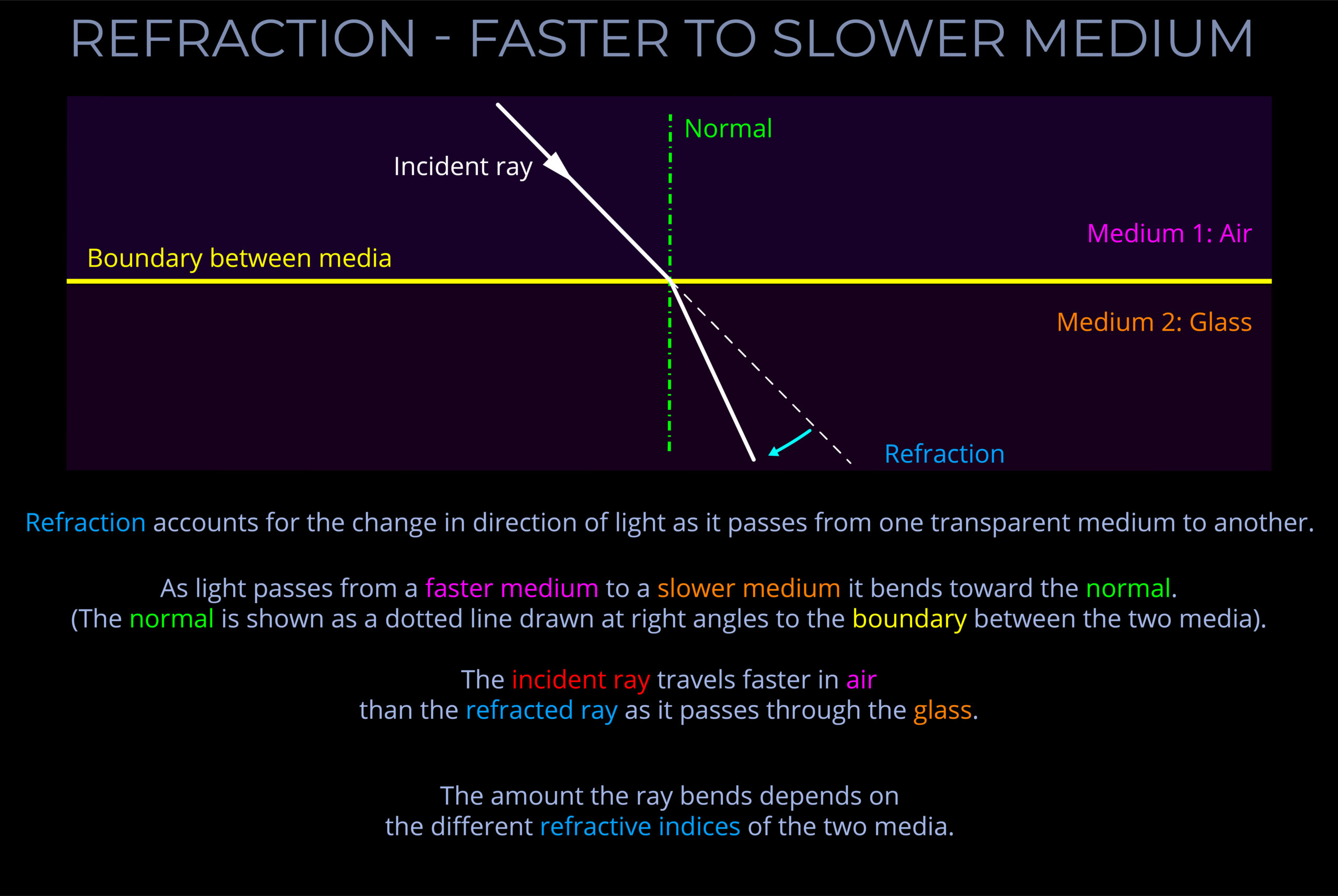
- When light crosses the boundary from a fast medium to a slower medium, it will bend towards the normal.
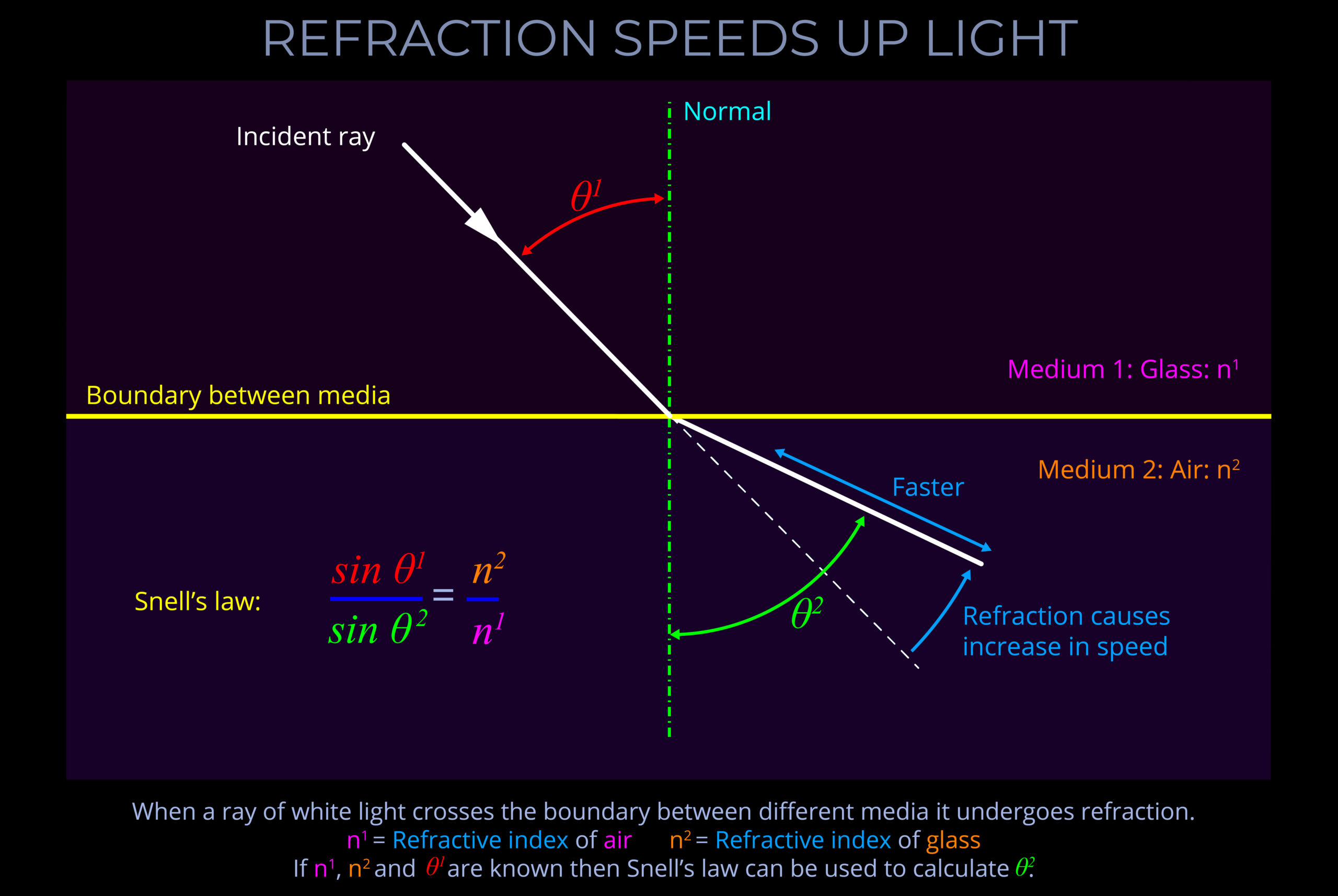
- When light crosses the boundary from a slow medium to a faster medium, the light ray will bend away from the normal.
- In optics, the “normal” is a line drawn in a ray diagram that is perpendicular, or at a right angle (90 degrees), to the boundary between two media.
- The phenomenon of light bending when it crosses the boundary between different media is known as refraction.
- The speed of light in a medium is determined by its refractive index, which is a measure of how much the medium slows down light compared to its speed in a vacuum.
- The speed at which light travels through different media, such as air, glass, or water, is not a constant. Some media are considered “fast” because light passes through them more quickly than others.
- Light travels through a vacuum at 299,792 kilometres per second.
- Light travels at slower speeds through other media compared to a vacuum. The exact speed of light in a medium depends on its optical properties, particularly its refractive index.
- While a vacuum is devoid of matter, in the context of optics, a vacuum is considered a reference point for comparing the speeds of light in other media. It’s not contradictory to refer to a vacuum as a “medium” in this context; rather, it’s a baseline for comparison.
- Within the Earth’s atmosphere, light can travel at speeds near the speed of light. However, when the air is full of water droplets or dust, light travels at significantly lower speeds.
- Understanding whether a medium is considered “fast” or “slow” is valuable in predicting the behaviour of light when it crosses the boundary between different media. As such:
- When light crosses the boundary from a fast medium to a slower medium, it will bend towards the normal.
- When light crosses the boundary from a slow medium to a faster medium, the light ray will bend away from the normal.