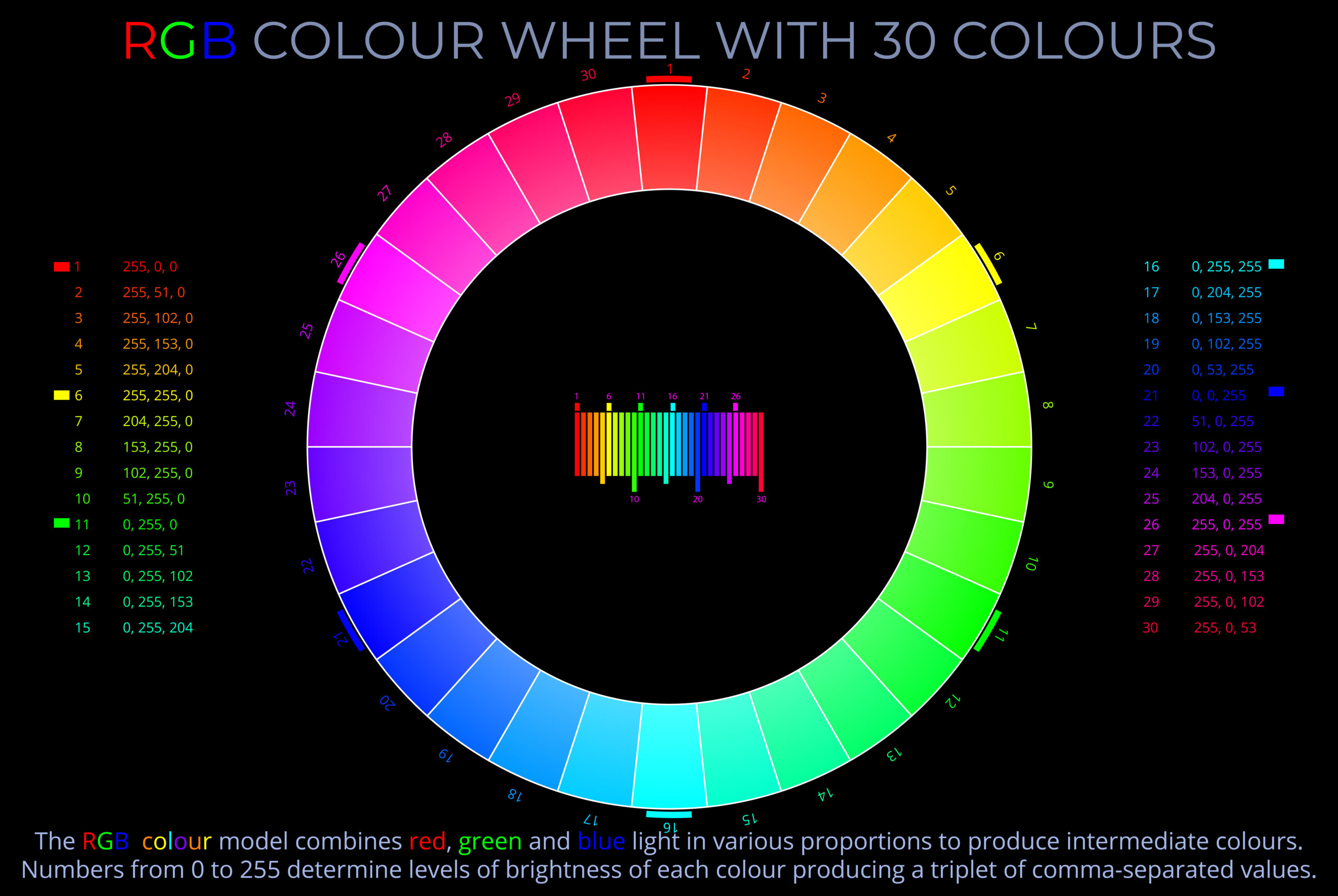
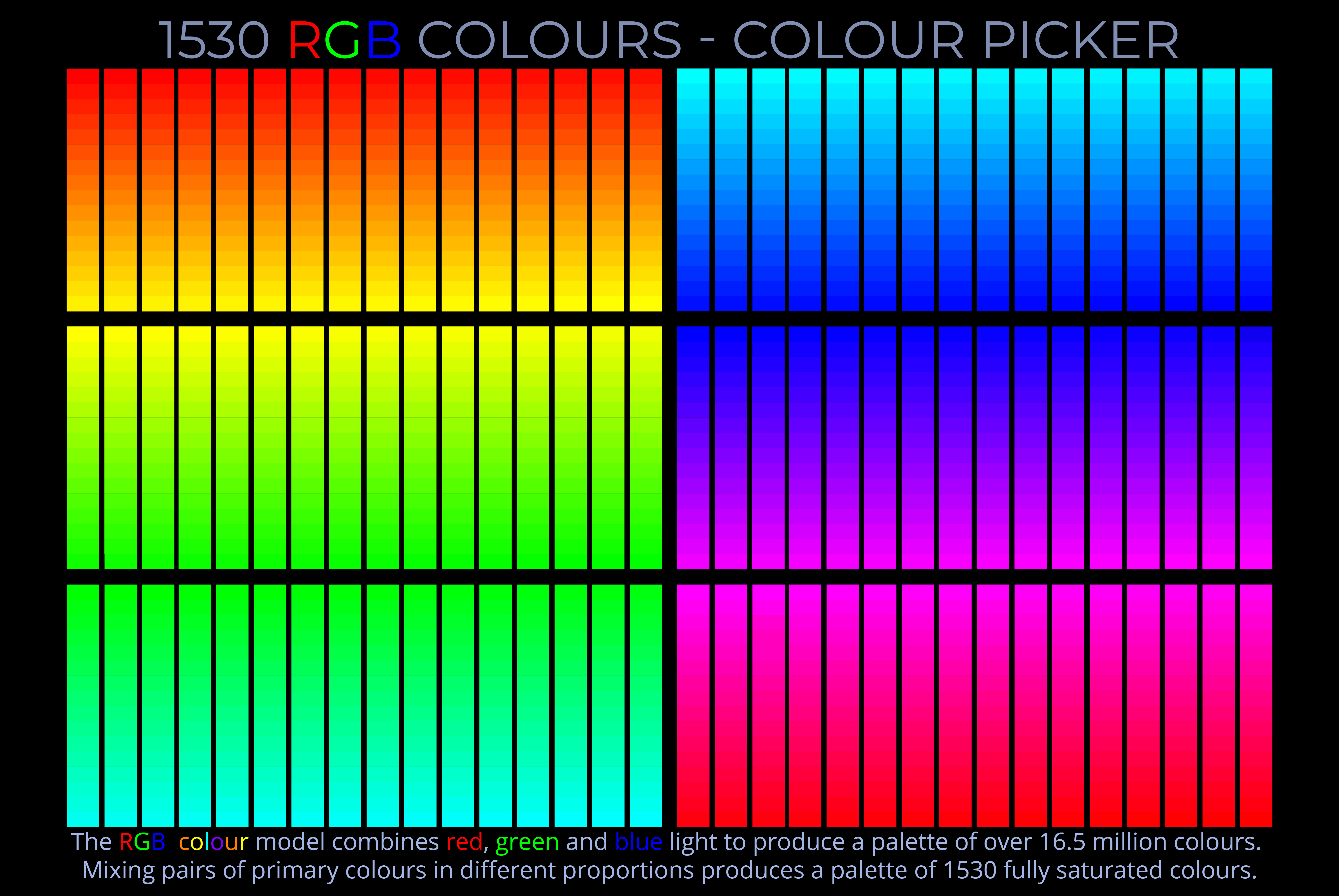
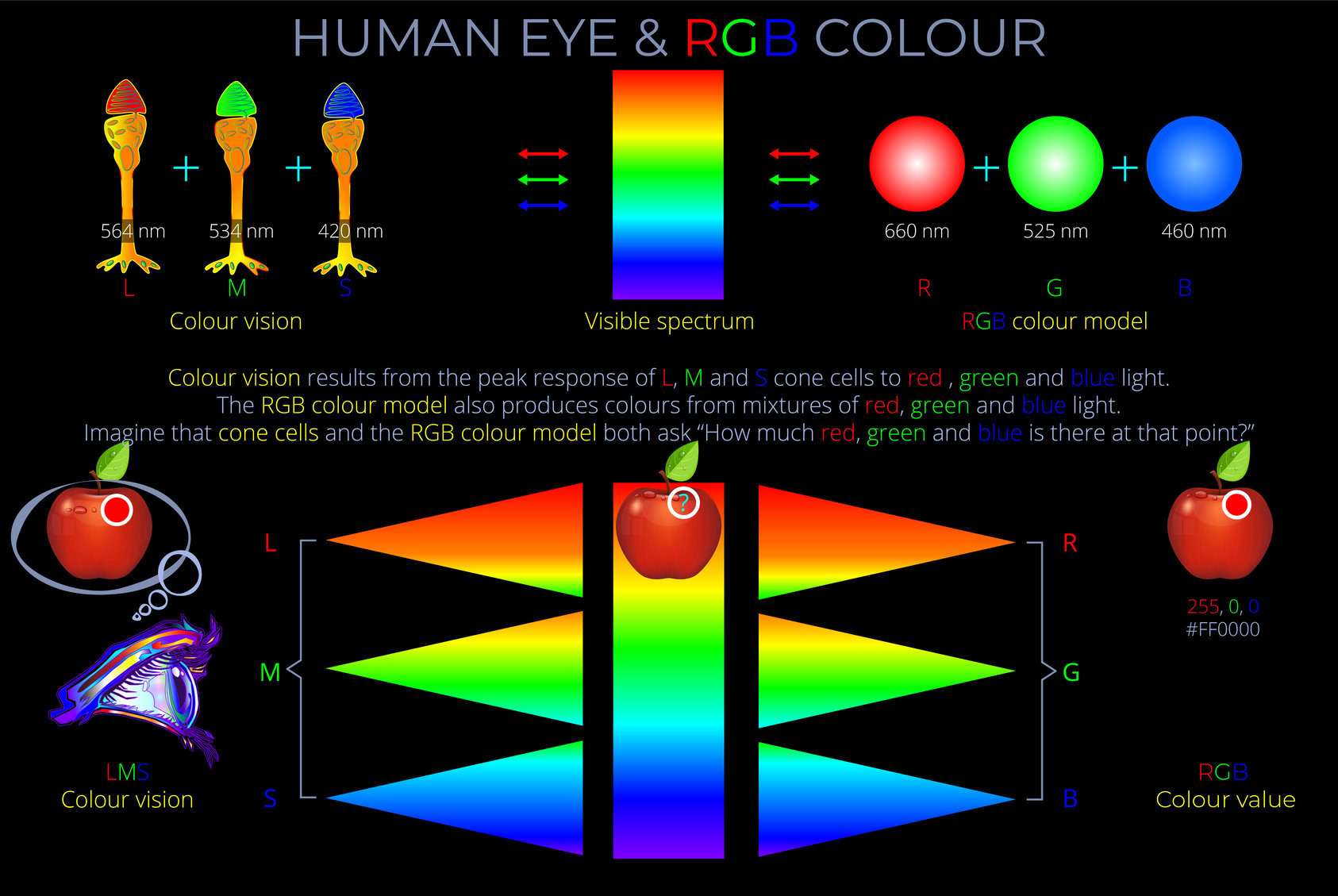
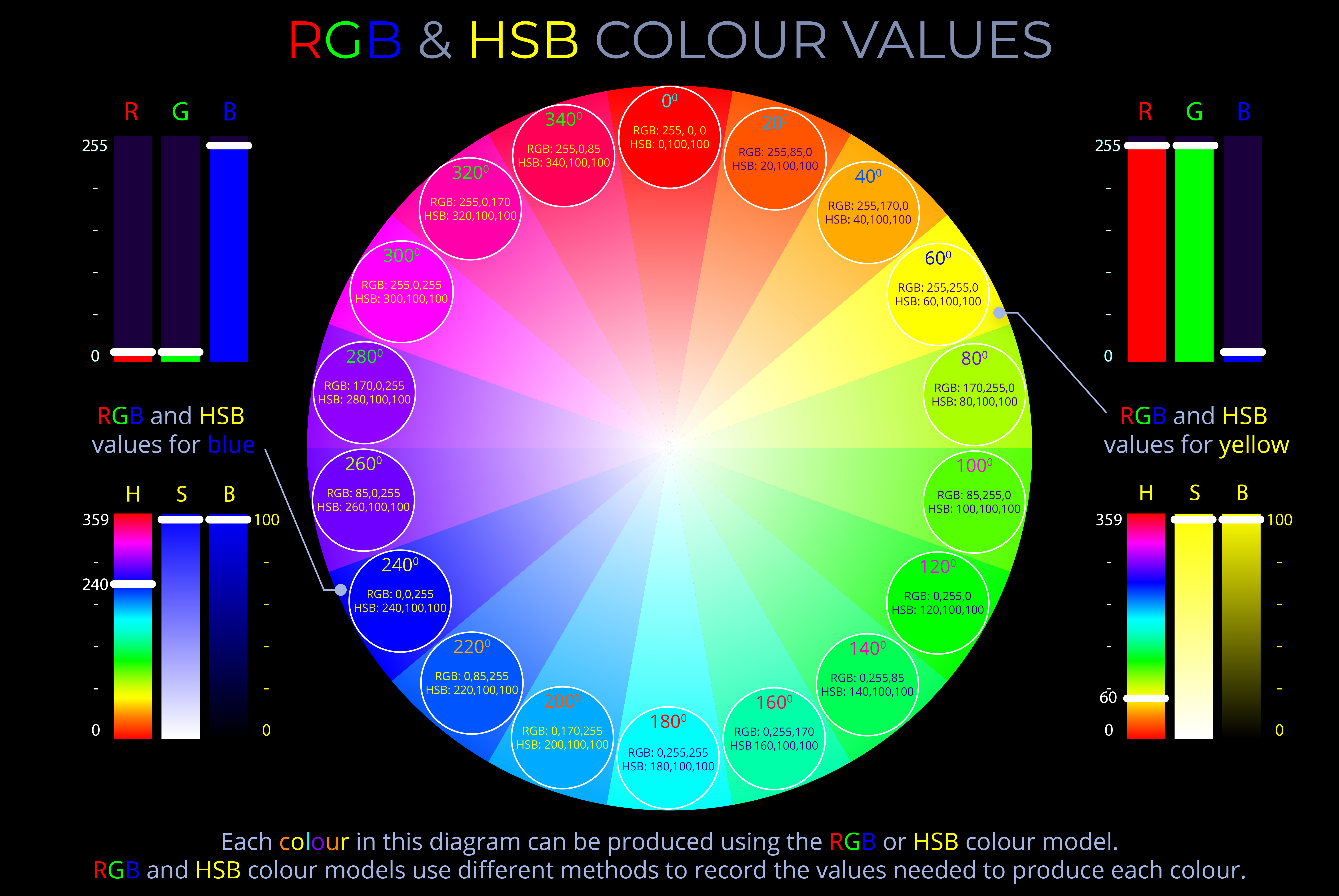
THE RETINA
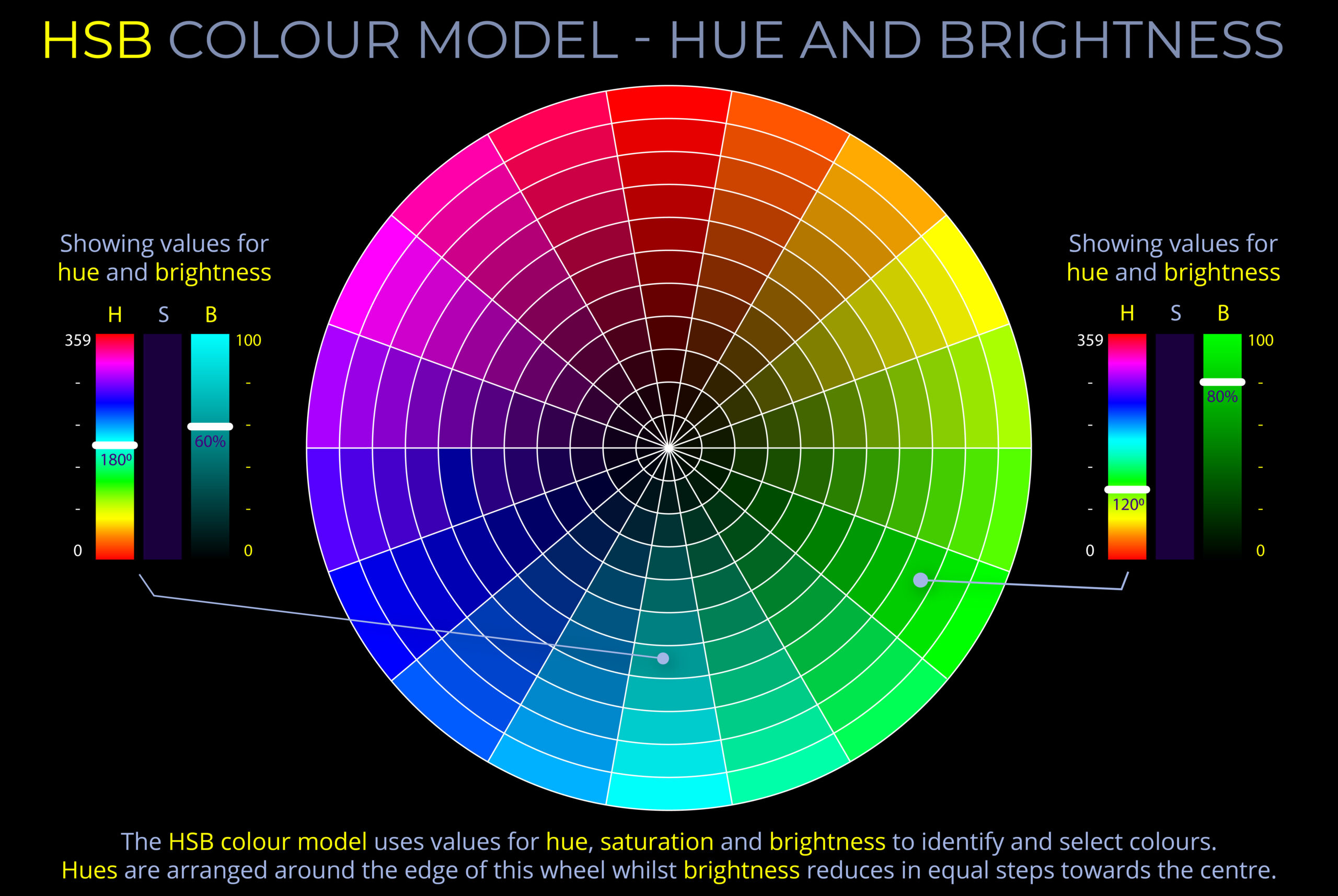
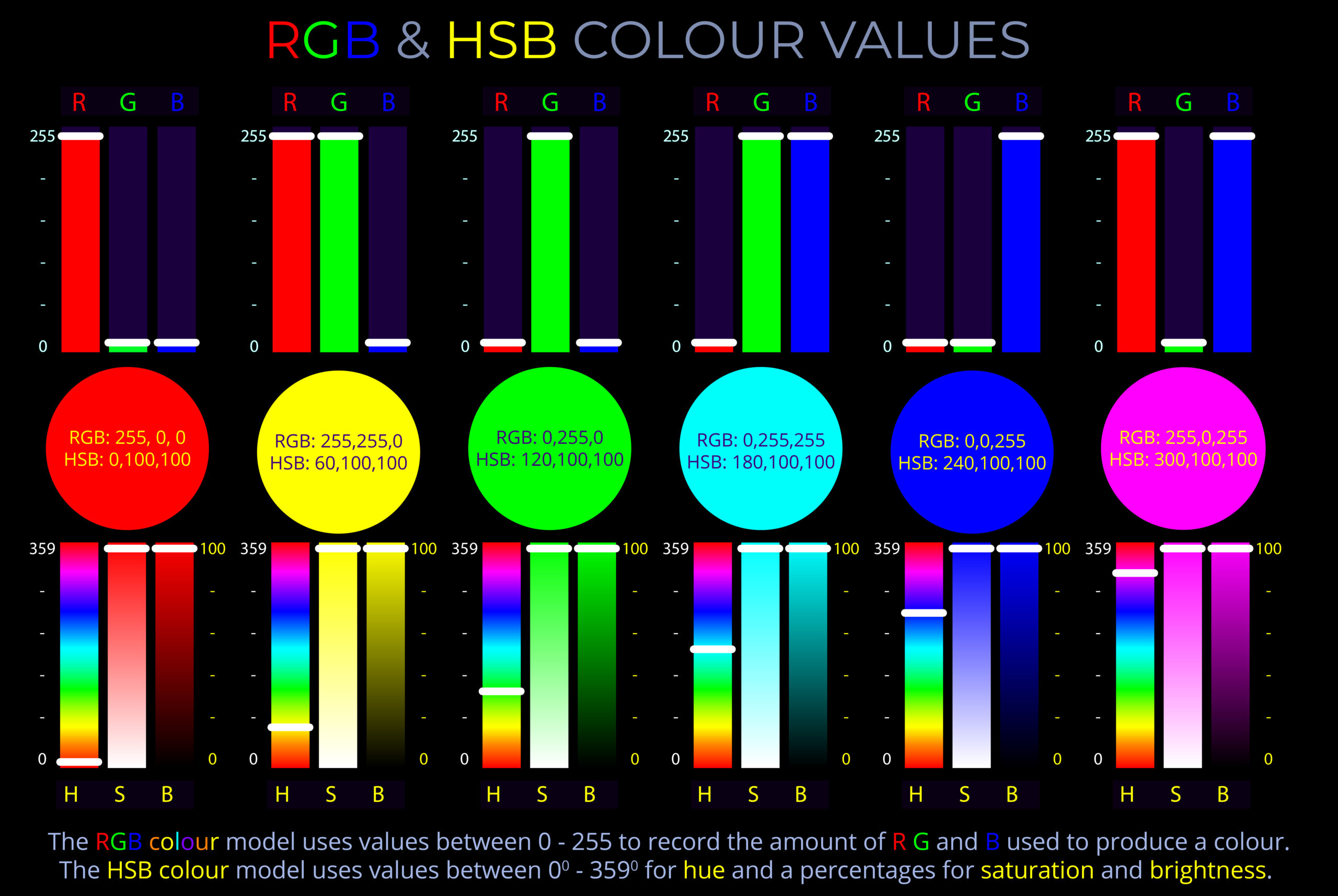
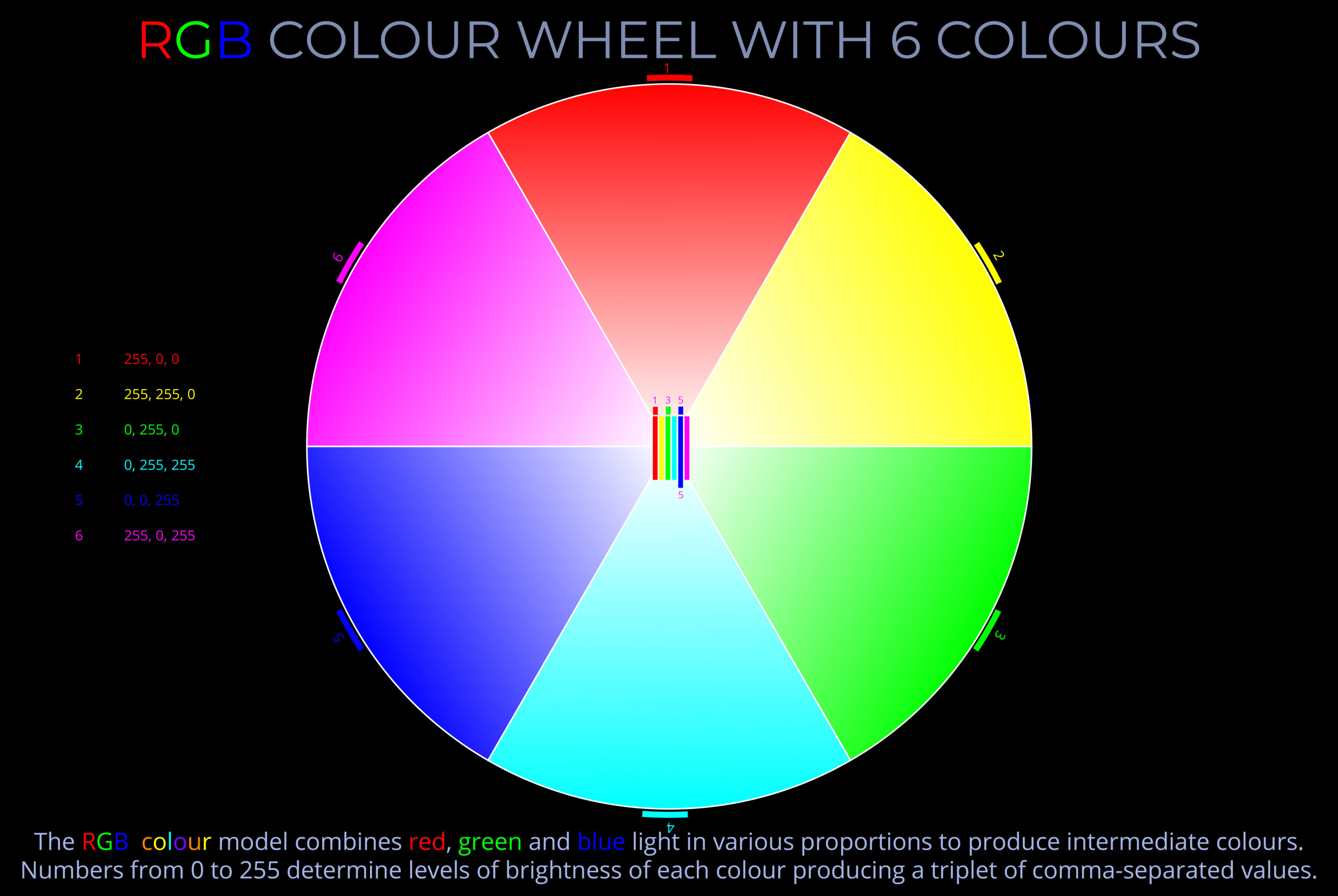
Human beings see the world in colour because of the way their visual system processes light. The retina contains light-sensitive receptors, rod and cone cells, that respond to light stimuli. It is the variety of wavelengths and intensities of light entering the eyes that produces the impression of colour.
The retina is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue inside our eyes. It forms a sheet of tissue barely 200 micrometres (μm) thick, but its neural networks carry out almost unimaginably complicated feats of image processing.
The physiology of the eye results in a tiny, focused, two-dimensional image of the visual world being projected onto the retina’s surface. Because of the optics of lenses, it appears upside down and the wrong way around. But no worry, sorting that out is child’s play for the human brain! The real challenge is that the photosensitive receptors in the retina must produce precise chemical responses to light and translate every minute detail of the image into electrical impulse ready to be sent to the brain where they produce visual impressions of the world. In a very limited sense, the retina serves a similar function to a photosensitive chip in a camera.
As research continues to reveal ever-increasing amounts of detail about these signalling processes across and beyond the retina, it required new thinking, not only of the retina’s function but also of the mechanisms within the brain that shape these signals into behaviourally useful perceptions.
The retina consists of 60-plus distinct neuron types, each of which plays a specialized role in turning variations in the patterns of wavelengths and intensities of light into visual information. Neurons are electrically excitable nerve cells that collect, process and transmit vast amounts of this information through both chemical and electrical signals. Retinal neurons work together to convert the signals produced by a hundred and twenty million rods and cones and send them along around one million fibres within the optic nerve of each eye to connections with higher brain functions. In this process rods and cones are first responders whilst ganglion cells are the final port of call before information leaves the retina.
There are three principal forms of processing that take place within the retina itself. The first organises the outputs of the rod and cone photoreceptors and begins to compose them into around 12 parallel information streams as they travel through bipolar cells. The second connects these streams to specific types of retinal ganglion cells. The third modulates the information using feedback from horizontal and amacrine cells to create the diverse encodings of the visual world that the retina transmits towards the brain.
As mentioned above, the image of the outside world focused on the retina is upside down and the wrong way around. But the human retina is also inverted in the sense that the light-sensitive rod and cone cells are not located on the surface where the image forms, but instead are embedded inside, where the retina attaches to the fabric of the eyeball. As a result, light striking the retina, passes through layers of other neurons (ganglion, bipolar cells etc.) and blood-carrying capillaries, before reaching the photoreceptors.
The overlying neural fibres do not significantly degrade vision in the inverted retina. The neurons are relatively transparent and accompanying Müller cells act as fibre-optic channels to transport photons directly to photoreceptors. However, some estimates suggest that overall, around 15% of all the light entering the eye is lost en-route to the retina. To counter this, the fovea centralis, at the centre of our field of vision, is free of rods and there are no blood vessels running through it, so optimising the level of detail where we need it most.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Retina