A colour wheel is a diagram based on a circle divided into segments and can be used to explore the effect of mixing adjacent colours.
An RGB colour wheel provides a graphic representation of the RGB colour model.
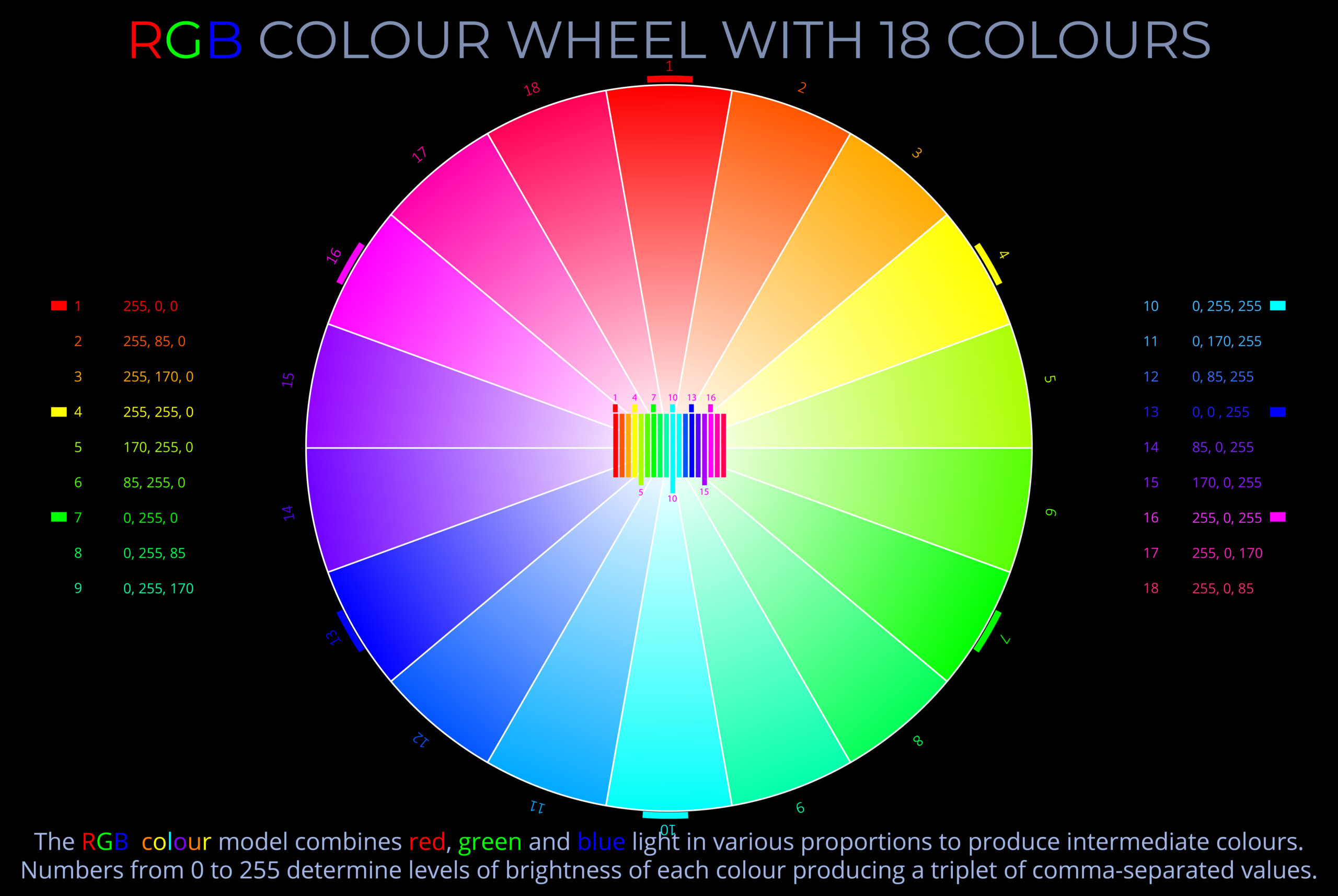
- RGB colour wheels have a minimum of three segments or spokes. These are filled with the additive primary colours red, green and blue.
- Starting with the three primary colours, an RGB colour wheel can demonstrate the effect of mixing adjacent segments to produce progressively more subtle gradations of intermediate hues.
- An RGB colour wheel is particularly useful when trying to visually identify and specify:
- A particular RGB colour
- The relationship between different RGB colours
- Find the colour value (code) for an RGB colour.
- LED light sources producing very narrow bands of wavelengths can be used when demonstrating RGB colour wheels by projecting red, green and blue LEDs onto a neutrally toned surface.
- The peak wavelength for selected colours might typically be red = 625 nanometres, green = 500 nm and blue = 440 nm.
About RGB colour and colour perception
- The human eye, and so visual perception, is tuned to the visible spectrum and so to spectral colours between red and violet.
- RGB colour is a model used to reproduce colour in a way that matches perception.
- An RGB colour wheel helps to simulate:
- The effect of projecting lights with wavelengths corresponding to the three primary colours, red, green and blue onto a neutral-coloured surface.
- The additional colours produced by mixing adjacent pairs of colours such as adjacent primary, secondary, tertiary colours etc.
- Every imaginable colour can be produced by the RGB colour model.
- Remember that the RGB is an additive colour model used when mixing light of different wavelengths.
- The CMYK subtractive colour model is often used when mixing paints, dyes and pigments.
About RGB secondary colours
- RGB secondary colours are the hues formed by combining two primary colours of light in equal proportions.
- The three RGB secondary colours are cyan, magenta, and yellow:
- When green and blue light sources overlap, they produce cyan.
- When blue and red light sources overlap, they produce magenta.
- When red and green light sources overlap, they produce yellow.
- Mixing adjacent RGB primary and secondary colours of equal intensity results in tertiary colours:
- Mixing red (primary) and yellow (secondary) creates orange.
- Mixing yellow (secondary) and green (primary) creates lime green.
- Mixing green (primary) and cyan (secondary) creates spring green.
- Mixing cyan (secondary) and blue (primary) creates turquoise.
- Mixing blue (primary) and magenta (secondary) creates purple.
- Mixing magenta (secondary) and red (primary) produces fuchsia.
About RGB colour wheels & intermediate colours
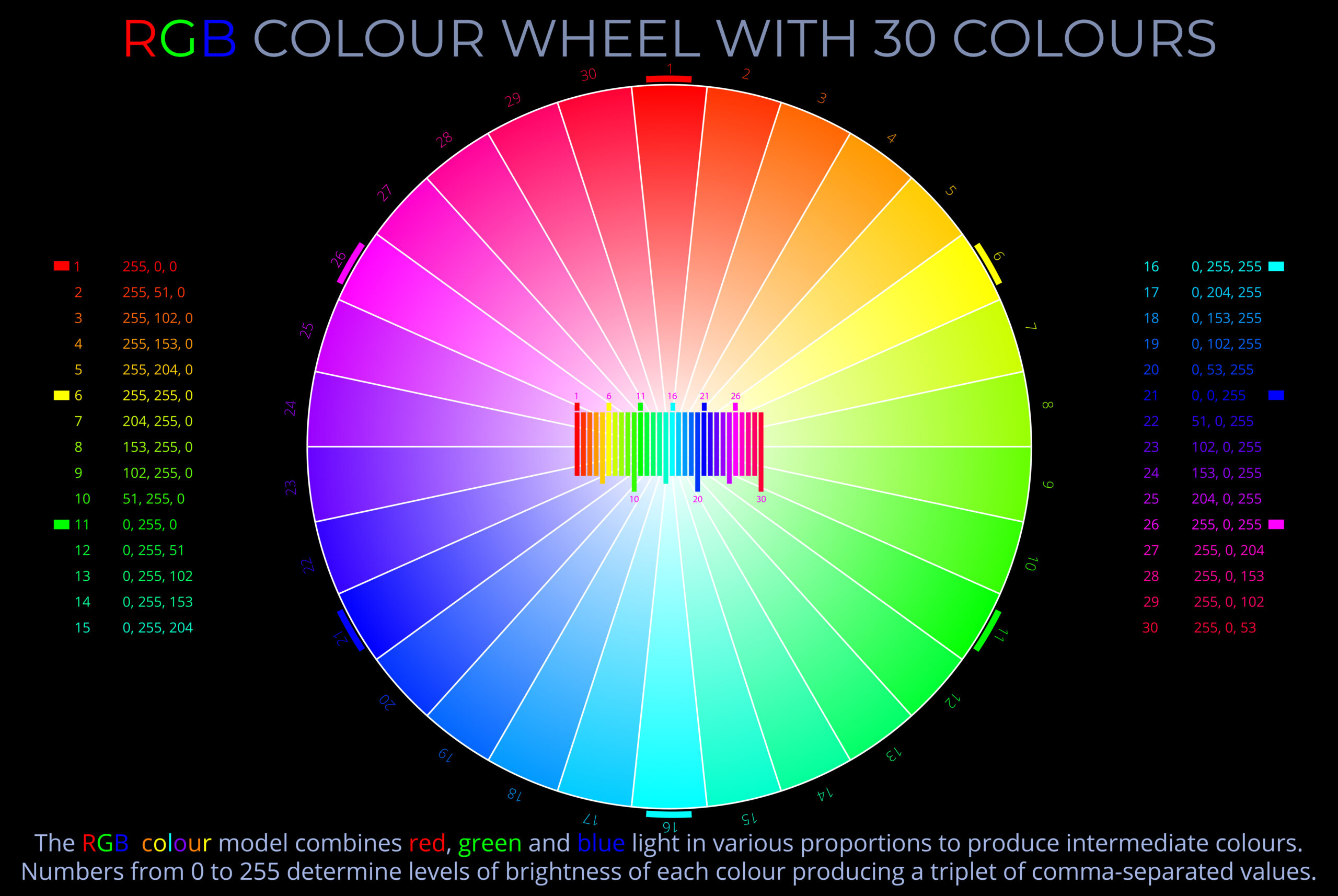
- Intermediate colours on an RGB colour wheel are produced by mixing equal intensities of adjacent pairs of colours.
- Secondary colours are created by mixing two primary colours in equal amounts. The RGB secondary colours are yellow (red + green), cyan (green + blue) and magenta (red + blue).
- Tertiary colours are created by mixing a primary colour with a secondary colour. For example, mixing equal amounts of red and yellow creates the tertiary colour orange.
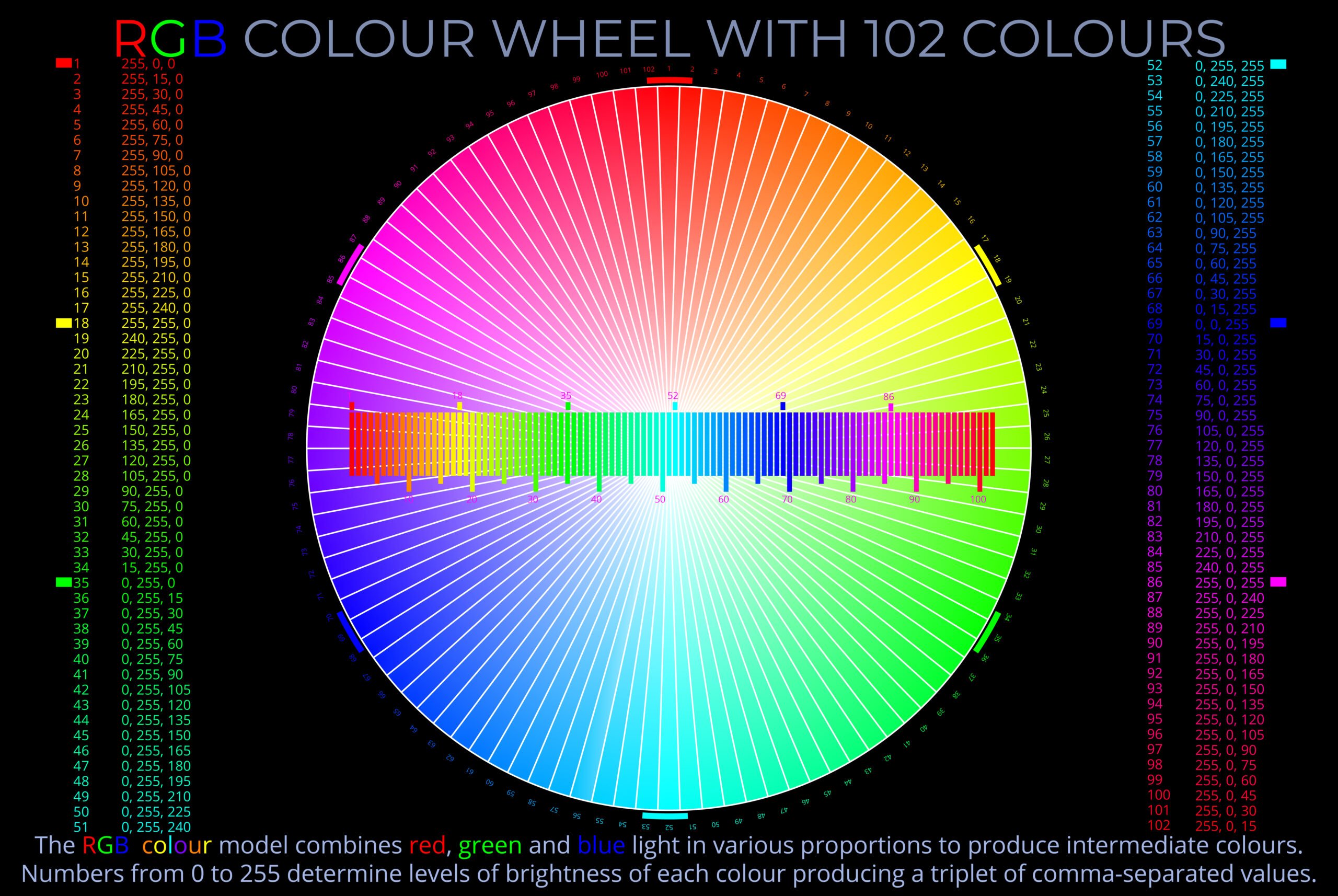
- The range of colours that can be produced by an RGB colour wheel is limited only by the system of notation and the resolution of the device they are displayed on.
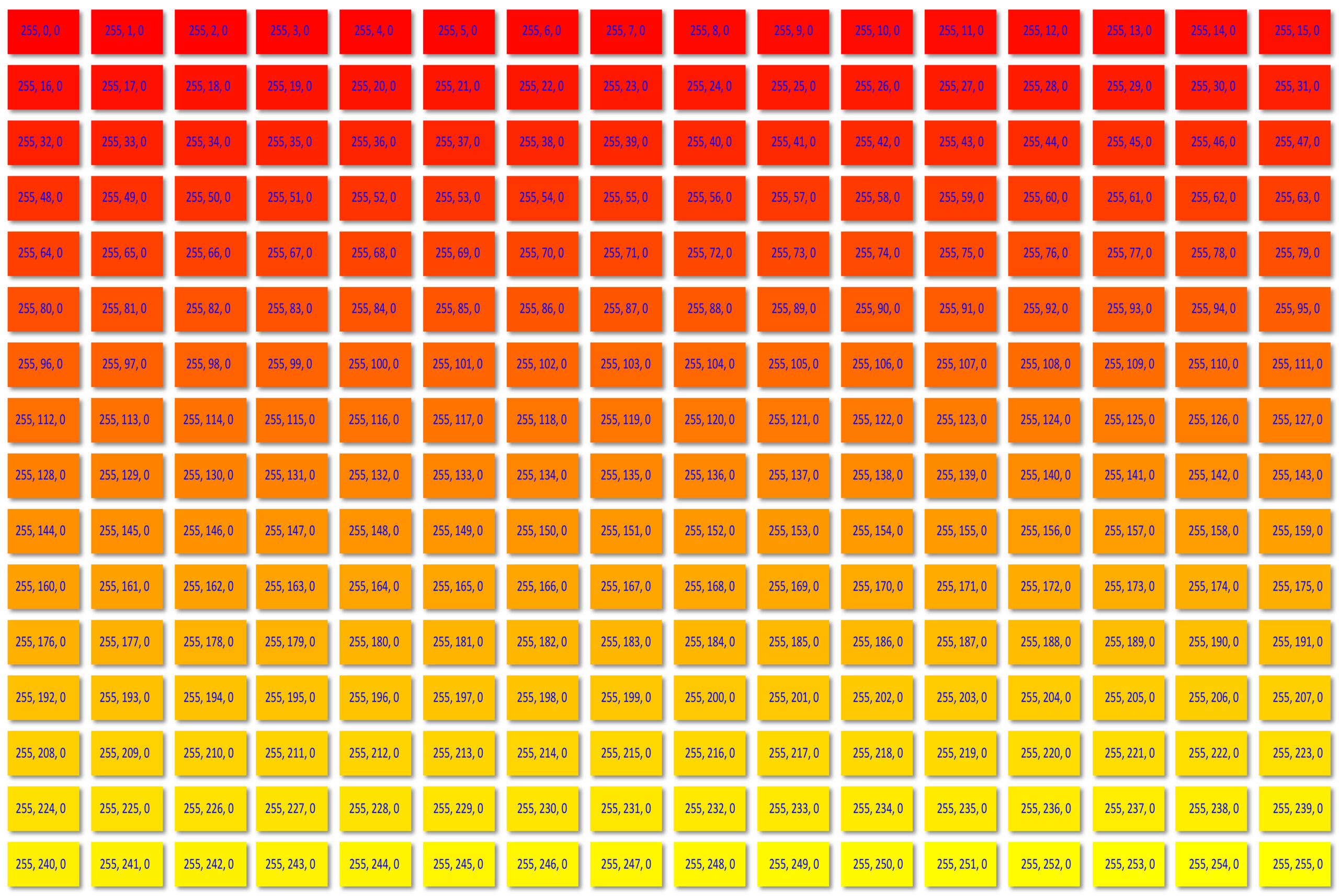
- The best way to find the correct code for an intermediate colour on a colour wheel is to work from a table (calculate a colour) or swatches (visually match a colour). You can find examples of tables here.