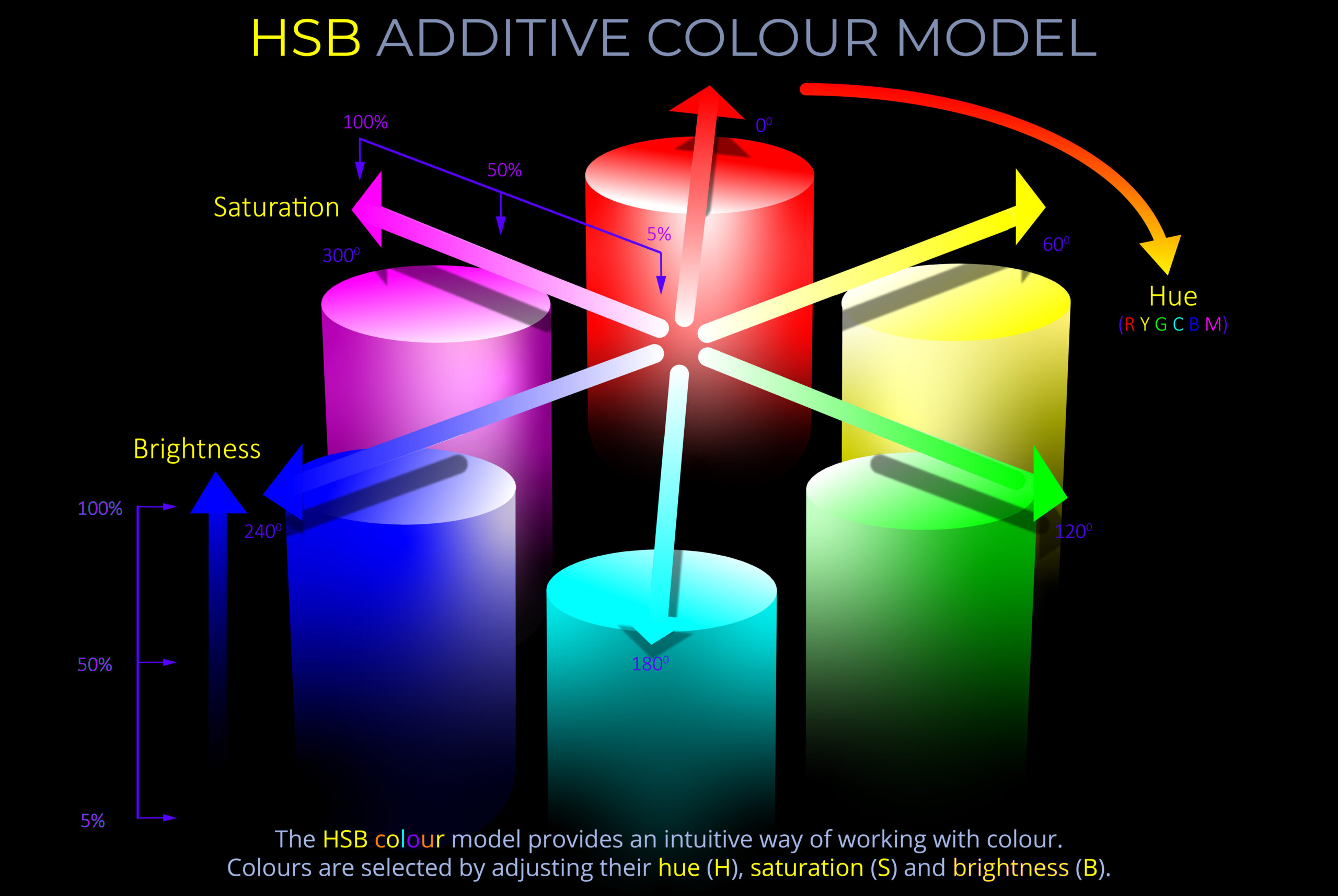
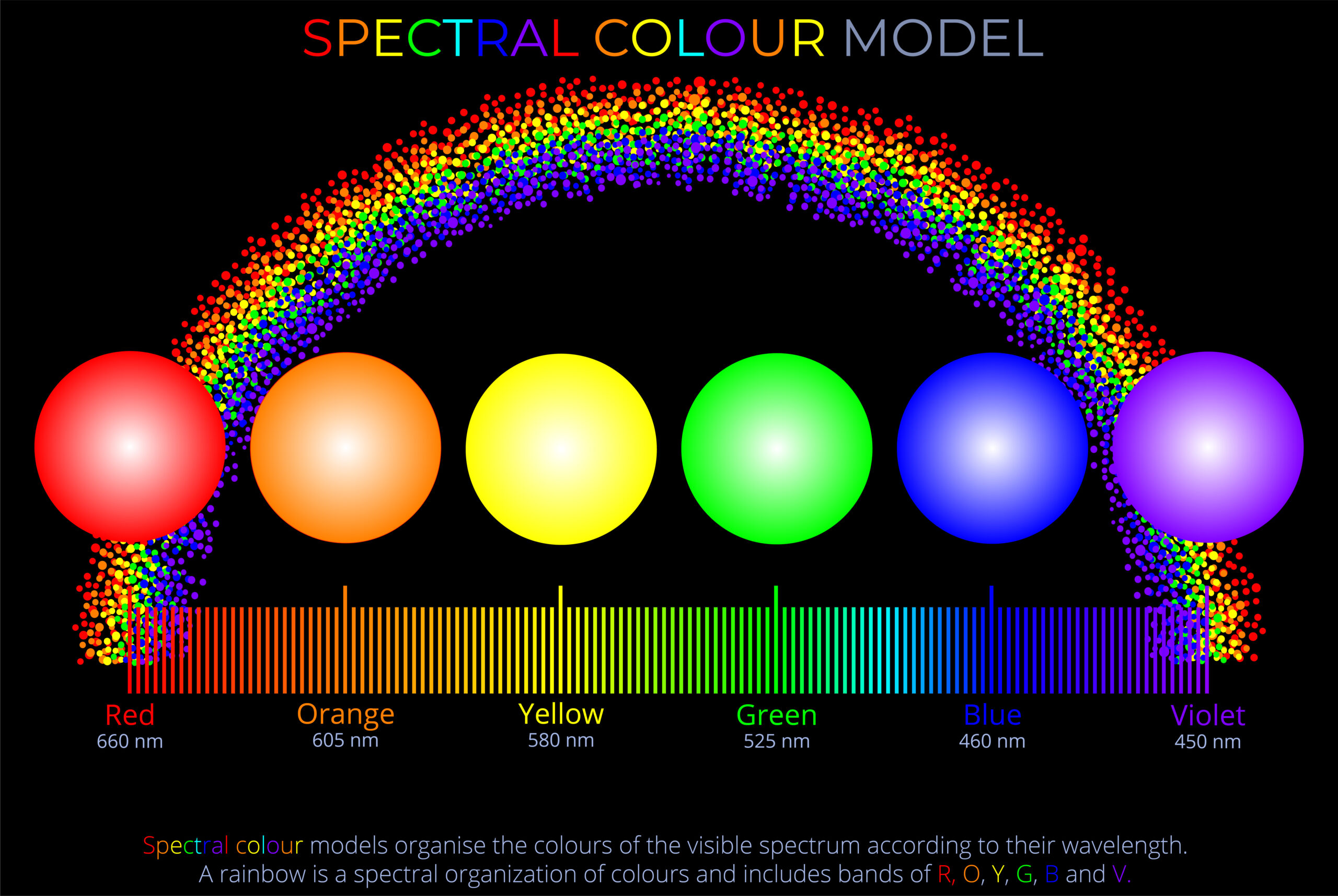
The RYB colour model deals with a subtractive method of colour mixing, commonly used in traditional art and painting where opaque pigments are in use.
- The three primary colours in RYB are red, yellow, and blue.
- By mixing these primaries in pairs and in the correct proportions, artists can create secondary colours like:
- Orange (red and yellow),
- Green (yellow and blue), and
- Purple (blue and red).
- Overlapping all three primaries creates darker and more complex hues.
- While historically significant, the RYB model has been largely replaced by RGB and CMYK in modern digital design and printing due to the incompatibility of RYB with these technologies.
- Many commercial and industrial paint shops have adopted computer-based systems that rely on tinting or colour-matching machines that can accurately reproduce wide ranges of specified paint colours that exactly match colour swatches or colours identified using RGB, CMYK, LAB or Pantone colour values.
- The RYB colour model is a subtractive method of colour mixing commonly used in traditional art and painting with opaque pigments.
- The three primary colours in RYB are red, yellow, and blue.
- By mixing these primaries in pairs and in the correct proportions, artists can create secondary colours like:
- Orange (red and yellow),
- Green (yellow and blue), and
- Purple (blue and red).
- Overlapping all three primaries creates darker and more complex hues.
- While historically significant, the RYB model has been largely replaced by RGB and CMYK in modern digital design and printing due to the incompatibility of RYB with these technologies.