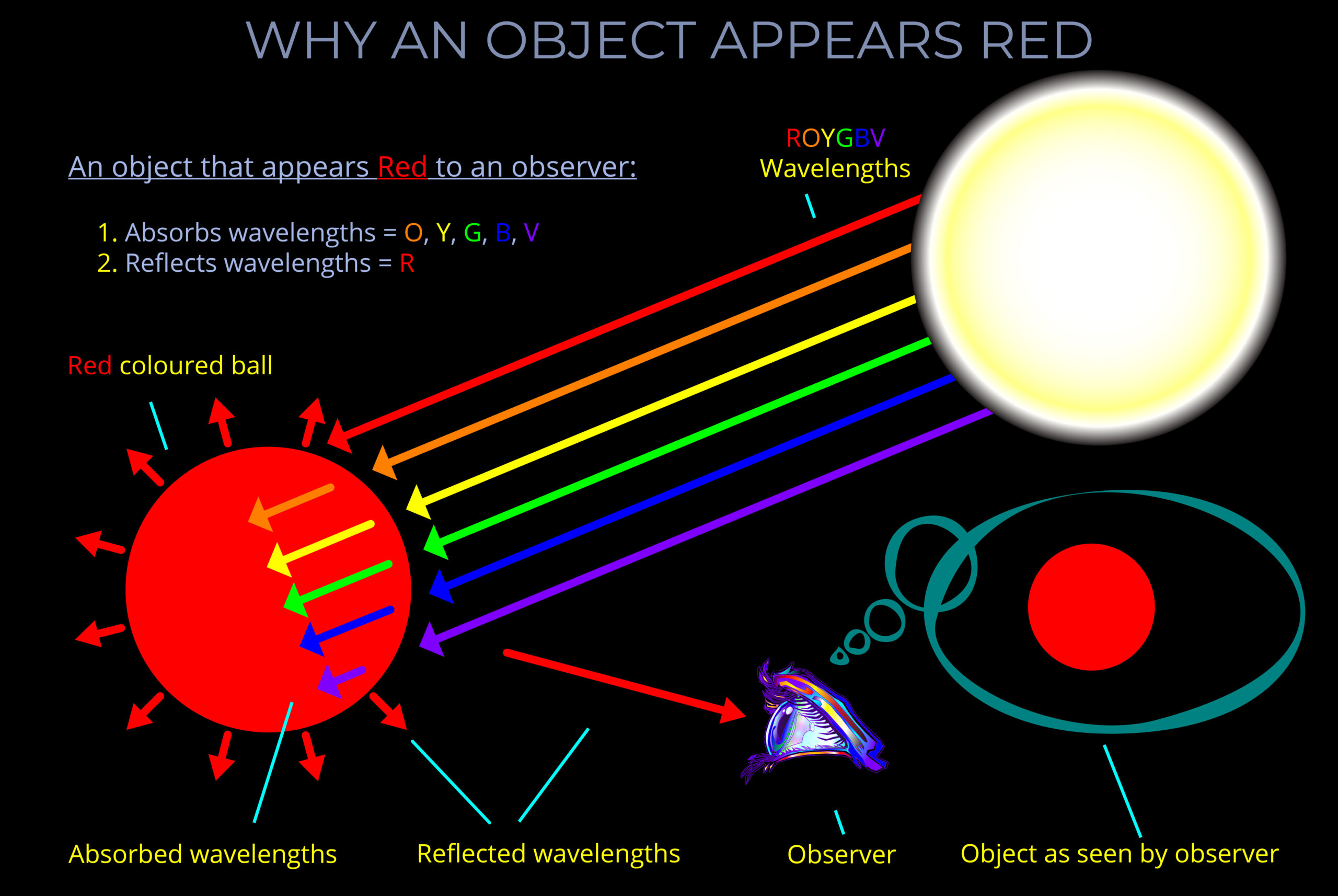
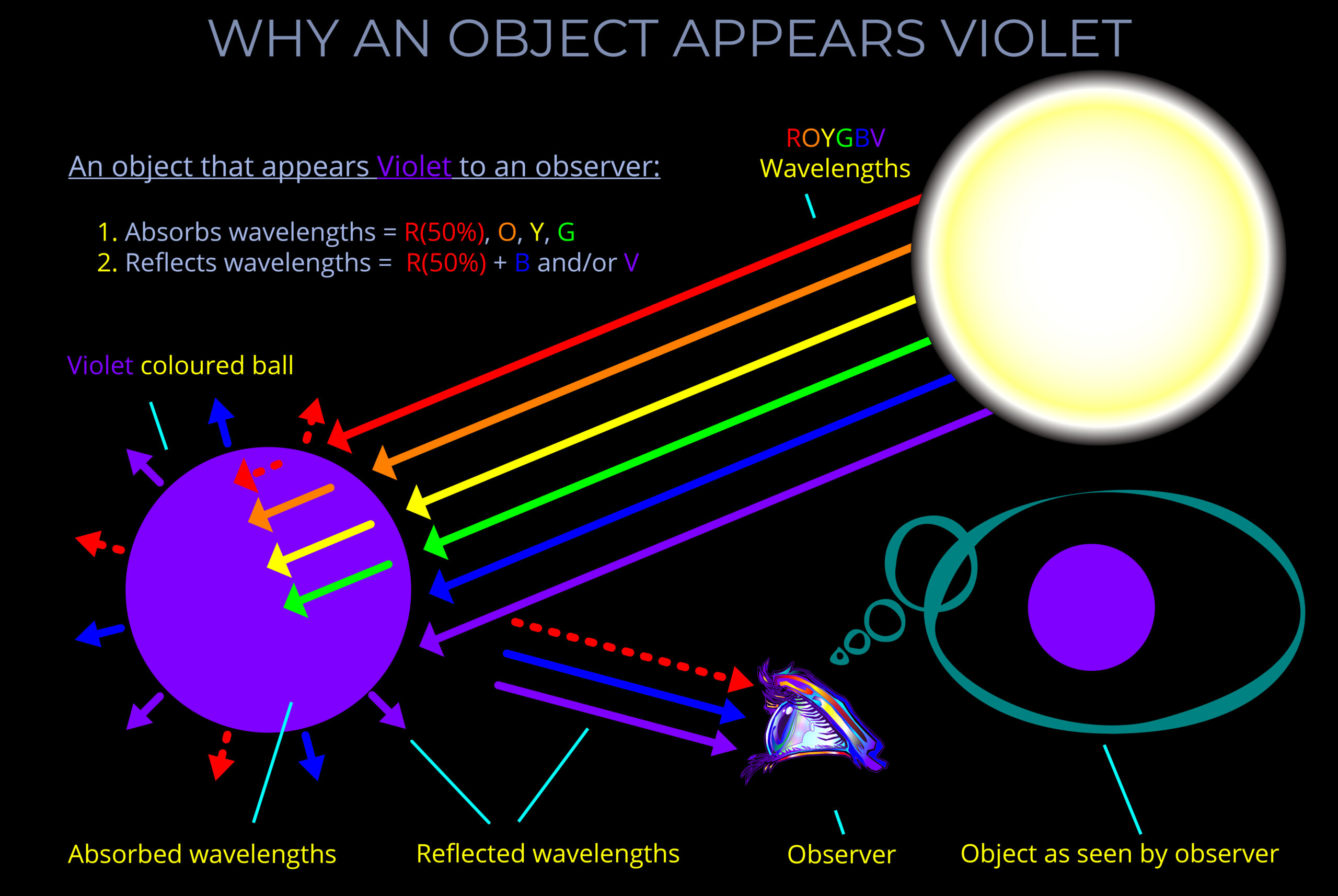
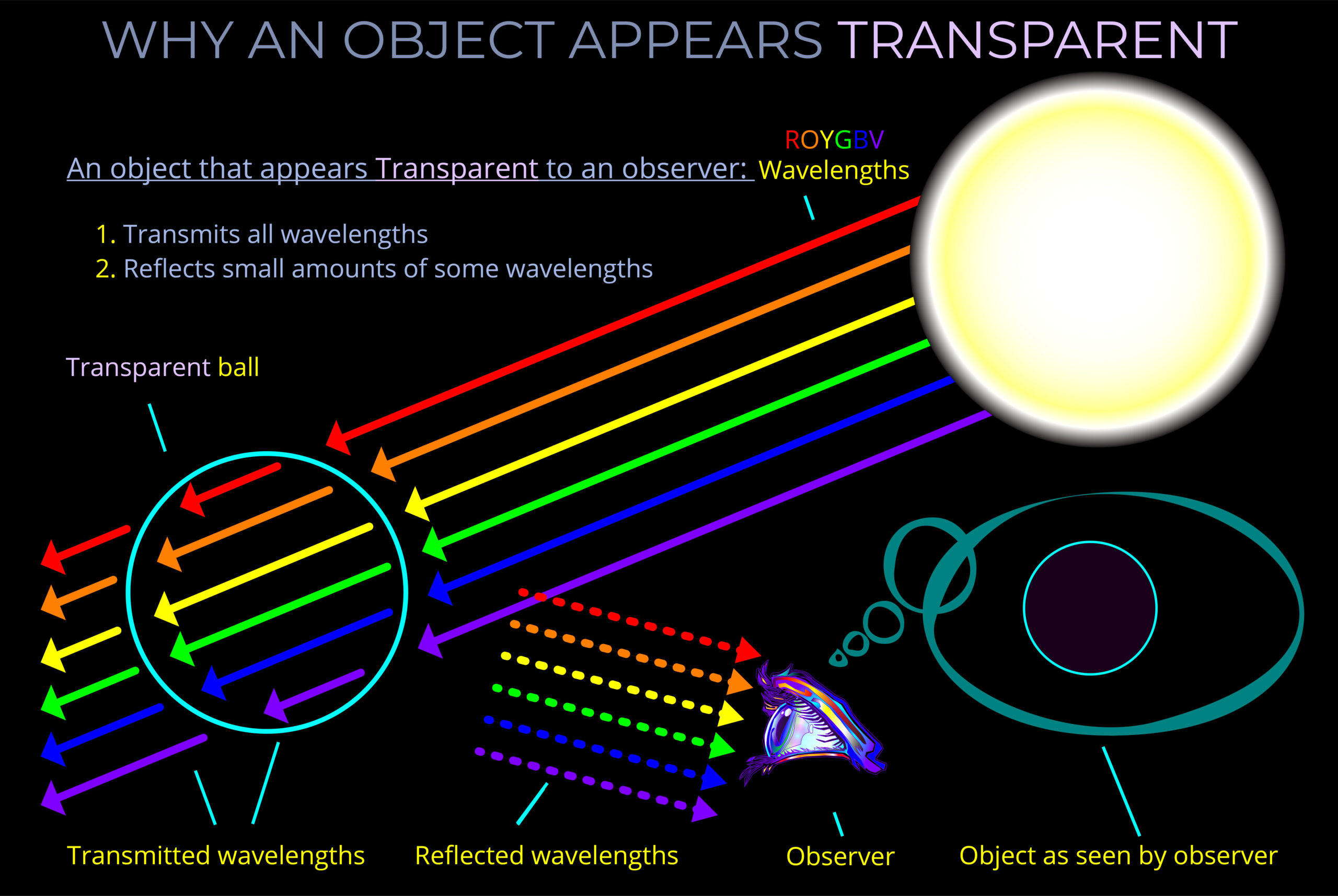
When light strikes an object, some wavelengths are absorbed and their energy is converted to heat, others undergo reflection or transmission.
- When light is absorbed by an object or medium, its energy excites electrons, which emit heat.
- Absorption of a particular wavelength of light by a material occurs when the frequency of the wave matches the resonant frequency of electrons orbiting atomic nuclei in the material.
- The opposite of absorption is transmission which refers to the process of electromagnetic radiation passing through a medium. When electromagnetic waves move through a material without being absorbed or reflected, we say they are transmitted. If no radiation is reflected or absorbed at all, the material achieves 100% transmission.
- Electrons selectively absorb photons whose frequencies match their resonant frequencies.
- Resonant frequency refers to the frequency at which electrons are most efficiently excited by absorbed light, leading to the emission of heat.
- As electrons absorb energy from photons, they vibrate more vigorously, leading to collisions between atoms and the production of heat.
- When light is reflected from a surface, it bounces off at the same wavelength with little or no change in energy.
- When light is absorbed by an object or medium, its energy excites electrons, causing them to vibrate more vigorously and to collide with other atoms, which in turn produces heat.
- Materials selectively absorb photons whose frequencies match their own frequencies.
- Absorption of light occurs when the frequency of the wave matches the frequency of electrons orbiting atomic nuclei in a material.
- Reflected light bounces off a surface at the same wavelength with little or no change in energy.