Polarization of electromagnetic waves refers to the direction in which they oscillate, perpendicular to the direction of the wave’s propagation.
- Polarization can be induced in light waves by various means, such as reflection, refraction, and scattering.
- There are several types of polarization, including circular, elliptical and plane polarization.
- Circular polarization refers to waves that rotate in circles as they propagate, with the electric and magnetic fields perpendicular to each other.
- Elliptical polarization combines linear and circular polarization, in which the wave oscillates in an elliptical pattern.
- Plane polarization (sometimes called linear polarization) refers to waves that oscillate in a single plane, such as waves that are vertically or horizontally polarized.
Plane polarization in detail
- Plane polarizing filters only allow waves with a certain orientation of their electric field to pass through.
- Plane polarizing filters block all the waves where the electric field is not orientated with the polarizing plane.
To visualize plane polarization:
- Imagine pushing a large sheet of card through a window fitted with close-fitting vertical bars.
- Only by aligning the card with the slots between the bars can it pass through. Align the card at any other angle and its path is blocked.
- Now substitute the alignment of the electric field of an electromagnetic wave for the sheet of card, and plane polarization for the bars on the window.
Causes of polarization
-
- Objects and phenomena that can cause plane polarization include:
- Polarizers (polarizing filters): Polarizers selectively transmit light of a certain polarization while blocking light of other polarizations. They can be made from materials such as polarizing film or a grid of fine wires.
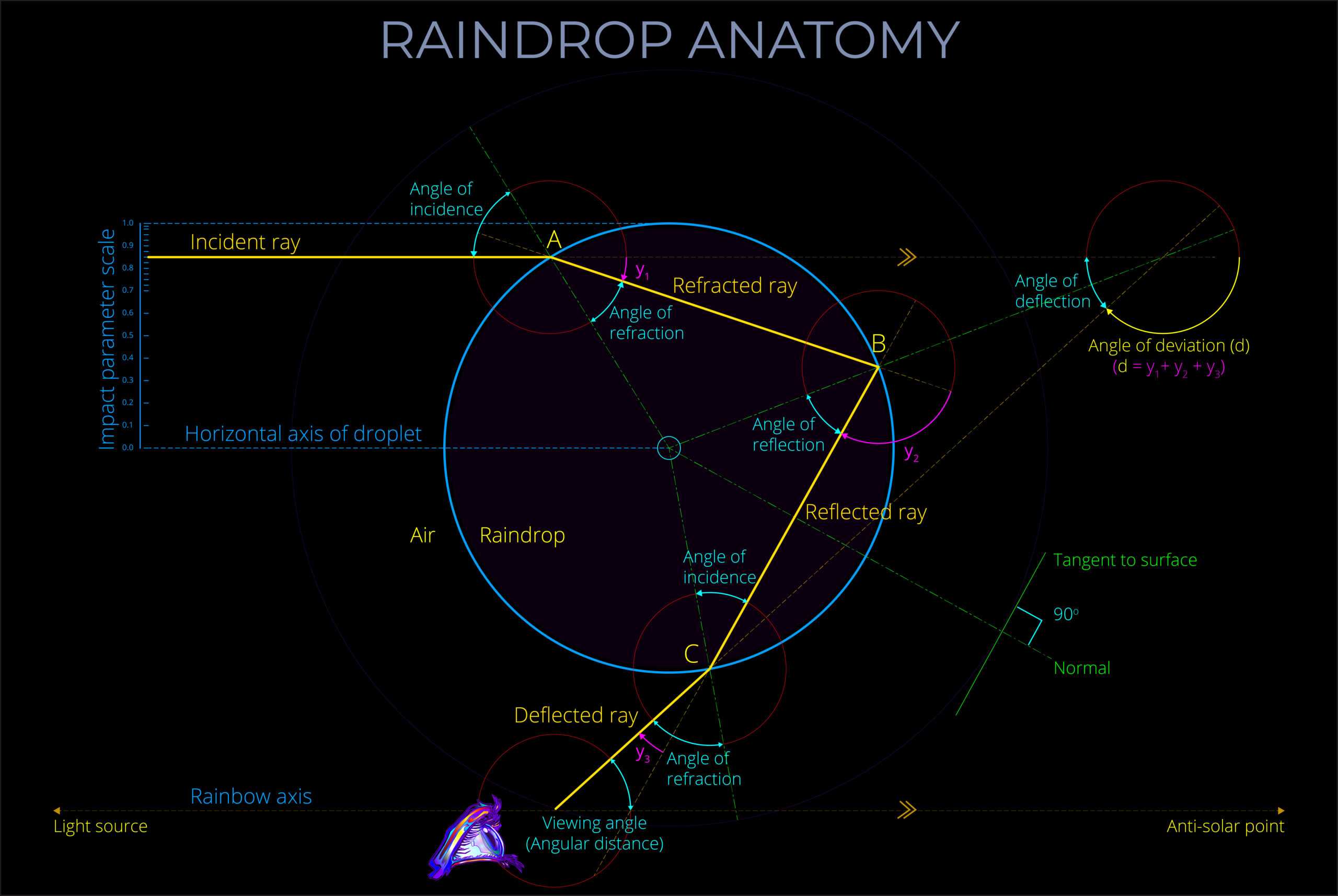
- Reflection: When light reflects off a non-metallic surface at an angle, it can become plane-polarized. This is because the electric field of the reflected light is perpendicular to the plane of incidence.
- Scattering: When light is scattered by small particles, such as dust or molecules in the atmosphere, it can become polarized. This is because the scattered light waves are preferentially oriented in certain directions.
- Liquid crystals: Liquid crystals are materials that can change their optical properties in response to an applied electric field. They are used in displays such as LCD screens to selectively polarize light in order to create an image.
- Objects and phenomena that can cause plane polarization include:
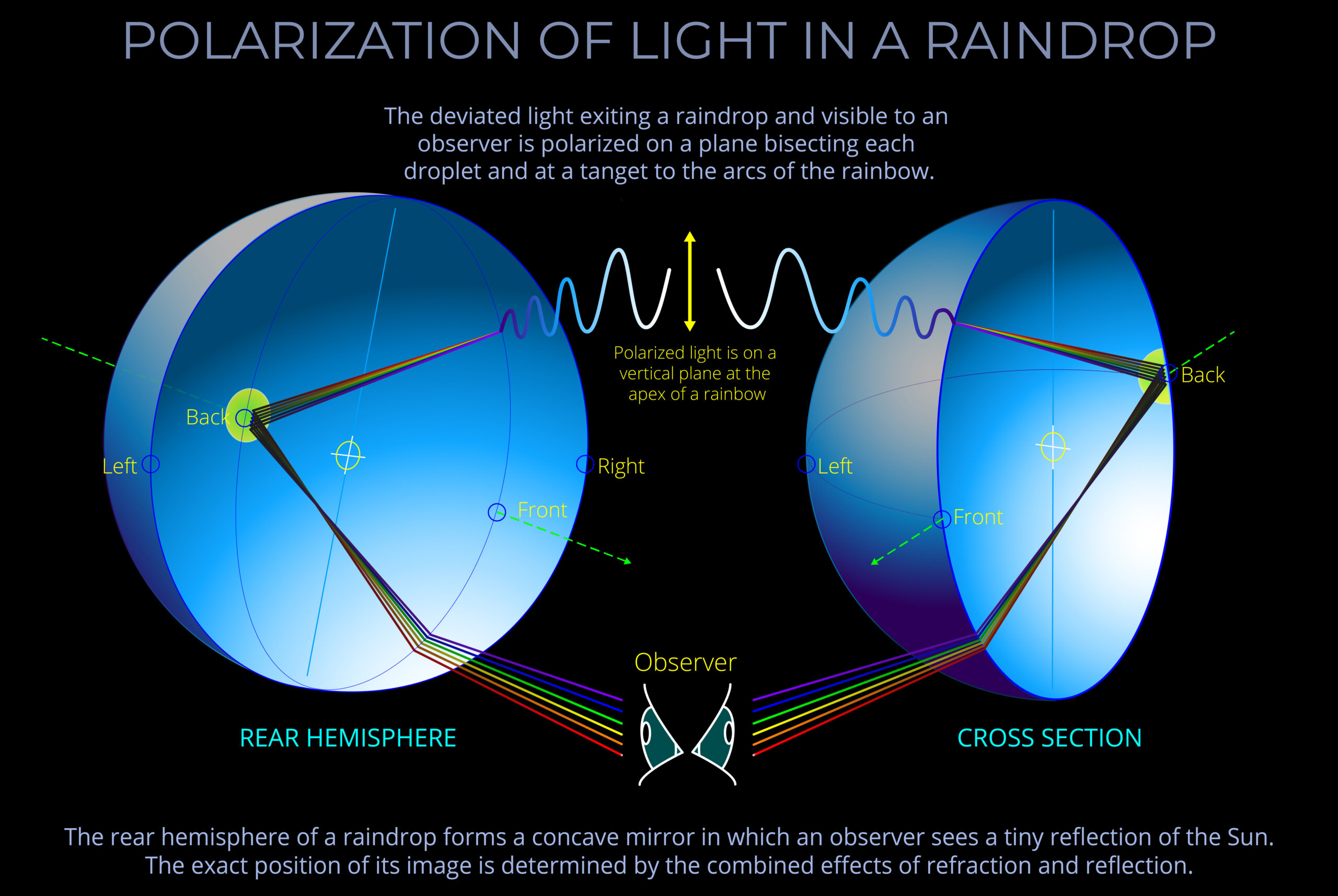
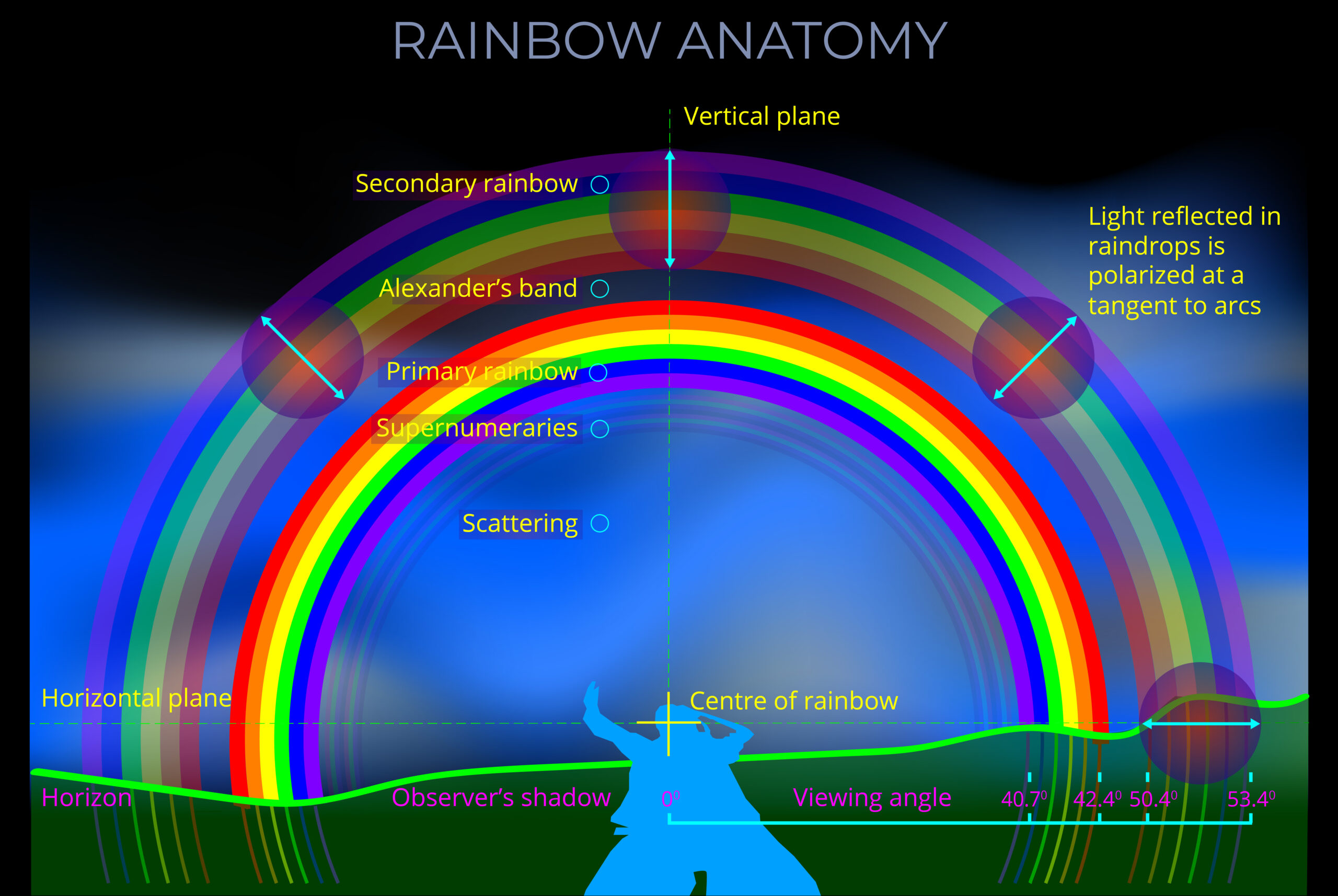
About plane polarization & rainbows
- Plane polarization is one of the optical effects that account for the appearance of rainbows.
- Plane polarization, also known as linear polarization, is a characteristic of electromagnetic waves, including light.
- When an electromagnetic wave is plane polarized, the electric field remains fixed in a particular direction as the wave propagates. As a result, the light oscillates on a single plane, hence the name.
- The polarization of light in rainbows contributes to the vividness and intensity of the colours we see.
- The light that produces rainbow effects is typically 96% polarized. This means that:
- The presence of other atmospheric phenomena, such as water droplets of varying sizes or ice crystals, can affect the amount of plane polarization and so influence the appearance of rainbows.
- Polarization of electromagnetic waves refers to the direction in which they oscillate, perpendicular to the direction of the wave’s propagation.
- Polarization can be induced in light waves by various means, such as reflection, refraction, and scattering.
- There are several types of polarization, including circular, elliptical and plane polarization.
- Circular polarization refers to waves that rotate in circles as they propagate, with the electric and magnetic fields perpendicular to each other.
- Elliptical polarization combines linear and circular polarization, in which the wave oscillates in an elliptical pattern.
- Plane polarization (sometimes called linear polarization) refers to waves that oscillate in a single plane, such as waves that are vertically or horizontally polarized.