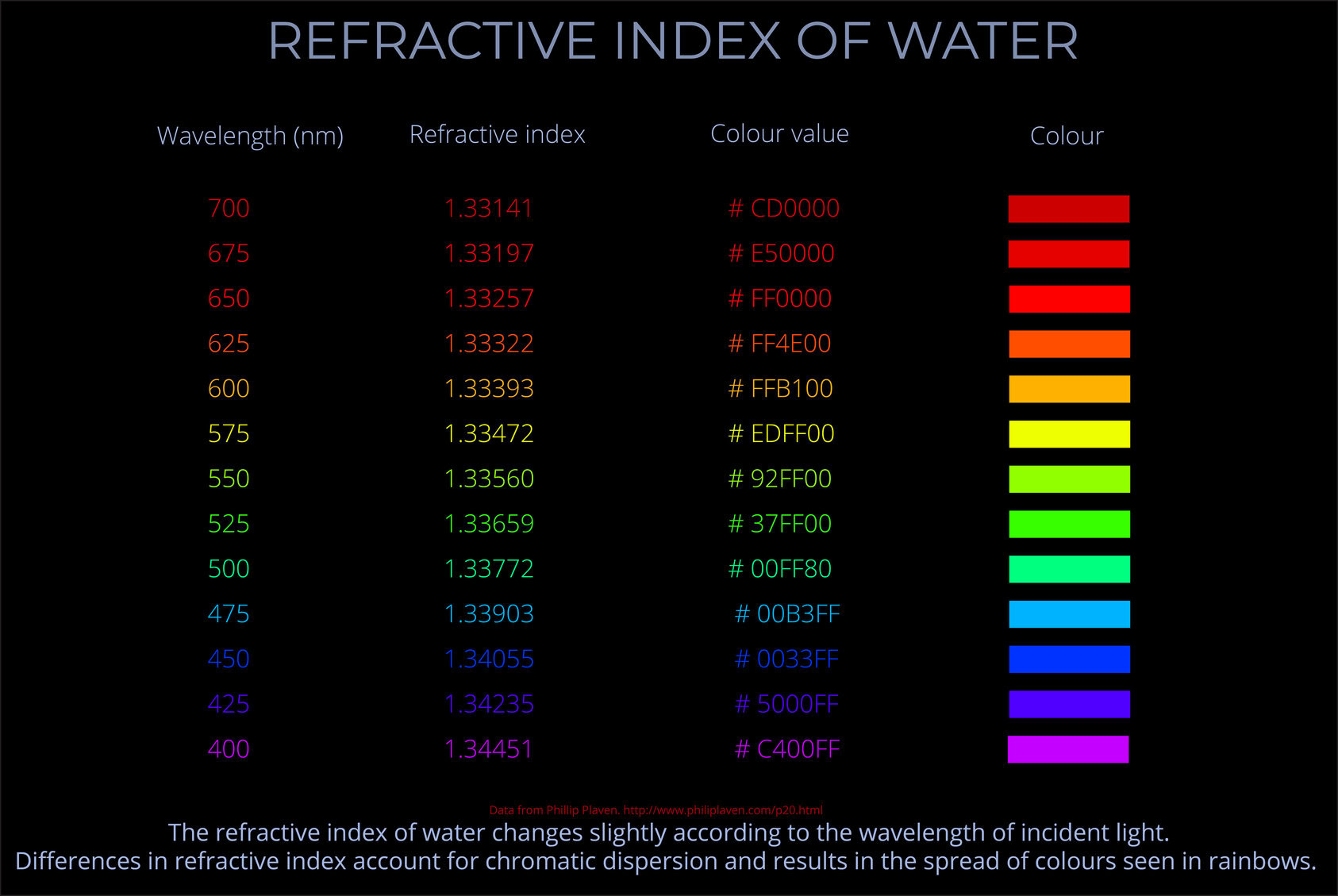
Refractive Index of Water
£0.00
This is one of a set of almost 40 diagrams exploring Rainbows.
Each diagram appears on a separate page and is supported by a full explanation.
- Follow the links embedded in the text for definitions of all the key terms.
- For quick reference don’t miss the summaries of key terms further down each page.
Description
Refractive Index of Water
TRY SOME QUICK QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS TO GET STARTED
About the diagram
About wavelength
About refractive index
About colour
Some key terms
The refractive index (index of refraction) of a medium measures how much the speed of light is reduced when it passes through a medium compared to its speed in a vacuum.
- Refractive index (or, index of refraction) is a measurement of how much the speed of light is reduced when it passes through a medium compared to the speed of light in a vacuum.
- The concept of refractive index applies to the full electromagnetic spectrum, from gamma-rays to radio waves.
- The refractive index can vary with the wavelength of the light being refracted. This phenomenon is called dispersion, and it is what causes white light to split into its constituent colours when it passes through a prism.
- The refractive index of a material can be affected by various factors such as temperature, pressure, and density.
Refraction refers to the way that electromagnetic radiation (light) changes speed and direction as it travels across the boundary between one transparent medium and another.
- Light bends towards the normal and slows down when it moves from a fast medium (like air) to a slower medium (like water).
- Light bends away from the normal and speeds up when it moves from a slow medium (like diamond) to a faster medium (like glass).
- These phenomena are governed by Snell’s law, which describes the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction.
- The refractive index (index of refraction) of a medium indicates how much the speed and direction of light are altered when travelling in or out of a medium.
- It is calculated by dividing the speed of light in a vacuum by the speed of light in the material.
- Snell’s law relates the angles of incidence and refraction to the refractive indices of the two media involved.
- Snell’s law states that the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is equal to the ratio of the refractive indices.
The refractive index (index of refraction) of a medium measures how much the speed of light is reduced when it passes through a medium compared to its speed in a vacuum.
- Refractive index (or, index of refraction) is a measurement of how much the speed of light is reduced when it passes through a medium compared to the speed of light in a vacuum.
- The concept of refractive index applies to the full electromagnetic spectrum, from gamma-rays to radio waves.
- The refractive index can vary with the wavelength of the light being refracted. This phenomenon is called dispersion, and it is what causes white light to split into its constituent colours when it passes through a prism.
- The refractive index of a material can be affected by various factors such as temperature, pressure, and density.