Facts about White Light
£0.00
This diagram introduces white light, the name given to light that contains all wavelength of the visible spectrum.
Remember that:
Description
Facts about White Light
TRY SOME QUICK QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS TO GET STARTED
About the diagram
About the diagram
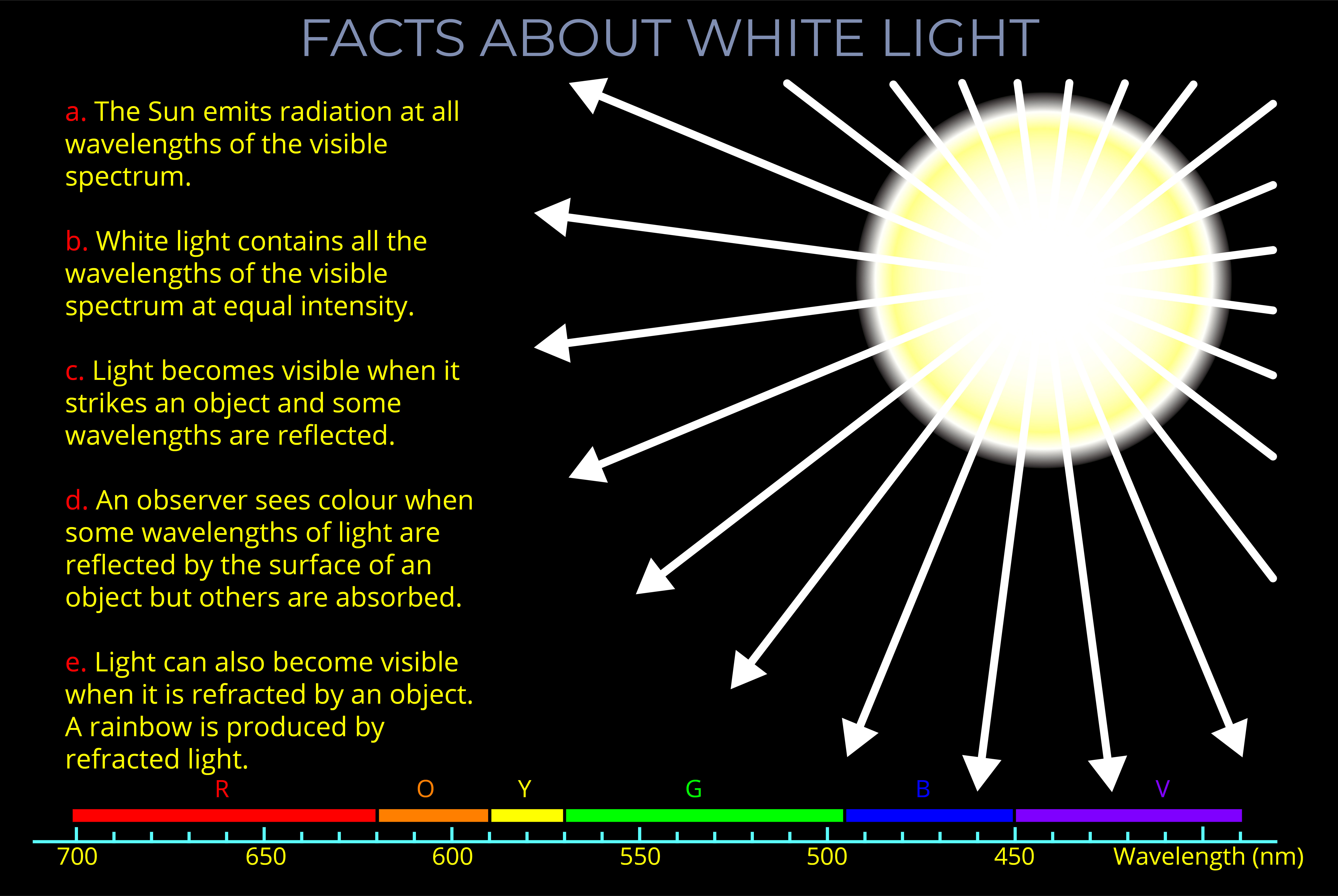
- This diagram introduces white light, the name given to light that contains all wavelengths of the visible spectrum.
Remember that:
- White light contains all the wavelengths of the visible spectrum, but to produce white light, each wavelength must be of equal intensity.
- White light contains all wavelengths of light that correspond with the colours of the rainbow.
- The white light human beings see does not include infrared and ultraviolet wavelengths of light because they are outside the visible spectrum.
Now let’s look at that in detail:
- White light is the name given to visible light that contains all wavelengths of the visible spectrum at equal intensities.
- As light travels through a vacuum or a medium it is described as white light if it contains all the wavelengths of visible light.
- As light travels through the air it is invisible to our eyes.
- The term white light doesn’t mean light is white as it travels through the air.
- When white light strikes a neutral-coloured object and all wavelengths are reflected it appears white to an observer.
- When some wavelengths are absorbed by an object and others are reflected then it is the reflected wavelengths that determine the colour an observer sees.
Some key terms
RGB colour is an additive colour model in which red, green and blue light is combined to reproduce a wide range of other colours.
- The primary colours in the RGB colour model are red, green and blue.
- In the RGB model, different combinations and intensities of red, green, and blue light are mixed to create various colours. When these three colours are combined at full intensity, they produce white light.
- Additive colour models are concerned with mixing light, not dyes, inks or pigments (these rely on subtractive colour models such as the RYB colour model and the CMY colour model).
- The RGB colour model works in practice by asking three questions of any colour: how red is it (R), how green is it (G), and how blue is it (B).
- The RGB model is popular because it can easily produce a comprehensive palette of 1530 vivid hues simply by adjusting the combination and amount of each of the three primaries it contains.
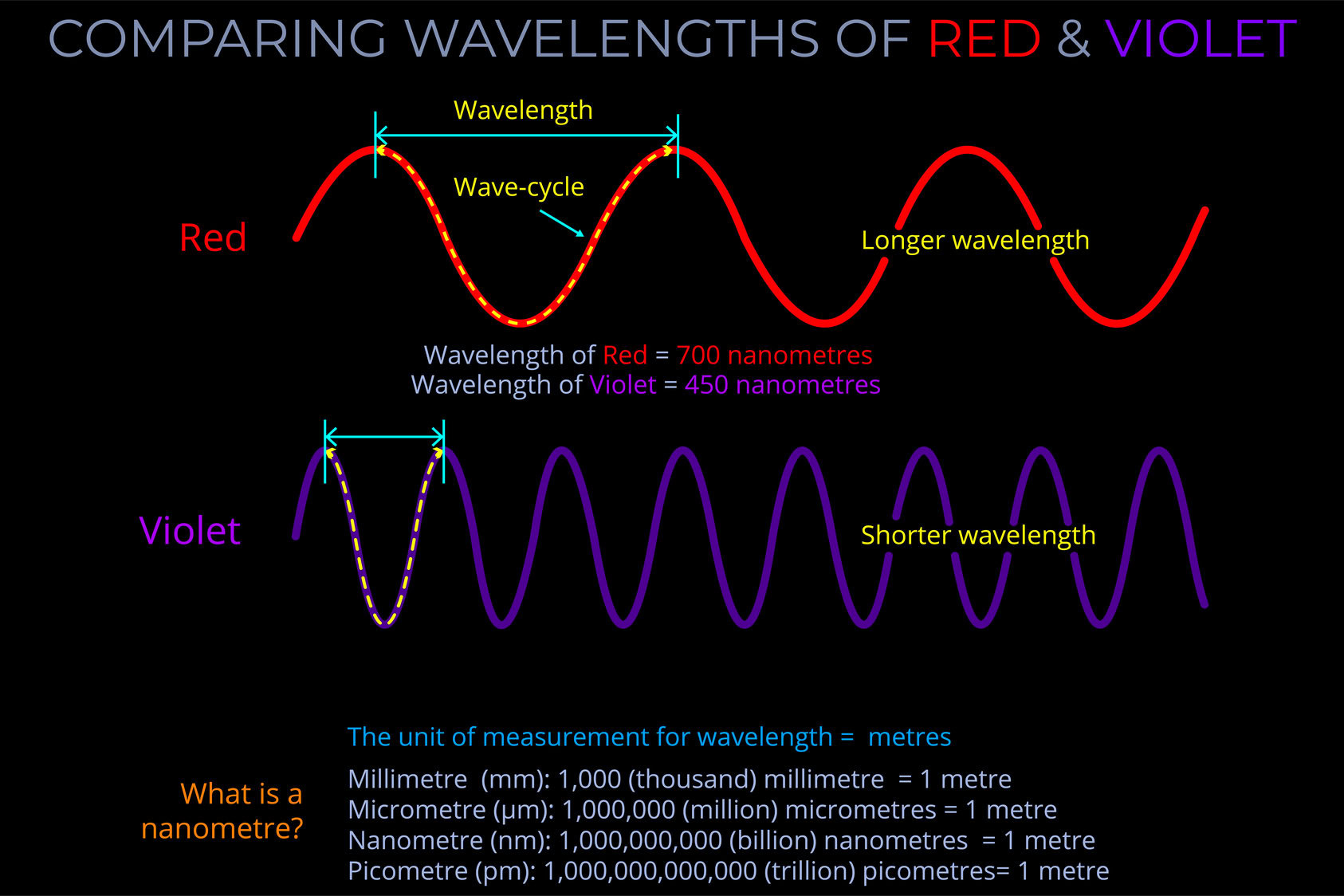
Wavelength measures a complete wave cycle, which is the distance from any point on a wave to the corresponding point on the next wave.
- While wavelength can be measured from any point on a wave, it is often simplest to measure from the peak of one wave to the peak of the next or from the bottom of one trough to the bottom of the next, ensuring the measurement covers the whole of the cycle.
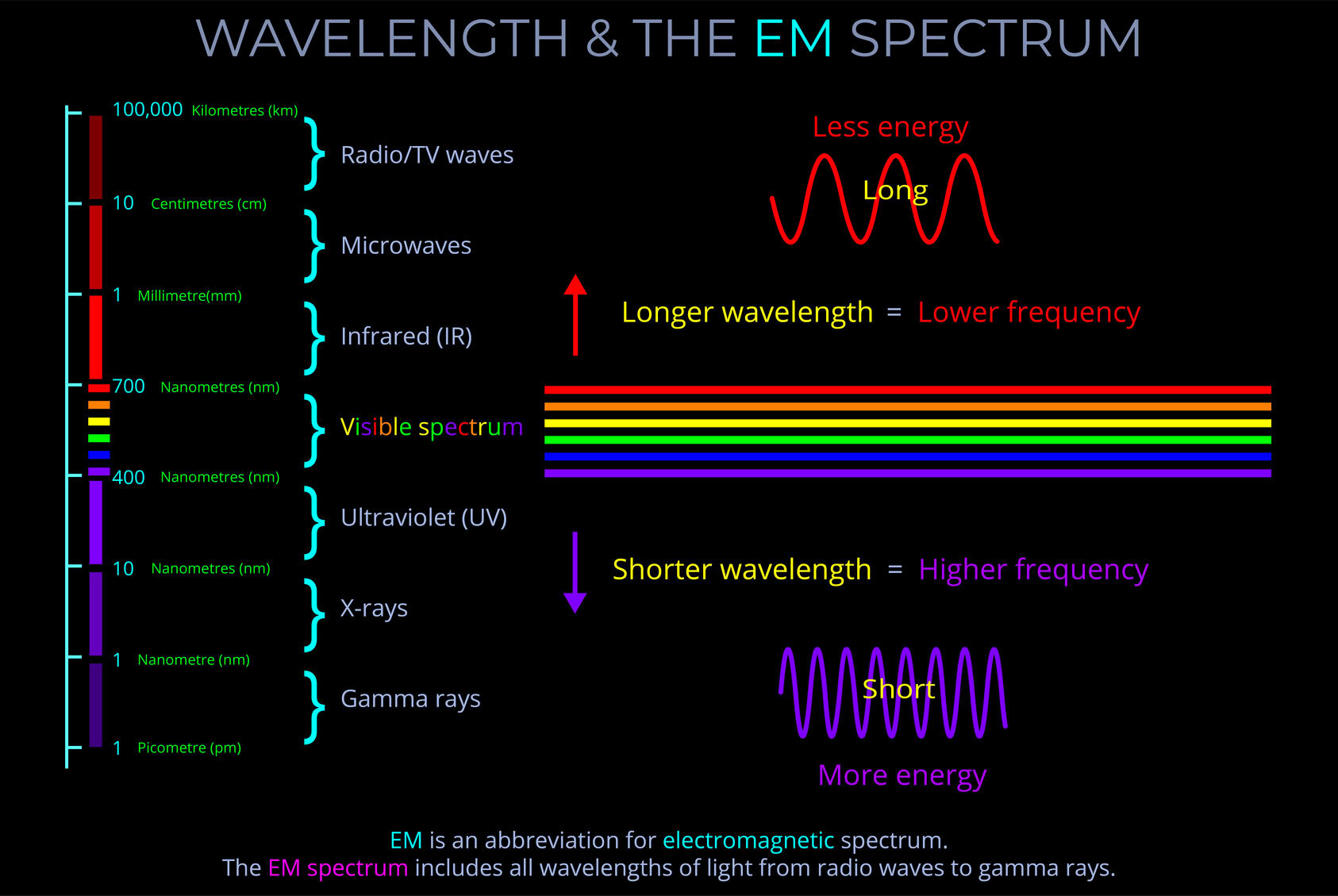
- The wavelength of an electromagnetic wave is usually given in metres.
- The wavelength of visible light is typically measured in nanometres, with 1,000,000,000 nanometres making up a metre.
- Radio waves, visible light, and gamma waves for example, each have different ranges of wavelengths within the electromagnetic spectrum.
The visible spectrum is the range of wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum that correspond with all the different colours we see in the world.
- As light travels through the air it is invisible to our eyes.
- Human beings don’t see wavelengths of light, but they do see the spectral colours that correspond with each wavelength and colours produced when different wavelengths are combined.
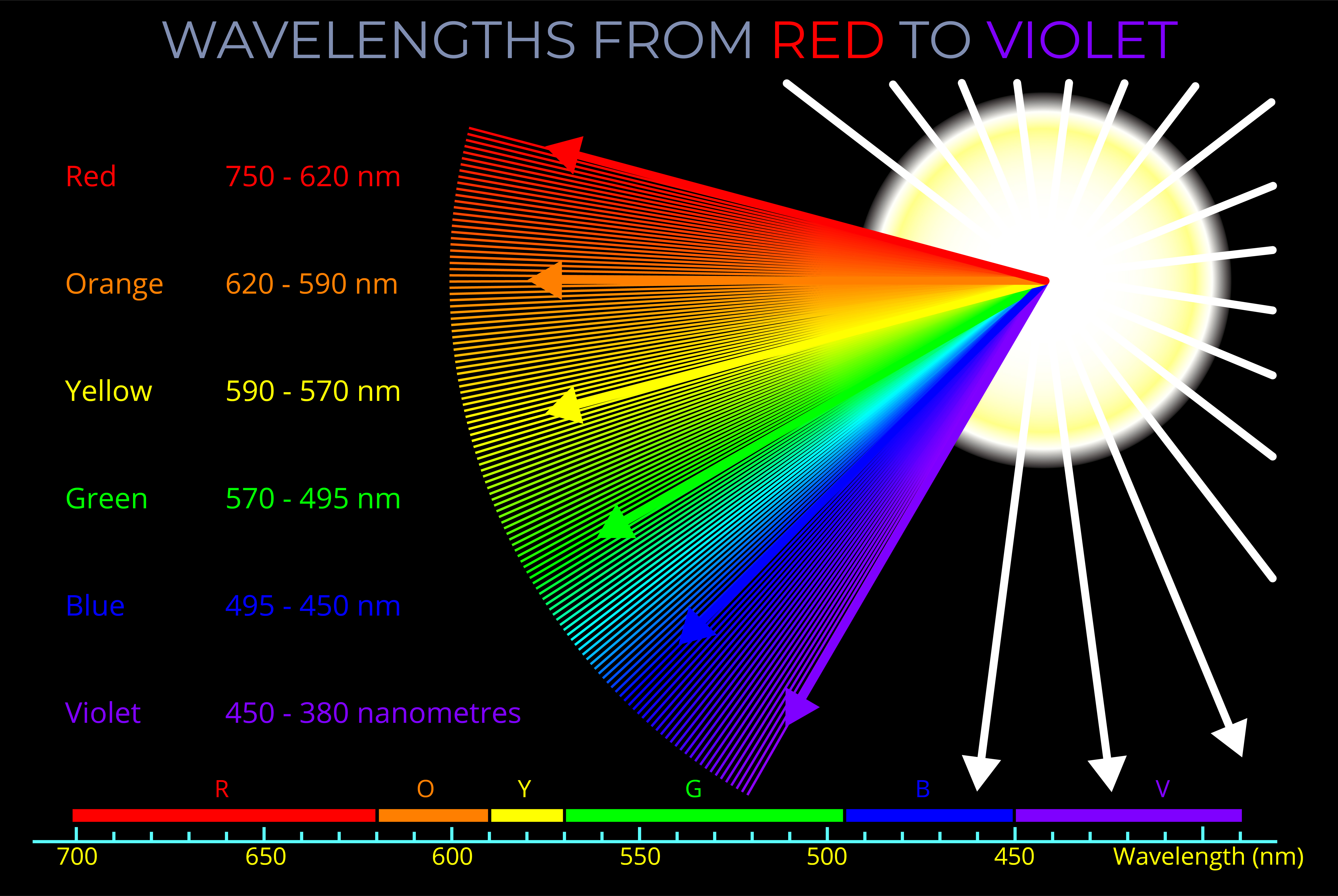
- The visible spectrum includes all the spectral colours between red and violet and each is produced by a single wavelength.
- The visible spectrum is often divided into named colours, though any division of this kind is somewhat arbitrary.
- Traditional colours referred to in English include red, orange, yellow, green, blue, and violet.
Electromagnetic radiation is a type of energy more commonly simply called light. Detached from its source, it is transported by electromagnetic waves (or their quanta, photons) and propagates through space at the speed of light.
- Electromagnetic radiation (EM radiation or EMR) includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visible) light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays.
- Man-made technologies that produce electromagnetic radiation include radio and TV transmitters, radar, MRI scanners, microwave ovens, computer screens, mobile phones, all types of lights and lamps, electric blankets, electric bar heaters, lasers and x-ray machines.
- At the quantum scale of electromagnetism, electromagnetic radiation is described in terms of photons rather than waves. Photons are elementary particles responsible for all electromagnetic phenomena.
- The term quantum refers to the smallest quantity into which something can be divided. A quantum of a thing is indivisible into smaller units so they have no sub-structure. A photon is a quantum of electromagnetic radiation.
- A single photon with a wavelength corresponding with gamma rays might carry 100,000 times the energy of a single photon of visible light.
Sunlight, also known as daylight or visible light, refers to the portion of electromagnetic radiation emitted by the Sun that is detectable by the human eye. It is one form of the broad range of electromagnetic radiation produced by the Sun. Our eyes are particularly sensitive to this specific range of wavelengths, enabling us to perceive the Sun and the world around us.
- Sunlight is only one form of electromagnetic radiation emitted by the Sun.
- Sunlight is only a very small part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
- Sunlight is the form of electromagnetic radiation that our eyes are sensitive to.
- Other types of electromagnetic radiation that we are sensitive to, but cannot see, are infrared radiation that we feel as heat and ultraviolet radiation that causes sunburn.
The visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum is called the visible spectrum.
- The visible spectrum is the range of wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum that correspond with all the different colours we see in the world.
- As light travels through the air it is invisible to our eyes.
- Human beings don’t see wavelengths of light, but they do see the spectral colours that correspond with each wavelength and colours produced when different wavelengths are combined.
- The visible spectrum includes all the spectral colours between red and violet and each is produced by a single wavelength.
- The visible spectrum is often divided into named colours, though any division of this kind is somewhat arbitrary.
- Traditional colours referred to in English include red, orange, yellow, green, blue, and violet.
Chromatic dispersion is the process where light, under specific conditions, splits into its constituent wavelengths, and the colours linked with each wavelength become visible to a human observer.
- Chromatic dispersion is the result of the connection between wavelength and refractive index..
- When light moves from one medium (like air) to another (like water or glass), each wavelength is influenced to a varying extent based on the refractive index of the involved media. The outcome is that every wavelength changes its direction and speed.
- If the light source emits white light, the individual wavelengths spread out, with red at one end and violet at the other.
- A familiar example of chromatic dispersion is when white light strikes raindrops and a rainbow becomes visible to an observer.
The electromagnetic spectrum includes electromagnetic waves with all possible wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation, ranging from low-energy radio waves through visible light to high-energy gamma rays.
- There are no precisely defined boundaries between the bands of electromagnetic radiation in the electromagnetic spectrum.
- The electromagnetic spectrum includes, in order of increasing frequency and decreasing wavelength: radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays and gamma rays.
- Visible light is only a very small part of the electromagnetic spectrum.