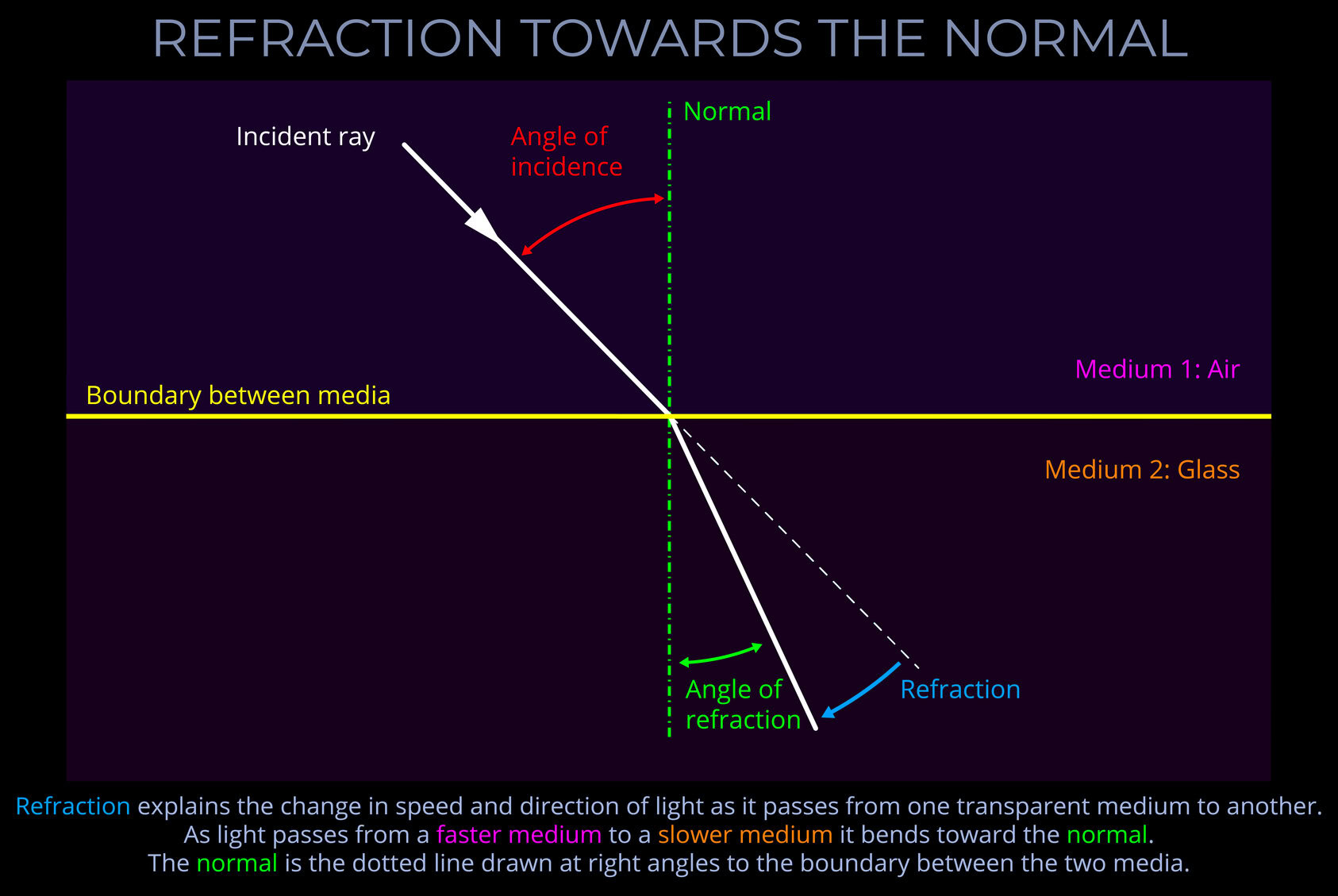
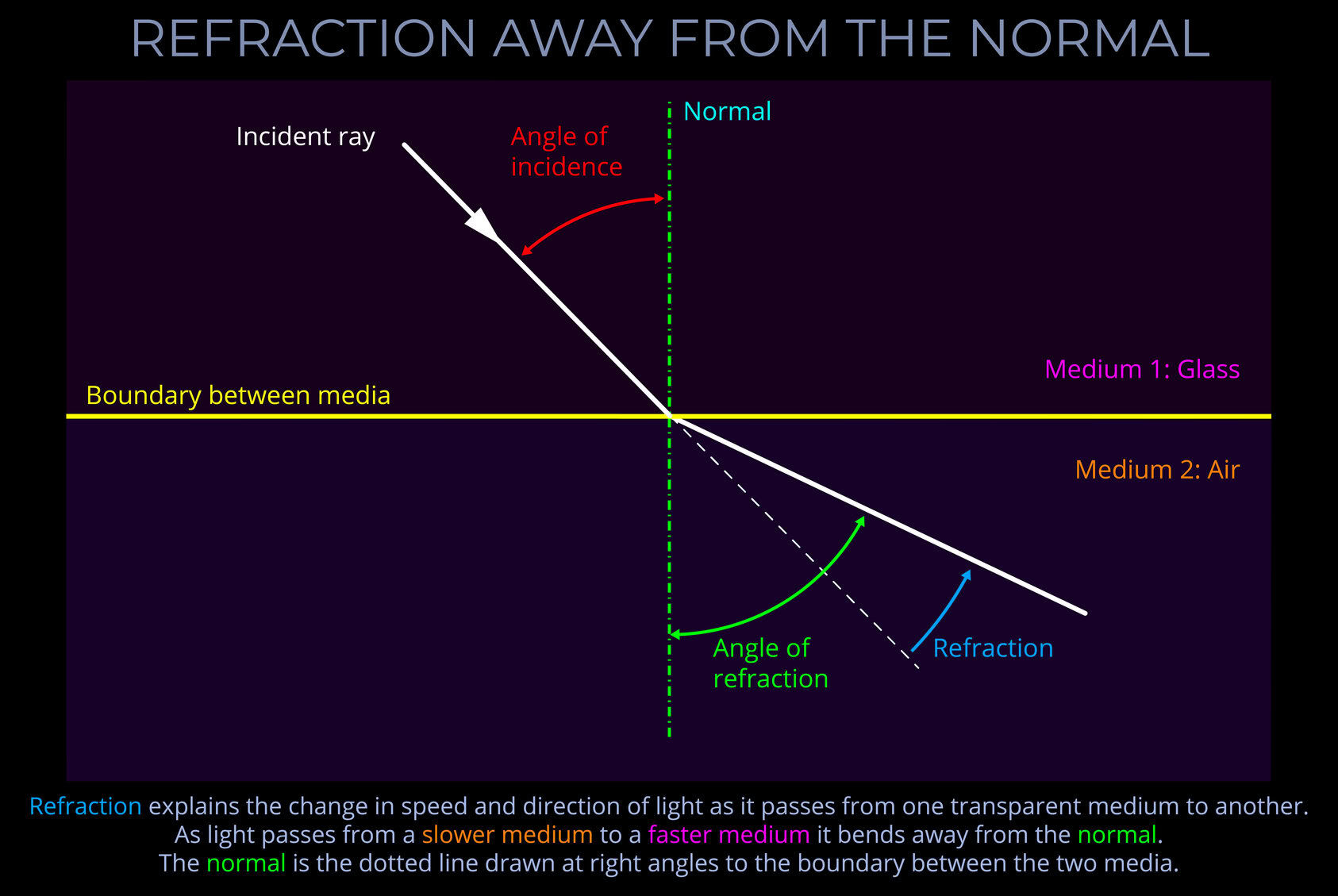
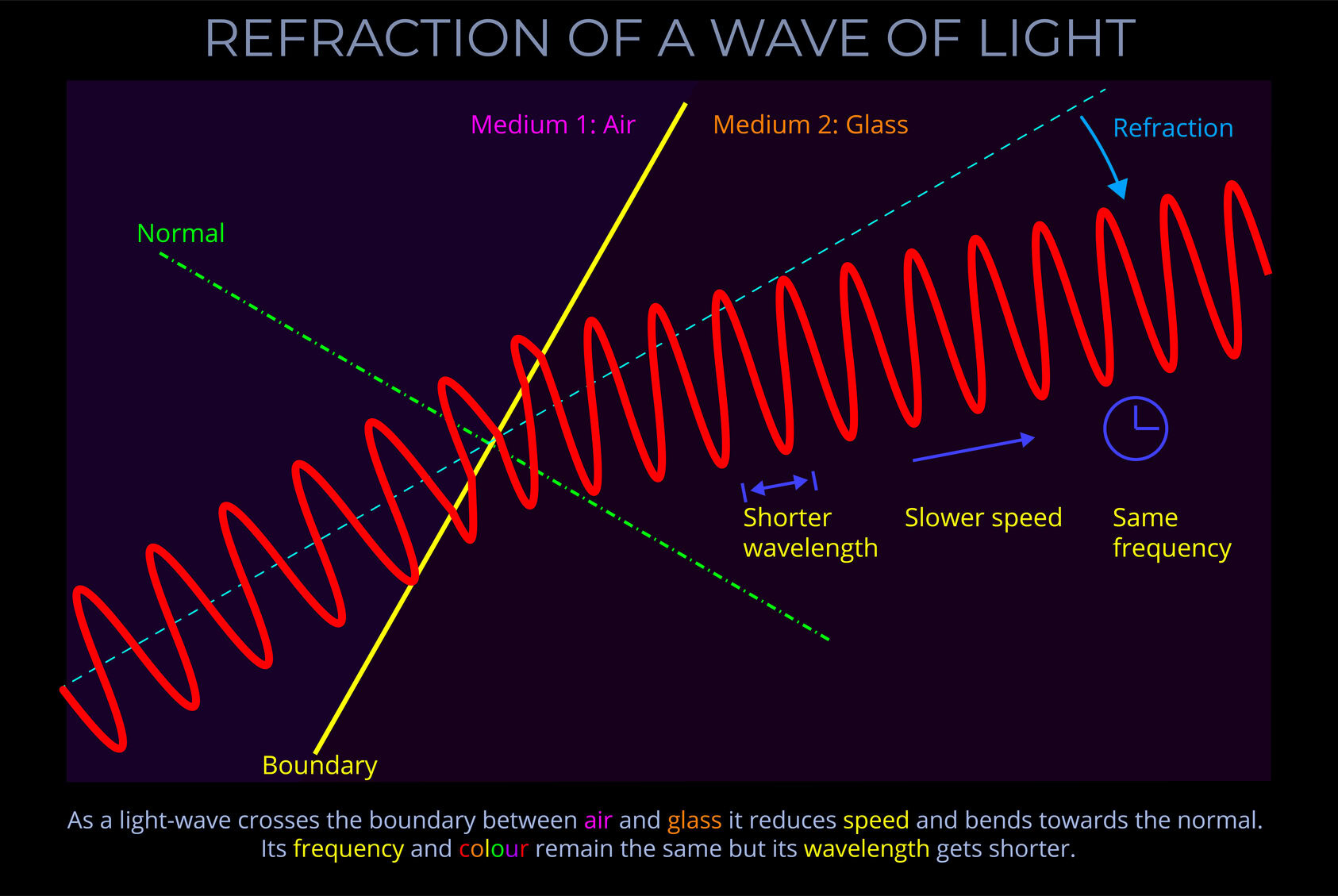
The angle of refraction indicates the extent to which light bends and changes direction as it passes from one transparent medium into another.
- The angle of refraction is measured between the refracted ray of light and the normal.
- The normal is an imaginary line drawn on a ray-tracing diagram perpendicular to the surface at the point of incidence.
- Expressed more formally, in optics, the normal is a geometric construct, a line drawn perpendicular to the interface between two media at the point of contact. This conceptually defined reference line is crucial for characterizing various light-matter interactions, such as reflection, refraction, and absorption.
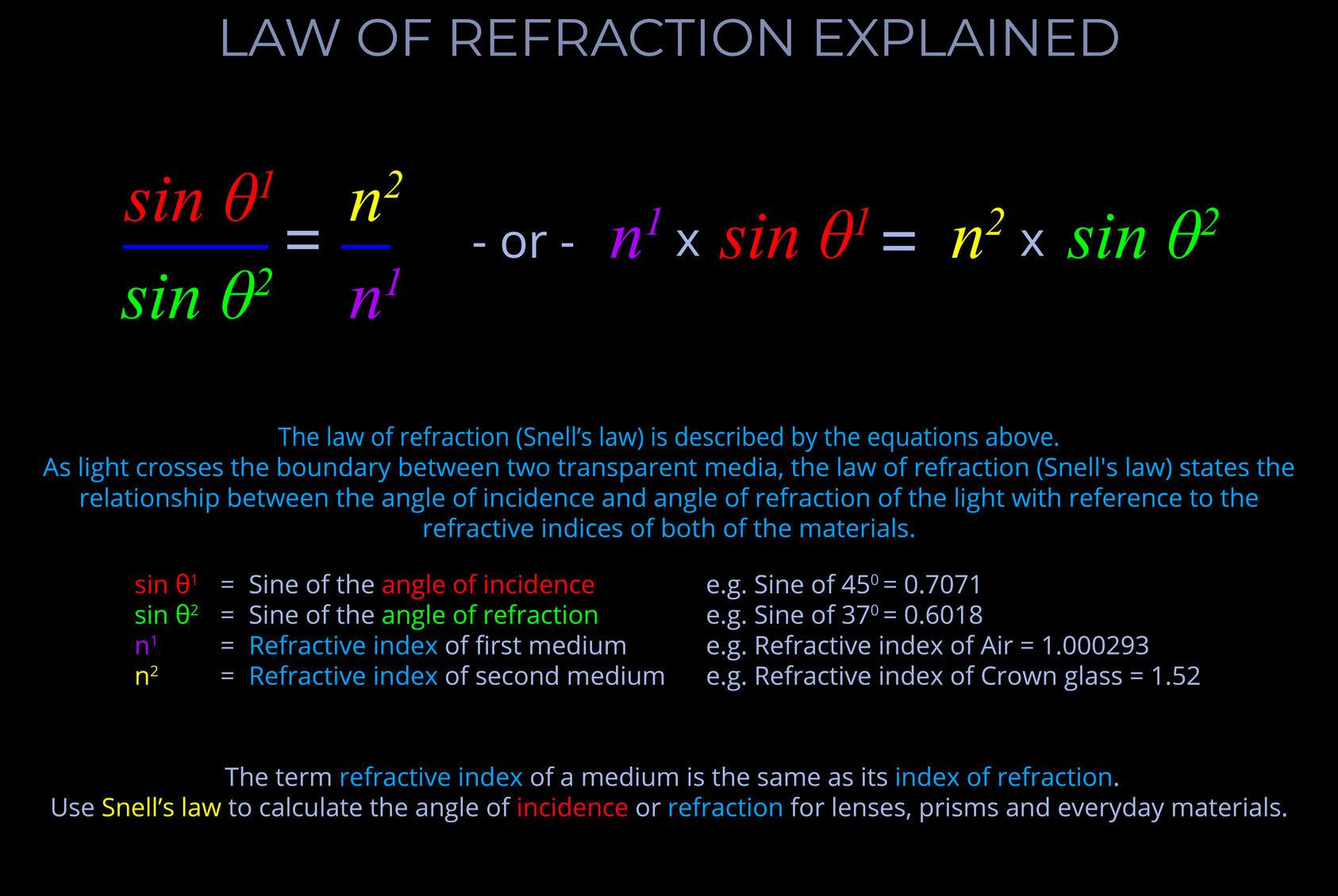
- The equation used to determine the angle of refraction is often referred to as Snell’s law or the law of refraction.
- The law of refraction describes the relationship between the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction when light crosses the boundary between two transparent media, such as from air to water.
- In the field of optics, Snell’s law is applied when drawing a ray-tracing diagram to calculate the angles of incidence and refraction and is also used experimentally to determine the refractive index of a given medium.
REFRACTIVE INDEX
- The refractive index of a medium can significantly affect the degree to which light is refracted when entering that medium.
- For instance, light is refracted more when it enters a medium with a high refractive index, such as glass than when it enters a medium with a low refractive index, like air.
- Total internal reflection occurs when light attempts to pass from a medium with a higher refractive index to one with a lower refractive index at an angle greater than the so-called “critical angle”. The outcome is that all the light is reflected back into the first medium instead of being refracted.
- For a full explanation go to the definition of Refractive index.
About lines that are normal to one another
- If one line is normal to another, then they are at right angles to one another.
- In geometry, a normal (or the normal) refers to a line drawn perpendicular to and intersecting another line, plane or surface.
- In the field of optics, the normal is a line drawn on a ray-tracing diagram perpendicular to (at 900 to), the boundary between two media.
- If the boundary between two media is curved then the normal is drawn at a tangent to the boundary.