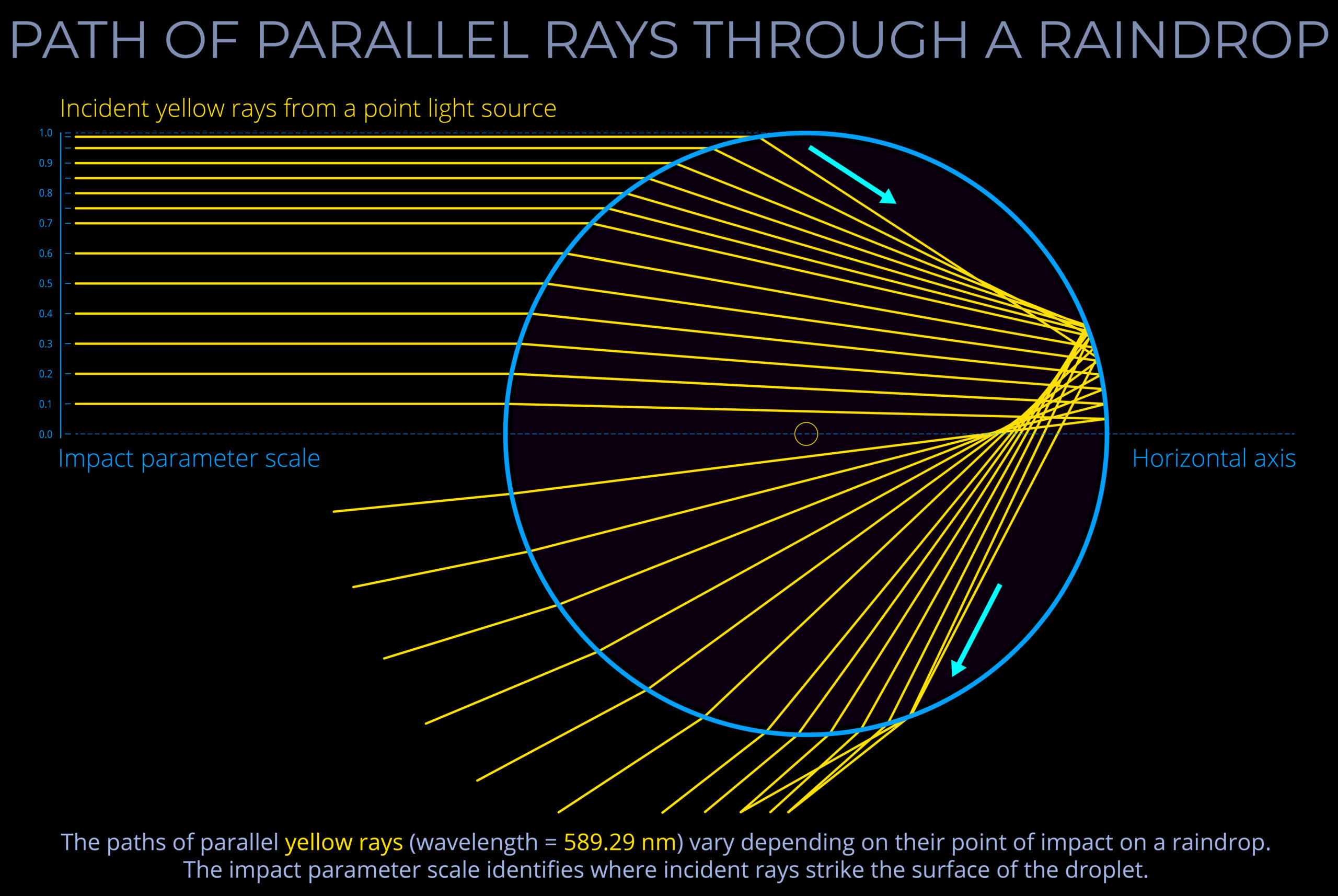
- Ray-tracing diagrams are used in geometric optics, where light is treated as rays that travel in straight lines and change speed and/or direction as they pass through different transparent media.
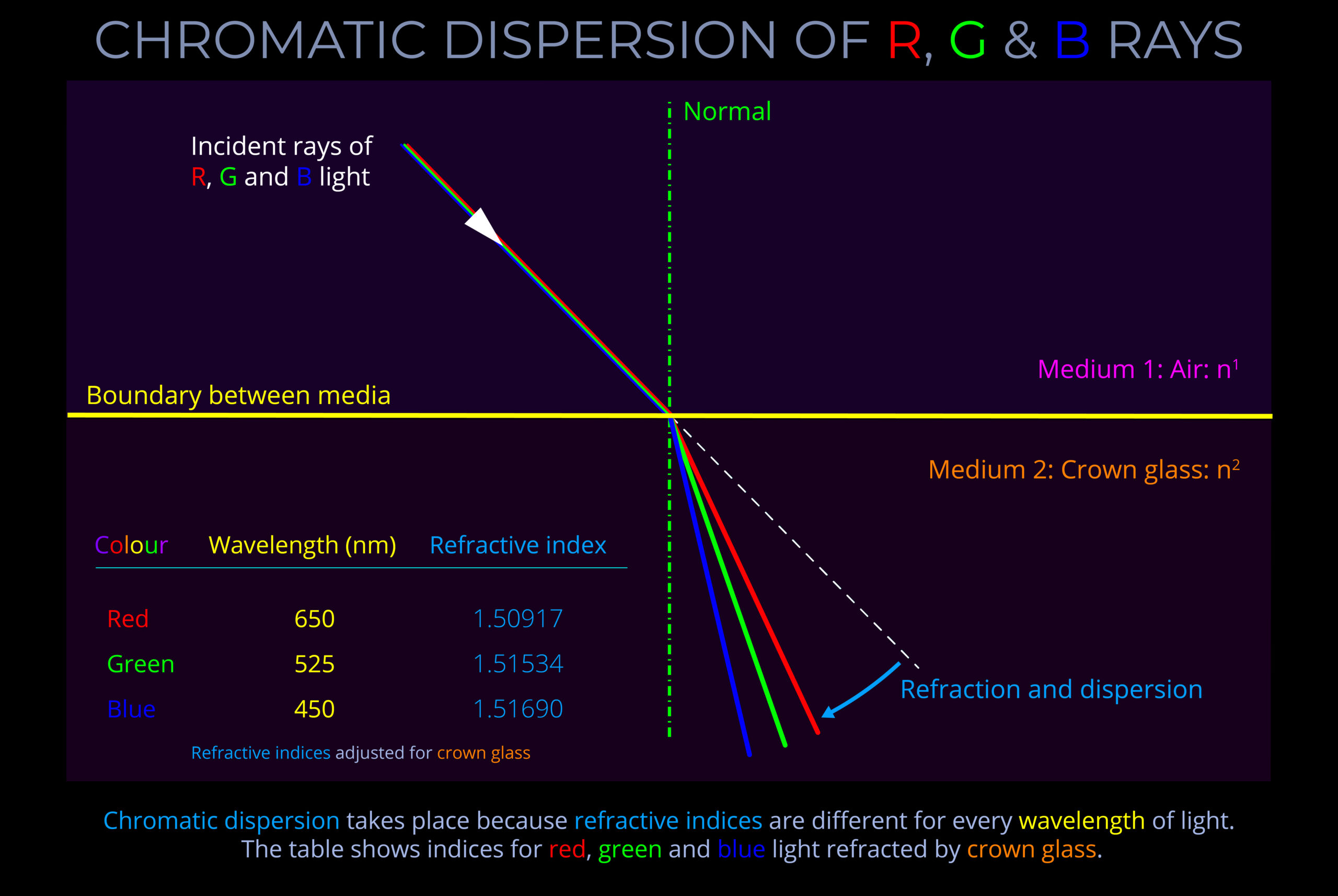
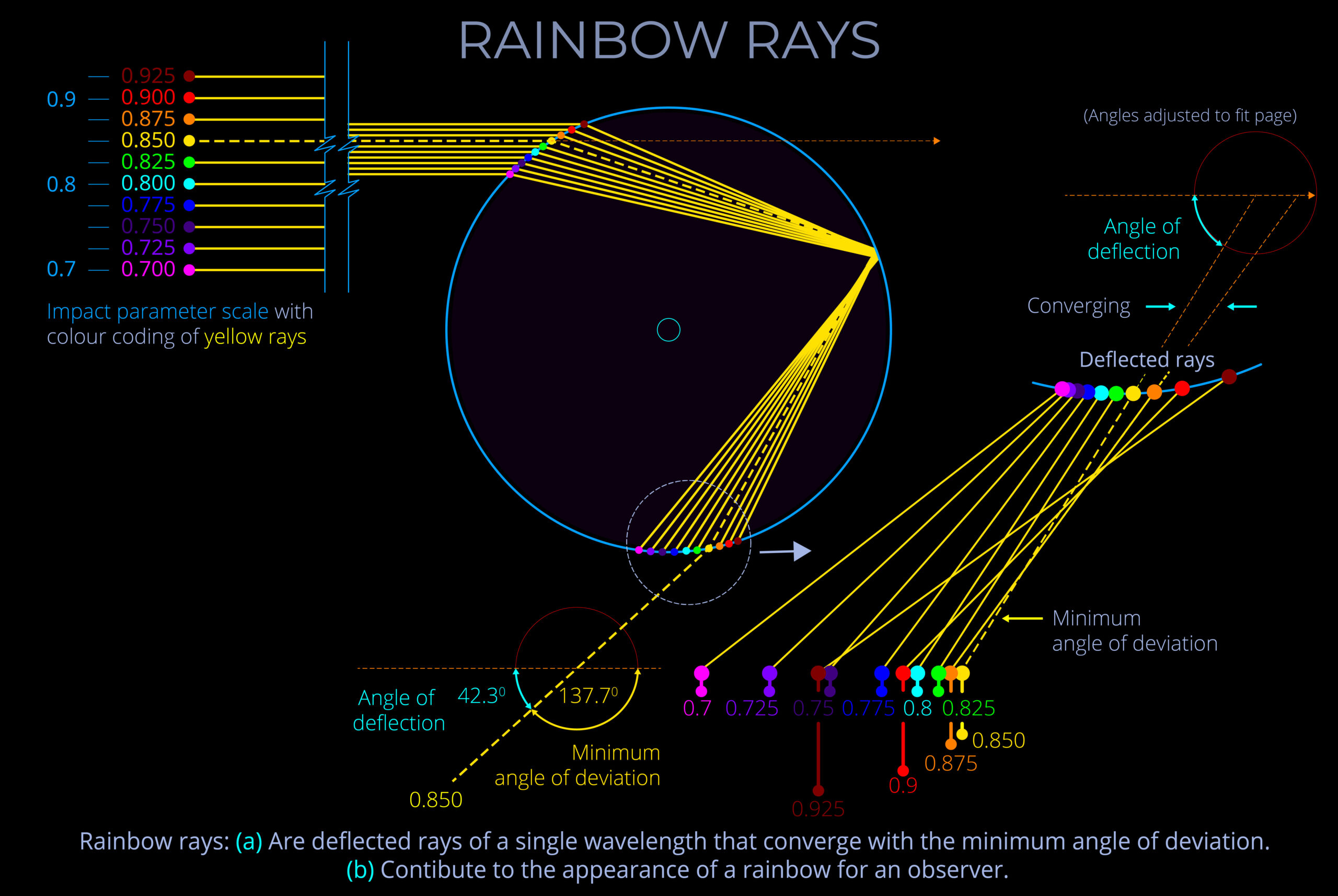
- The purpose of a ray-tracing diagram is to illustrate optical phenomena such as absorption, dispersion, polarization, reflection, refraction, scattering, and transmission.
- The accuracy of a ray-tracing diagram depends on the quality of the data used to create it, such as the refractive index of the materials and the angles of incidence and reflection.
- Ray-tracing can be used to design and optimize optical systems, such as lenses and mirrors.
- A ray-tracing diagram uses drawing conventions and labels to illustrate the path of light rays as they interact with different media, materials, or objects. Ray tracing diagrams help to understand the optical behaviour of the light.
- Ray-tracing diagrams are used in geometric optics, where light is treated as rays that travel in straight lines and change speed and/or direction as they pass through different transparent media.
- The purpose of a ray-tracing diagram is to illustrate optical phenomena such as absorption, dispersion, polarization, reflection, refraction, scattering, and transmission.
- The accuracy of a ray-tracing diagram depends on the quality of the data used to create it, such as the refractive index of the materials and the angles of incidence and reflection.
- Ray-tracing can be used to design and optimize optical systems, such as lenses and mirrors.