Rainbows Appear as Arcs of Colour
£0.00
This is one of a set of almost 40 diagrams exploring Rainbows.
Each diagram appears on a separate page and is supported by a full explanation.
- Follow the links embedded in the text for definitions of all the key terms.
- For quick reference don’t miss the summaries of key terms further down each page.
Description
Rainbows Appear as Arcs of Colour
TRY SOME QUICK QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS TO GET STARTED
About the Diagram
An overview of rainbows
About the diagram
- This diagram shows an observer looking up towards a curtain of rain as parallel rays of incident white light from the Sun are reflected back towards them.
- The observer sees the rainbow because of the combined effects of refraction, reflection and dispersion of light within each raindrop.
- In this primary rainbow, the observer sees bands of colour stacked one above the other with red at the top and violet at the bottom.
- The raindrops are all of a similar size and shape and are falling across the observer’s field of view.
- As raindrops pass a point that is at 42.20 from the axis they appear red. As they continue to fall each one changes colour, first to orange then yellow, green, blue and finally at 400, violet.
- Each colour of visible light corresponds with a different wavelength but instead of seeing a smooth and continuous range of colours the observer can see distinct bands of colour.
- Bands of colour result from the fact that the human eye perceives some colours more strongly than others.
Rainbows and light
Some key terms
A human observer is a person who engages in observation by watching things.
- In the presence of visible light, an observer perceives colour because the retina at the back of the human eye is sensitive to wavelengths of light that fall within the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
- The visual experience of colour is associated with words such as red, blue, yellow, etc.
- The retina’s response to visible light can be described in terms of wavelength, frequency and brightness.
- Other properties of the world around us must be inferred from light patterns.
- An observation can take many forms such as:
- Watching an ocean sunset or the sky at night.
- Studying a baby’s face.
- Exploring something that can’t be seen by collecting data from an instrument or machine.
- Experimenting in a laboratory setting.
- The observer effect is a principle of physics and states that any interaction between a particle and a measuring device will inevitably change the state of the particle. This is because the act of measurement itself imposes a disturbance on the particle’s wave function, which is the mathematical description of its state.
- The concept of observation refers to the act of engaging with an electron or other particle, achieved through measuring its position or momentum.
- In the context of quantum mechanics, observation isn’t a passive undertaking, observation actively alters a particle’s state.
- This means that any kind of interaction with an atom, or with one of its constituent particles, that provides insight into its state results in a change to that state. The act of observation is always intrusive and will always change the state of the object being observed.
- It can be challenging to reconcile this with our daily experience, where we believe we can observe things without inducing any change in them.
The visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum is called the visible spectrum.
- The visible spectrum is the range of wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum that correspond with all the different colours we see in the world.
- As light travels through the air it is invisible to our eyes.
- Human beings don’t see wavelengths of light, but they do see the spectral colours that correspond with each wavelength and colours produced when different wavelengths are combined.
- The visible spectrum includes all the spectral colours between red and violet and each is produced by a single wavelength.
- The visible spectrum is often divided into named colours, though any division of this kind is somewhat arbitrary.
- Traditional colours referred to in English include red, orange, yellow, green, blue, and violet.
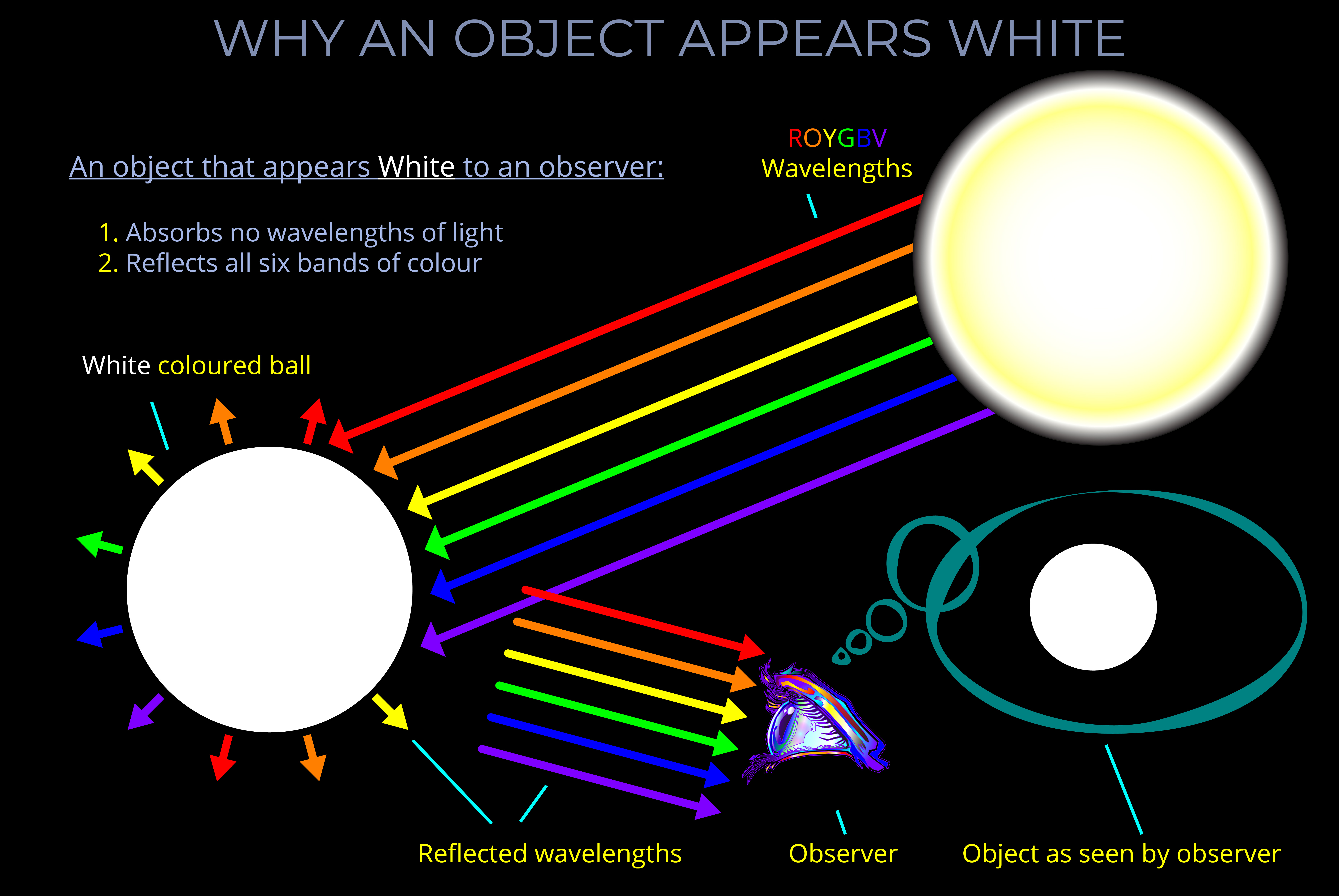
White light is the term for visible light that contains all wavelengths of the visible spectrum at equal intensities.
- The sun emits white light because sunlight contains all the wavelengths of the visible spectrum in roughly equal proportions.
- Light travelling through a vacuum or a medium is termed white light if it includes all wavelengths of visible light.
- Light travelling through a vacuum or air is not visible to our eyes unless it interacts with something.
- The term white light can have two meanings:
- It can refer to a combination of all wavelengths of visible light travelling through space, regardless of observation.
- What a person sees when all colours of the visible spectrum hit a white or neutral-coloured surface.
An observer perceives bands of colour when visible light separates into its component wavelengths and the human eye distinguishes a series of distinct adjacent colours.
- The human eye and brain together translate light into colour.
- When rain disperses sunlight and forms a rainbow, an observer will typically distinguish red, orange, yellow, green, blue and violet bands of colour.
- Although a rainbow contains electromagnetic waves with all possible wavelengths between red and violet, some ranges of wavelengths appear more intense to a human observer than others.
The visible spectrum is the range of wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum that correspond with all the different colours we see in the world.
- As light travels through the air it is invisible to our eyes.
- Human beings don’t see wavelengths of light, but they do see the spectral colours that correspond with each wavelength and colours produced when different wavelengths are combined.
- The visible spectrum includes all the spectral colours between red and violet and each is produced by a single wavelength.
- The visible spectrum is often divided into named colours, though any division of this kind is somewhat arbitrary.
- Traditional colours referred to in English include red, orange, yellow, green, blue, and violet.
The Sun is the star at the centre of our solar system.
- The energy emitted by the Sun is called electromagnetic radiation or solar radiation.
- The solar radiation that the human eye is sensitive to is often called sunlight or visible light.
- The term light is often used to refer to visible light but can also be used to refer to all the different forms of electromagnetic radiation.
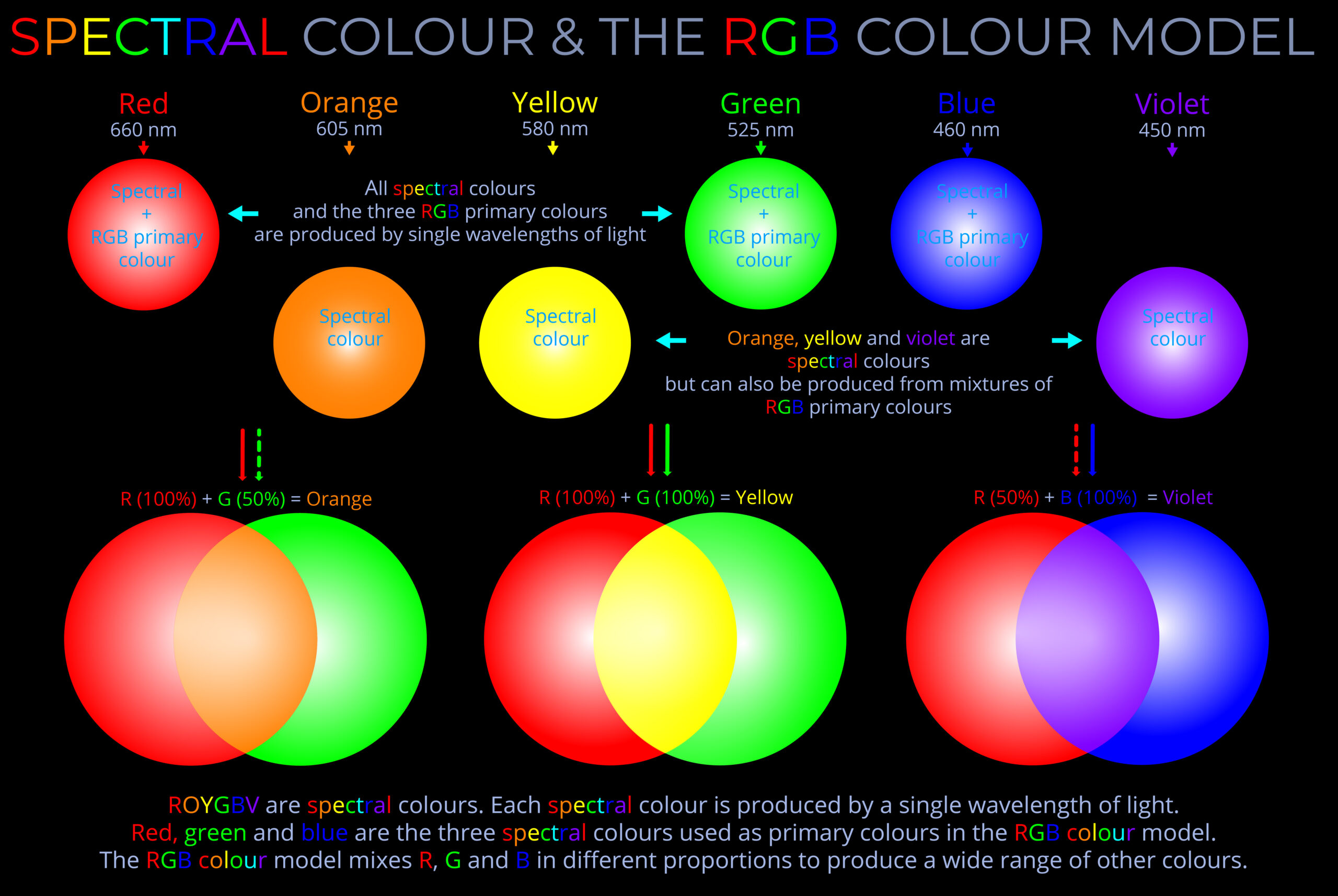
The spectral colour model represents the range of pure colours that correspond to specific wavelengths of visible light. These colours are called spectral colours because they are not created by mixing other colours but are produced by a single wavelength of light. This model is important because it directly reflects how human vision perceives light that comes from natural sources, like sunlight, which contains a range of wavelengths.
- The spectral colour model is typically represented as a continuous strip, with red at one end (longest wavelength) and violet at the other (shortest wavelength).
- Wavelengths and Colour Perception: In the spectral colour model, each wavelength corresponds to a distinct colour, ranging from red (with the longest wavelength, around 700 nanometres) to violet (with the shortest wavelength, around 400 nanometres). The human eye perceives these colours as pure because they are not the result of mixing other wavelengths.
- Pure Colours: Spectral colours are considered “pure” because they are made up of only one wavelength. This is in contrast to colours produced by mixing light (like in the RGB colour model) or pigments (in the CMY model), where a combination of wavelengths leads to different colours.
- Applications: The spectral colour model is useful in understanding natural light phenomena like rainbows, where each visible colour represents a different part of the light spectrum. It is also applied in fields like optics to describe how the eye responds to light in a precise, measurable way.
On a sunny day, if you stand with the Sun at your back and look at the ground, the shadow of your head will align with the antisolar point.
- The antisolar point is the position directly opposite the Sun, around which the arcs of a rainbow appear. An imaginary straight line can always be drawn that passes through the Sun, the eyes of an observer, and the antisolar point, which is the geometric centre of a rainbow.
- This concept corresponds with what an observer sees in real life: the idea that a rainbow has a center. From a side view, the centre of a rainbow is called the antisolar point, so named because it is opposite the Sun relative to the observer’s position.
- Unless observed from the air, the antisolar point is always below the horizon. Both primary and secondary rainbows share the same antisolar point, as do higher-order bows, such as fifth and sixth-order rainbows.