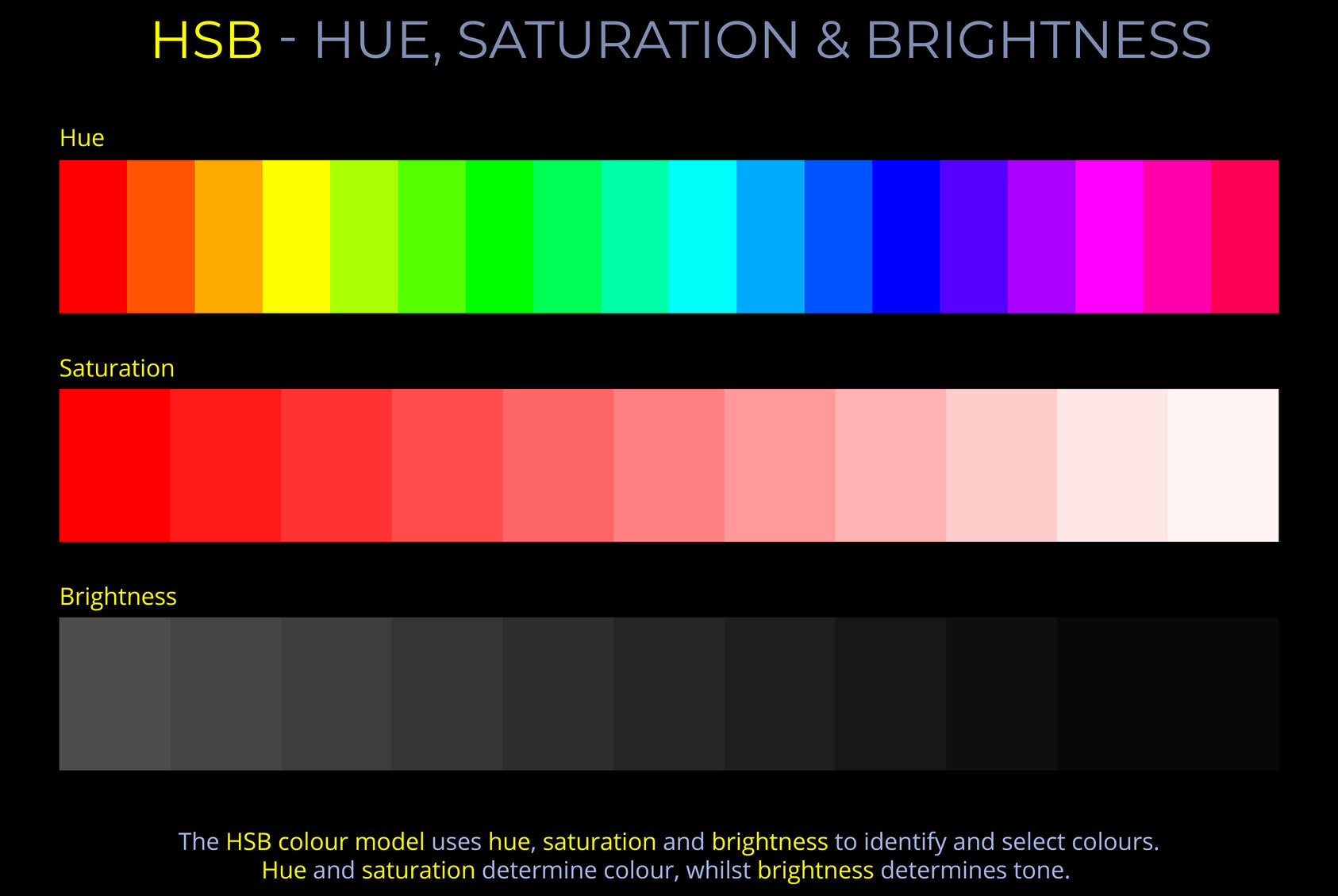
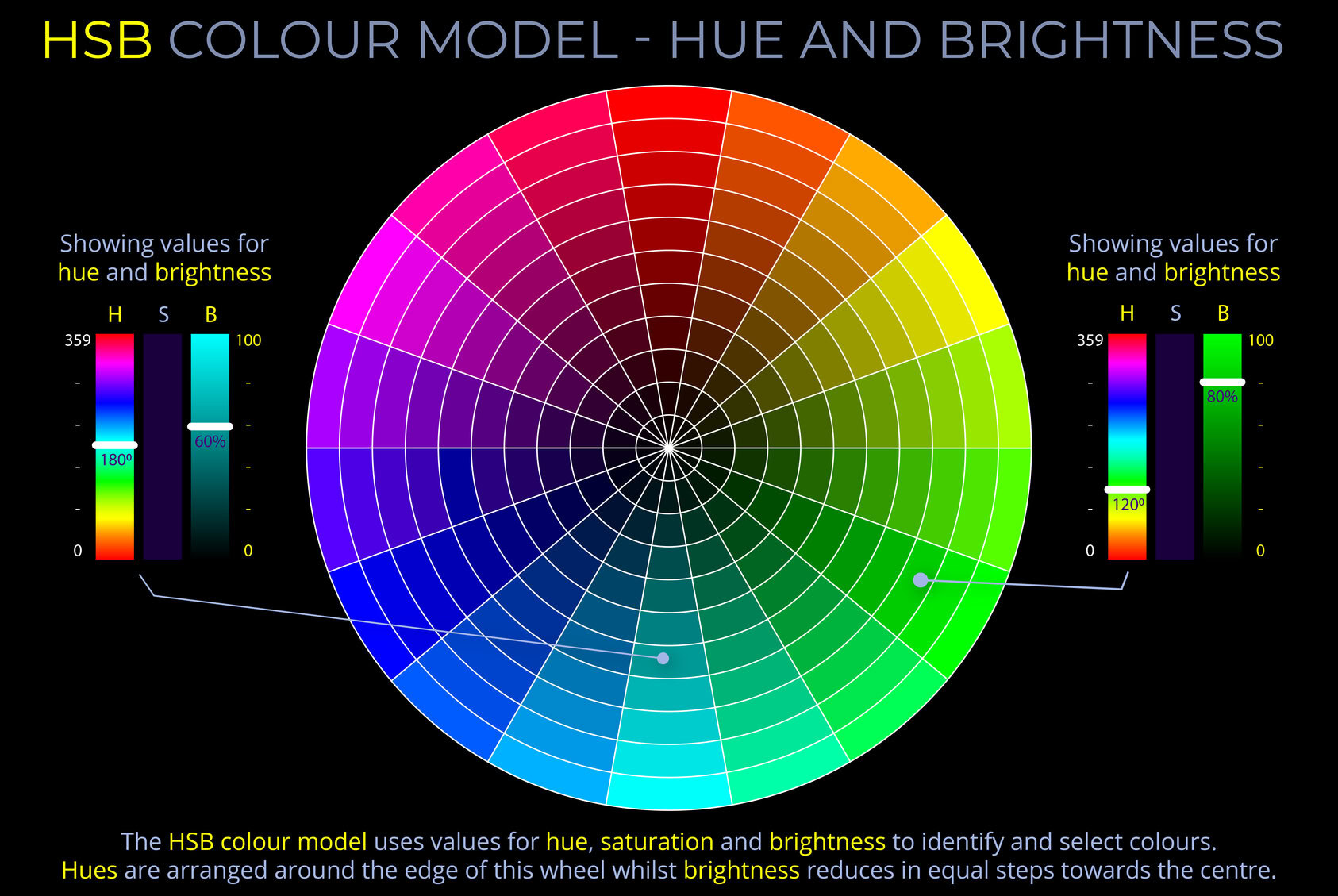
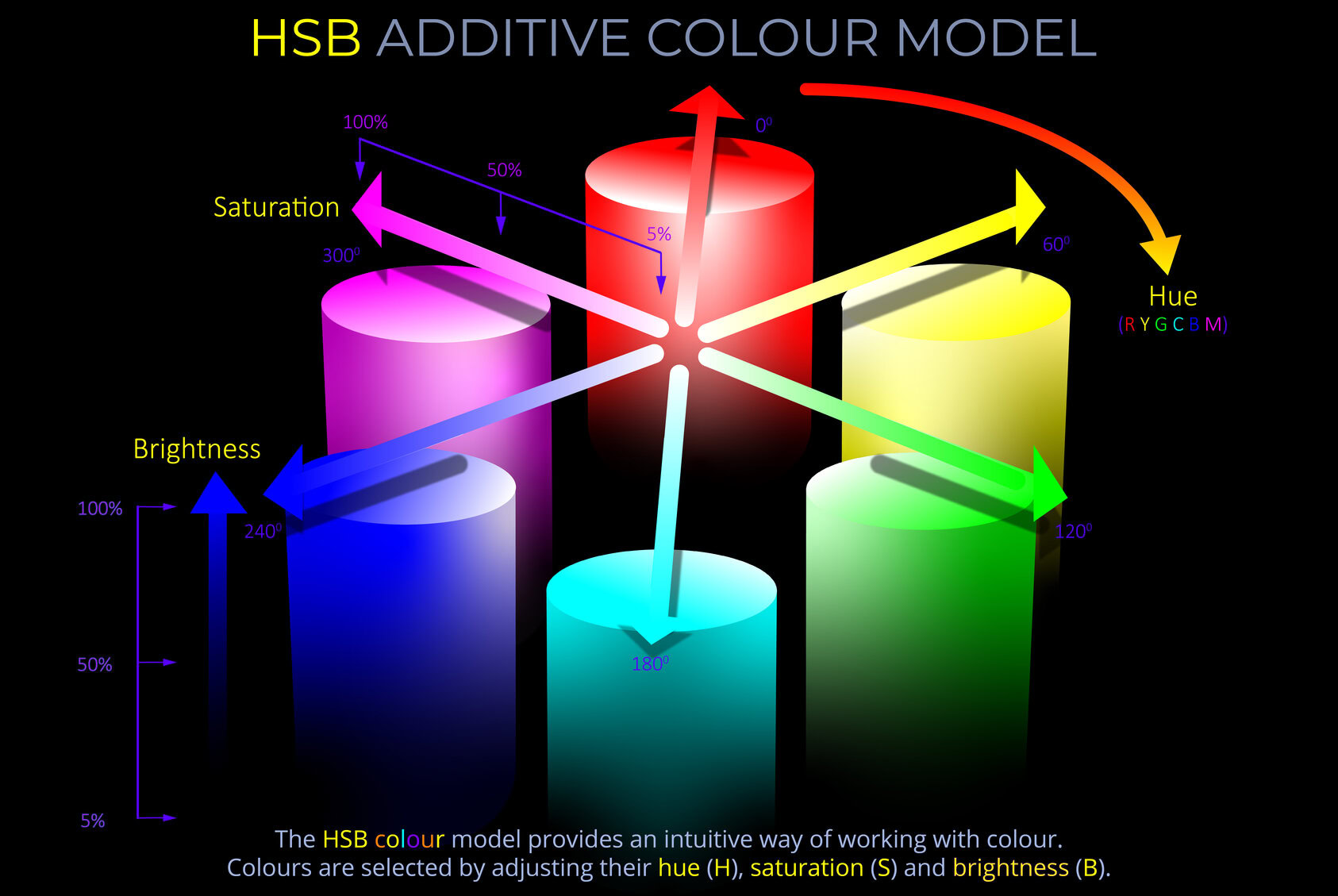
Hue is one of the three main properties of colour, alongside saturation and brightness and is described using names such as red, yellow, green or blue.
- Hue refers to the colour of an object or light source, and is determined by the dominant wavelength of light it emits or reflects.
- Hue is often used to describe colours in terms of their position on the colour wheel. Colour wheels are circular diagrams that arrange colours according to their hue.
- The most commonly used colour wheel is the RGB colour wheel, which includes primary colours of red, green and blue, as well as secondary and tertiary colours.
- Hues can be warm or cool, depending on their position on the colour wheel. Warm hues are those that include red, orange and yellow, while cool hues include blue, green and purple.
- The perceived brightness and saturation of a hue can be affected by its surrounding colours, as well as by lighting conditions.
- The perception of hue is also influenced by cultural and personal associations, as well as context and other environmental factors.
- In the fields of art, design and visual communication, a good understanding of hue is essential for creating effective and visually appealing colour schemes.
- In digital imaging and colour reproduction, hue can be adjusted through techniques such as colour correction and colour grading, to achieve the desired colour balance and tone.
About the term hue here at lightcolourvision.org
- At lightcolourvision.org, we use the term “hue” to refer to the attribute of a colour that distinguishes it from other colours on the colour spectrum.
- Colour models analyse and describe colours and their attributes in various ways. Some are grounded in the way the human eye perceives colours, others provide mathematical explanations.
- The RGB colour model is a widely used additive colour model that describes colours in terms of the amounts of red, green, and blue light that are combined to create the colour.
- In the HSB colour model, hue is one of the three attributes that describe a colour, alongside saturation and brightness.
- The HSB colour model is commonly used in digital design and is a popular way to describe colours on electronic devices like televisions, computers, and mobile phones.
- The CMYK colour model is used in print and focuses on the colours created by mixing cyan, magenta, yellow, and black inks on paper. Because the CMYK model doesn’t explicitly use the term “hue,” it is not a primary concern when designing for print.
References
- Hue is one of the three main properties of colour, alongside saturation and brightness and is described using names such as red, yellow, green or blue.
- Hue refers to the colour of an object or light source, and is determined by the dominant wavelength of light it emits or reflects.
- Hue is often used to describe colours in terms of their position on the colour wheel. Colour wheels are circular diagrams that arrange colours according to their hue.
- The most commonly used colour wheel is the RGB colour wheel, which includes primary colours of red, green and blue, as well as secondary and tertiary colours.
- Hues can be warm or cool, depending on their position on the colour wheel. Warm hues are those that include red, orange and yellow, while cool hues include blue, green and purple.
- The perceived brightness and saturation of a hue can be affected by its surrounding colours, as well as by lighting conditions.
- The perception of hue is also influenced by cultural and personal associations, as well as context and other environmental factors.