Using The RGB Colour Model
£0.00
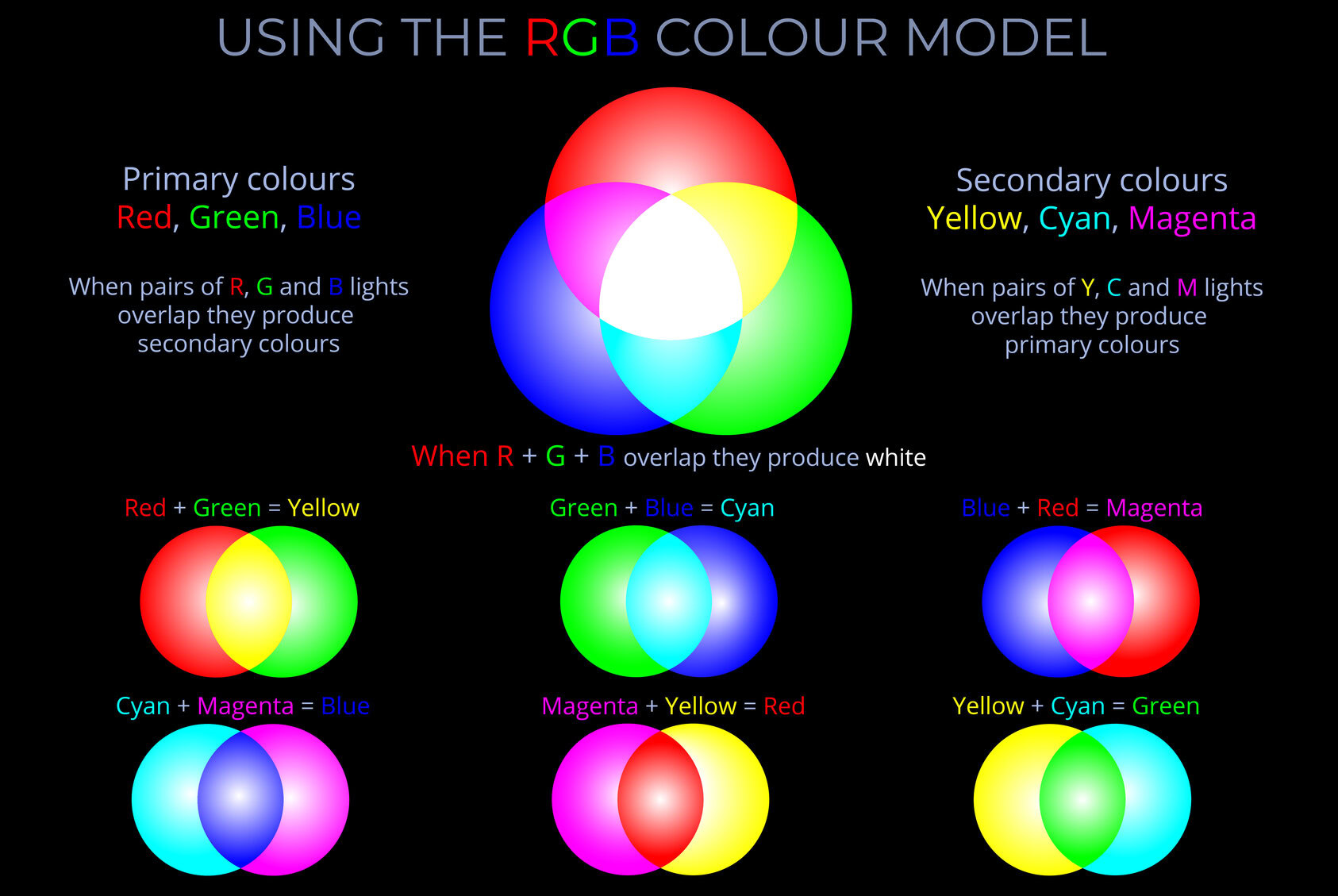
This diagram explores the RGB colour model. It looks at how wavelengths of light corresponding with the RGB primary colours are combined to produce secondary colours.
What you need to remember:
- Mixing different wavelengths of light to produce other colours, is called an additive colour model or an additive approach to colour.
- Red, green and blue (RGB) are additive primary colours. This means that when these wavelengths of light are projected onto a dark surface they combined to produce other colours.
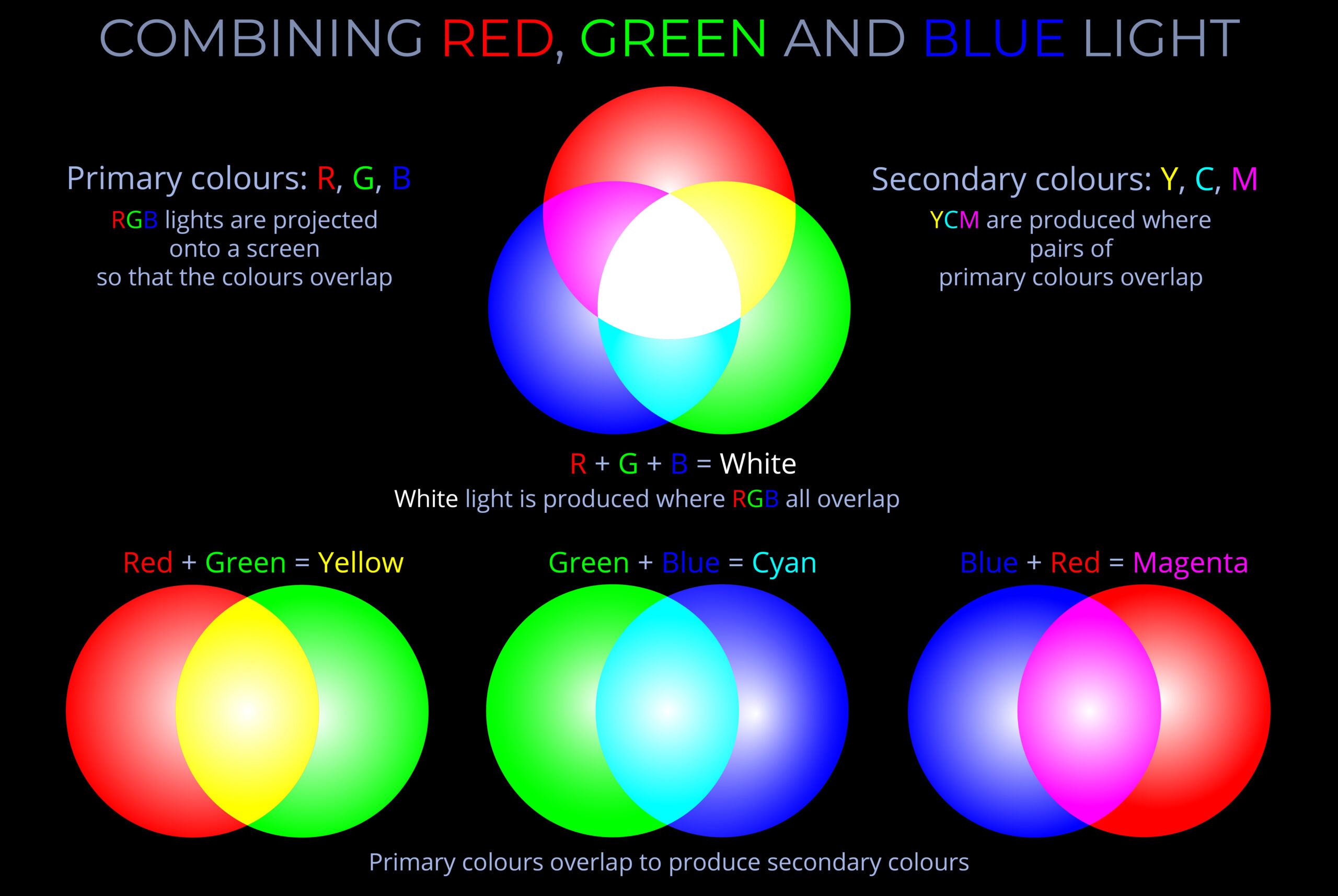
- If wavelengths of light corresponding with all three additive primary colours are projected in equal amounts onto a dark surface the result is white.
- If wavelengths of light corresponding with all three additive primary colours are projected in unequal amounts onto a dark surface many thousands of colours can be produced.
- Secondary colours are the colours produced when pairs of primary colours are combined in equal or unequal proportions.
Description
Using The RGB Colour Model
TRY SOME QUICK QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS TO GET STARTED
About the diagram
About the diagram
- This diagram explores the RGB colour model. It looks at how wavelengths of light corresponding with the RGB primary colours are combined to produce secondary colours.
What you need to remember
- Mixing different wavelengths of light to produce other colours, is called an additive colour model or an additive approach to colour.
- Red, green and blue (RGB) are additive primary colours. This means that when these wavelengths of light are projected onto a dark surface they combine to produce other colours. The colour produced depends on the intensity of each light source.
- If wavelengths of light corresponding with all three additive primary colours are projected in equal amounts onto a dark surface the result is white.
- If wavelengths of light corresponding with all three additive primary colours are projected in unequal amounts onto a dark surface many thousands (or millions) of colours can be produced.
- Secondary colours are the colours produced when pairs of primary colours are combined in equal or unequal proportions.
Understanding the diagram
- Three circles of light are projected onto a dark surface in the top half of the diagram. These are the additive primary colours – red, green and blue.
- Where the primary colours overlap they produce the secondary colours – yellow, magenta and cyan.
- Where all three primary colours overlap they produce white.
- The bottom of the diagram shows which primary colours are mixed in pairs to produce each secondary colour. and which secondary colours produce each primary colour.
Some key terms
Primary colours are a set of colours from which others can be produced by mixing (pigments, dyes etc.) or overlapping (coloured lights).
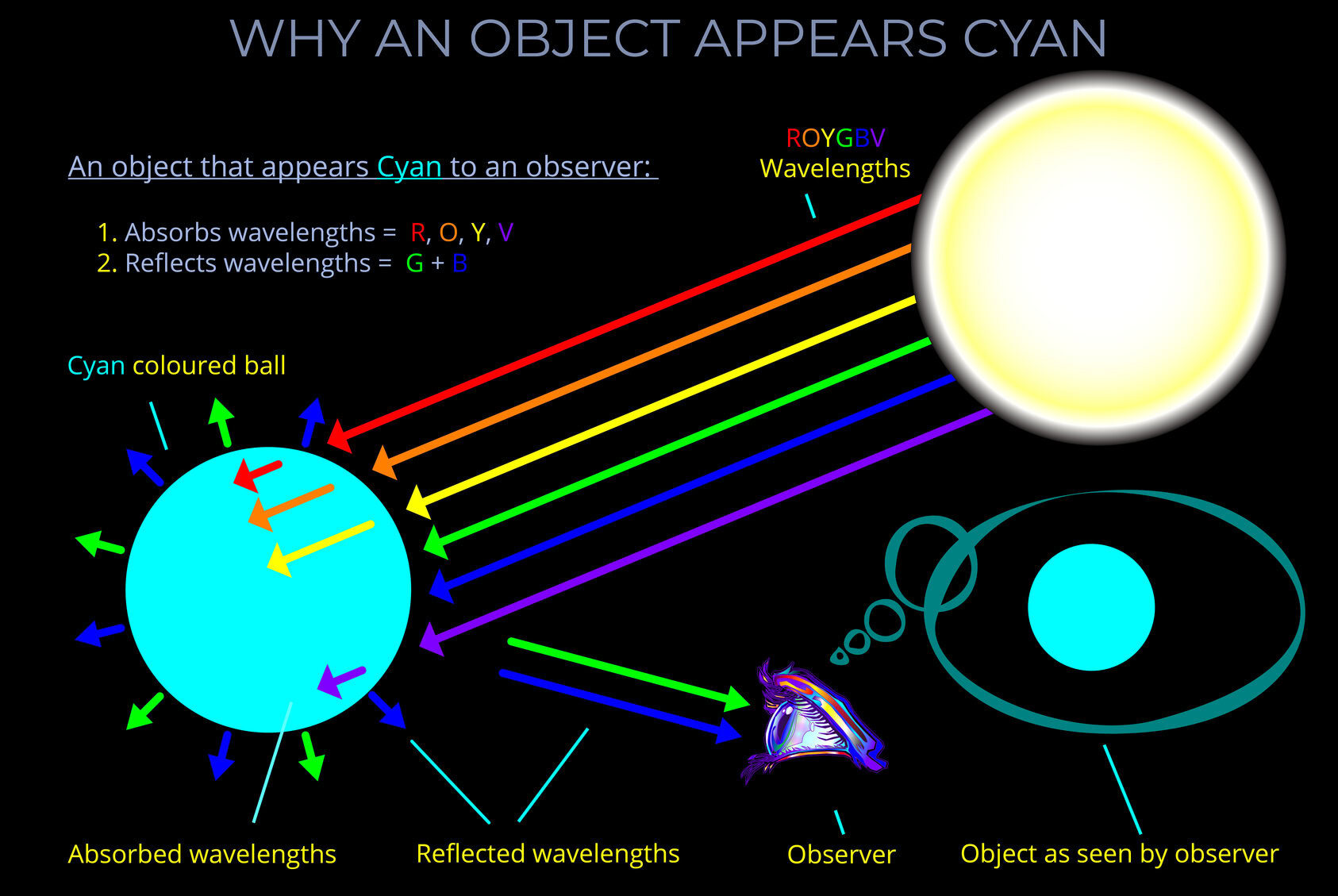
- The human eye, and so human perception, is tuned to the visible spectrum and so to spectral colours between red and violet. It is the sensitivity of the eye to the electromagnetic spectrum that results in the perception of colour.
- A set of primary colours is a set of pigmented media or coloured lights that can be combined in varying amounts to produce a wide range of colours.
- This process of combining colours to produce other colours is used in applications intended to cause a human observer to experience a particular range of colours when represented by electronic displays and colour printing.
- Additive and subtractive models have been developed that predict how wavelengths of visible light, pigments and media interact.
- RGB colour is a technology used to reproduce colour in ways that match human perception.
- The primary colours used in a colour space such as CIELAB, NCS, Adobe RGB (1998) and sRGB are the result of an extensive investigation of the relationship between visible light and human colour vision.
RGB colour is an additive colour model in which red, green and blue light is combined to reproduce a wide range of other colours.
- The primary colours in the RGB colour model are red, green and blue.
- In the RGB model, different combinations and intensities of red, green, and blue light are mixed to create various colours. When these three colours are combined at full intensity, they produce white light.
- Additive colour models are concerned with mixing light, not dyes, inks or pigments (these rely on subtractive colour models such as the RYB colour model and the CMY colour model).
- The RGB colour model works in practice by asking three questions of any colour: how red is it (R), how green is it (G), and how blue is it (B).
- The RGB model is popular because it can easily produce a comprehensive palette of 1530 vivid hues simply by adjusting the combination and amount of each of the three primaries it contains.
A colour model is a system or framework used to understand, organise, and manipulate colour. It ranges from basic concepts, such as the sequence of colours in a rainbow, to more advanced models like RGB, CMYK, and CIE, which are essential for accurate colour reproduction in various fields, including digital media, printing, and manufacturing.
- A colour model, underpinned by colour theory, provides a precise and replicable approach to understanding:
- How the human eye perceives light and interprets colour.
- Different types of colour, including those produced by mixing lights, pigments, or inks.
- How to manage the diverse ways colour is processed by devices such as cameras, digital screens, and printers.
- Colour models enable us to:
- Make sense of colour in relation to human vision and the world around us.
- Use colours in logical, predictable, and replicable ways.
- Understand how to mix specific colours, whether using lights, pigments, inks, or dyes.
- Specify colours using names, codes, notations, or equations.
- Organise and apply colour for different purposes, from fabrics and interiors to vehicles.
- For more information see https://lightcolourvision.org/dictionary/definition/colour-model/
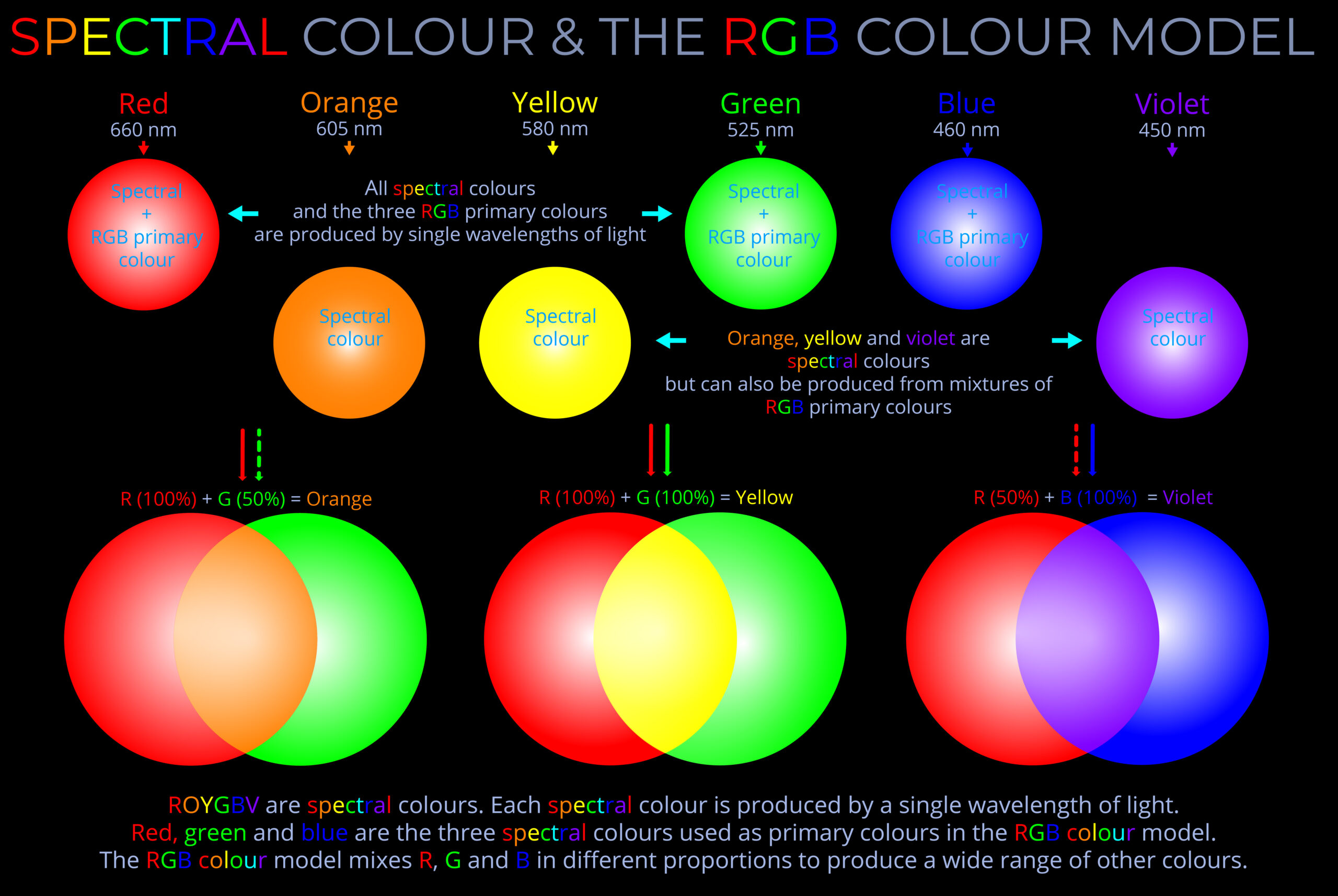
ROYGBV are the initials for the sequence of colours that make up the visible spectrum: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, and violet.
- The visible spectrum refers to the range of colours visible to the human eye.
- White light, when passed through a prism, separates into a sequence of individual colours corresponding with ROYGBV which is the range of colours visible to the human eye.
- White light separates into ROYGBV because different wavelengths of light bend at slightly different angles as they enter and exit the prism.
- ROYGBV helps us remember the order of these spectral colours starting from the longest wavelength (red) to the shortest (violet).
- A rainbow spans the continuous range of spectral colours that make up the visible spectrum.
- The visible spectrum is the small band of wavelengths within the electromagnetic spectrum that corresponds with all the different colours we see in the world.
- The fact that we see the distinct bands of colour in a rainbow is an artefact of human colour vision.
A secondary colour is created by mixing two primary colours in equal parts. The primary colours may belong to either an additive colour model, which combines wavelengths of light, or a subtractive colour model, which mixes pigments or dyes.
- In additive colour models such as the RGB colour model, which deals with the effects of mixing coloured light, a secondary colour results from overlapping the primary colours: red, green, and blue. The secondary colours produced by combining pairs of primary colours in the RGB model are cyan, magenta, and yellow.
- In subtractive colour models such as the CMY colour model, which is concerned with mixing dyes and inks, a secondary colour results from overlapping the primary colours: cyan, magenta, and yellow. The secondary colours produced by combining pairs of primary colours in the CMY model are red, green, and blue.
An additive colour model explains how different coloured lights (such as LEDs or beams of light) are mixed to produce other colours.
- Additive colour refers to the methods used and effects produced by combining or mixing different wavelengths of light.
- The RGB colour model and HSB colour model are examples of additive colour models.
- Additive colour models such as the RGB colour model and HSB colour model can produce vast ranges of colours by combining red, green, and blue lights in varying proportions.
- An additive approach to colour is used to achieve precise control over the appearance of colours on digital screens of TVs, computers, and phones.