Facts about the Sun
£0.00
This diagram introduces the Sun, the star at the centre of our solar system. It lists some useful facts that help explain why it is so important in our lives.
Remember that:
- The sun is unlike anything else in our experience. Its age, size, temperature are all on a scale apart from life on planet Earth.
- It explodes with the force of a billion one-megaton nuclear bombs every single second of every single day.
- Without the energy produced by the sun, life as we know it would not be possible.
Description
Facts about the Sun
START OFF WITH THESE QUICK QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
About the diagram
About the diagram
- This diagram introduces the Sun, the star at the centre of our solar system. It lists some useful facts that help explain why it is so important in our lives.
Remember that:
- The sun is unlike anything else in our experience. Its age, size, and temperature are all on a scale apart from our own lives on planet Earth.
- It explodes with the force of a billion one-megaton nuclear bombs every single second of every single day.
- Without the energy produced by the sun, life as we know it would not be possible.
Some key terms
Thermonuclear fusion, also known as nuclear fusion, is a powerful process where atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus. This process releases enormous amounts of energy, millions of times greater than what we get from traditional chemical reactions like burning fossil fuels.
- There are two forms of thermonuclear fusion (nuclear fusion):
- Uncontrolled Fusion: This is the process where atomic nuclei merge spontaneously and release a tremendous amount of uncontrollable energy.
- It is the natural process happening within stars and the principle behind thermonuclear weapons.
- Controlled Fusion: Scientists are actively researching ways to achieve controlled fusion, where atomic nuclei are combined in a controlled environment.
- This would allow us to harness the immense energy released for constructive purposes like generating clean and sustainable power, reducing reliance on fossil fuels, and potentially powering future space exploration endeavours.
Solar radiation is the electromagnetic radiation emitted by the sun.
- Electromagnetic radiation is a type of energy that is commonly known as light. Detached from its source, it is transported by electromagnetic waves (or by their quanta, particles called photons) and propagates through space.
- Electromagnetic radiation includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visible) light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays.
- Electromagnetic radiation is sometimes called EM radiation or electromagnetic radiant energy (EMR).
- All forms of electromagnetic radiation can be described in terms of both waves or particles.
- All forms of electromagnetic radiation travel at 299,792 kilometres per second in a vacuum.
Electromagnetic radiation is a type of energy more commonly simply called light. Detached from its source, it is transported by electromagnetic waves (or their quanta, photons) and propagates through space at the speed of light.
- Electromagnetic radiation (EM radiation or EMR) includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visible) light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays.
- Man-made technologies that produce electromagnetic radiation include radio and TV transmitters, radar, MRI scanners, microwave ovens, computer screens, mobile phones, all types of lights and lamps, electric blankets, electric bar heaters, lasers and x-ray machines.
- At the quantum scale of electromagnetism, electromagnetic radiation is described in terms of photons rather than waves. Photons are elementary particles responsible for all electromagnetic phenomena.
- The term quantum refers to the smallest quantity into which something can be divided. A quantum of a thing is indivisible into smaller units so they have no sub-structure. A photon is a quantum of electromagnetic radiation.
- A single photon with a wavelength corresponding with gamma rays might carry 100,000 times the energy of a single photon of visible light.
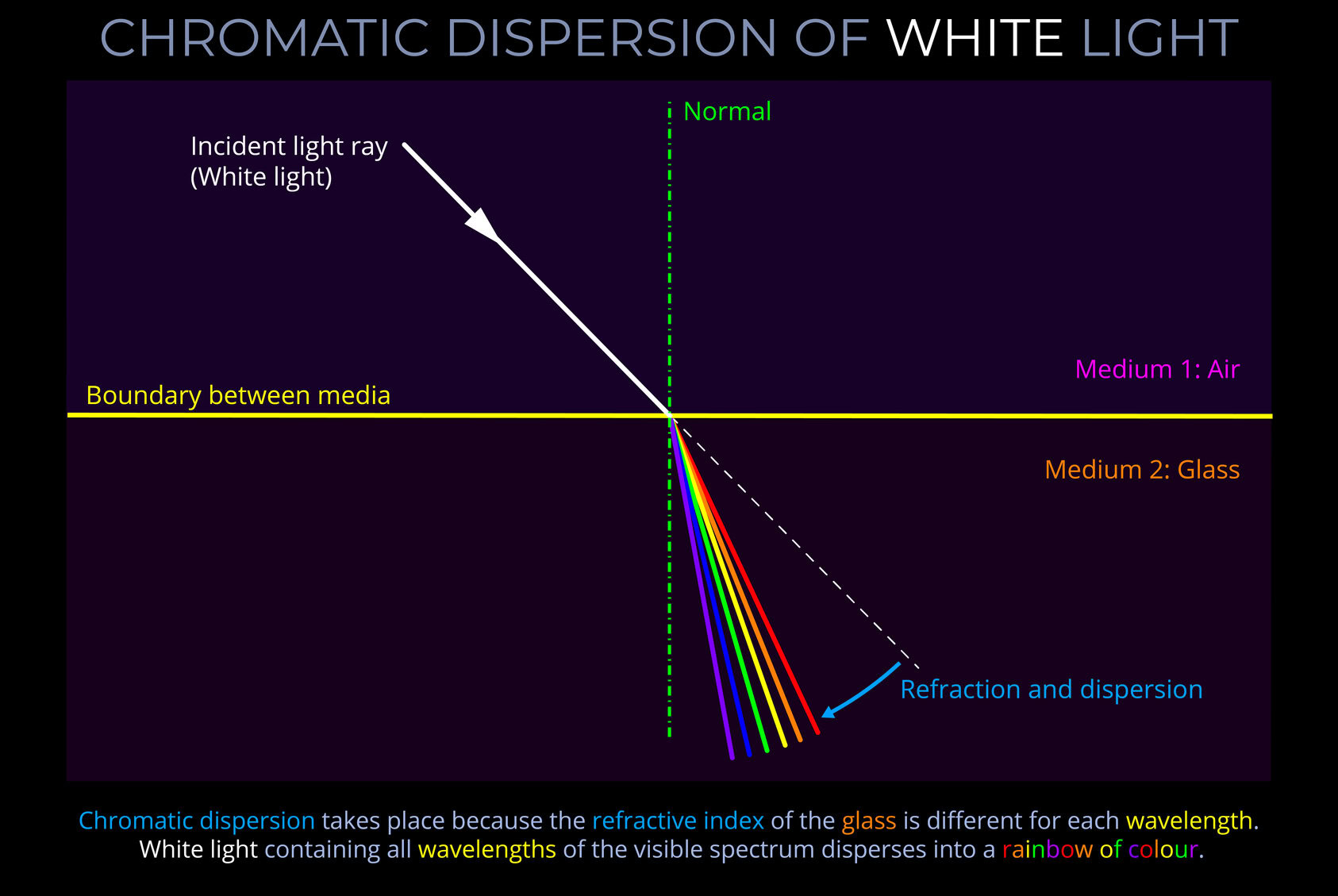
Sunlight, also known as daylight or visible light, refers to the portion of electromagnetic radiation emitted by the Sun that is detectable by the human eye. It is one form of the broad range of electromagnetic radiation produced by the Sun. Our eyes are particularly sensitive to this specific range of wavelengths, enabling us to perceive the Sun and the world around us.
- Sunlight is only one form of electromagnetic radiation emitted by the Sun.
- Sunlight is only a very small part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
- Sunlight is the form of electromagnetic radiation that our eyes are sensitive to.
- Other types of electromagnetic radiation that we are sensitive to, but cannot see, are infrared radiation that we feel as heat and ultraviolet radiation that causes sunburn.