Combining Spectral Colours to Make White
£0.00
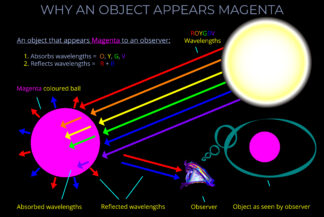
This diagram looks at three situations in which an observer will see white light reflected off a dark surface.
Three different light sources are shown in the diagram.
- Each light source produces a different combination of wavelengths and each wavelength has the same intensity.
- The light source at the top of the diagram contains three component colours: RGB (red, green, blue).
- The light source on the left contains six component colours – ROYGBV (red, orange, yellow, green, blue and violet).
- The light source on the right contains a continuous spectrum of wavelengths which means it contains many thousands of component colours.
- In each case, the light source is projected onto a dark neutral coloured surface.
Description
Combining Spectral Colours to Make White
TRY SOME QUICK QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS TO GET STARTED
About the diagram
About the diagram
- This diagram looks at three situations in which an observer will see white light reflected off a dark surface.
- Three different light sources are shown in the diagram.
- Each light source produces a different combination of wavelengths and each wavelength has the same intensity.
- The light source at the top of the diagram contains three component colours: RGB (red, green, blue).
- The light source on the left contains six component colours – ROYGBV (red, orange, yellow, green, blue and violet).
- The light source on the right contains a continuous spectrum of wavelengths which means it contains many thousands of component colours.
- In each case, the light source is projected onto a dark neutral coloured surface.
Remember that:
The surface where the light sources are focused appear white:
- When wavelengths corresponding with the three primary colours (RGB) are reflected off the surface towards an observer.
- When wavelengths corresponding with ROYGBV are reflected off the surface towards an observer.
- When all the wavelengths of the visible spectrum are reflected off the surface towards an observer.
Some key terms
The visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum is called the visible spectrum.
- The visible spectrum is the range of wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum that correspond with all the different colours we see in the world.
- As light travels through the air it is invisible to our eyes.
- Human beings don’t see wavelengths of light, but they do see the spectral colours that correspond with each wavelength and colours produced when different wavelengths are combined.
- The visible spectrum includes all the spectral colours between red and violet and each is produced by a single wavelength.
- The visible spectrum is often divided into named colours, though any division of this kind is somewhat arbitrary.
- Traditional colours referred to in English include red, orange, yellow, green, blue, and violet.
The electromagnetic spectrum includes electromagnetic waves with all possible wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation, ranging from low-energy radio waves through visible light to high-energy gamma rays.
- There are no precisely defined boundaries between the bands of electromagnetic radiation in the electromagnetic spectrum.
- The electromagnetic spectrum includes, in order of increasing frequency and decreasing wavelength: radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays and gamma rays.
- Visible light is only a very small part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
The visible spectrum is the range of wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum that correspond with all the different colours we see in the world.
- As light travels through the air it is invisible to our eyes.
- Human beings don’t see wavelengths of light, but they do see the spectral colours that correspond with each wavelength and colours produced when different wavelengths are combined.
- The visible spectrum includes all the spectral colours between red and violet and each is produced by a single wavelength.
- The visible spectrum is often divided into named colours, though any division of this kind is somewhat arbitrary.
- Traditional colours referred to in English include red, orange, yellow, green, blue, and violet.
ROYGBV are the initials for the sequence of colours that make up the visible spectrum: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, and violet.
- The visible spectrum refers to the range of colours visible to the human eye.
- White light, when passed through a prism, separates into a sequence of individual colours corresponding with ROYGBV which is the range of colours visible to the human eye.
- White light separates into ROYGBV because different wavelengths of light bend at slightly different angles as they enter and exit the prism.
- ROYGBV helps us remember the order of these spectral colours starting from the longest wavelength (red) to the shortest (violet).
- A rainbow spans the continuous range of spectral colours that make up the visible spectrum.
- The visible spectrum is the small band of wavelengths within the electromagnetic spectrum that corresponds with all the different colours we see in the world.
- The fact that we see the distinct bands of colour in a rainbow is an artefact of human colour vision.
RGB colour is an additive colour model in which red, green and blue light is combined to reproduce a wide range of other colours.
- The primary colours in the RGB colour model are red, green and blue.
- In the RGB model, different combinations and intensities of red, green, and blue light are mixed to create various colours. When these three colours are combined at full intensity, they produce white light.
- Additive colour models are concerned with mixing light, not dyes, inks or pigments (these rely on subtractive colour models such as the RYB colour model and the CMY colour model).
- The RGB colour model works in practice by asking three questions of any colour: how red is it (R), how green is it (G), and how blue is it (B).
- The RGB model is popular because it can easily produce a comprehensive palette of 1530 vivid hues simply by adjusting the combination and amount of each of the three primaries it contains.
White light is the term for visible light that contains all wavelengths of the visible spectrum at equal intensities.
- The sun emits white light because sunlight contains all the wavelengths of the visible spectrum in roughly equal proportions.
- Light travelling through a vacuum or a medium is termed white light if it includes all wavelengths of visible light.
- Light travelling through a vacuum or air is not visible to our eyes unless it interacts with something.
- The term white light can have two meanings:
- It can refer to a combination of all wavelengths of visible light travelling through space, regardless of observation.
- What a person sees when all colours of the visible spectrum hit a white or neutral-coloured surface.
Primary colours are a set of colours from which others can be produced by mixing (pigments, dyes etc.) or overlapping (coloured lights).
- The human eye, and so human perception, is tuned to the visible spectrum and so to spectral colours between red and violet. It is the sensitivity of the eye to the electromagnetic spectrum that results in the perception of colour.
- A set of primary colours is a set of pigmented media or coloured lights that can be combined in varying amounts to produce a wide range of colours.
- This process of combining colours to produce other colours is used in applications intended to cause a human observer to experience a particular range of colours when represented by electronic displays and colour printing.
- Additive and subtractive models have been developed that predict how wavelengths of visible light, pigments and media interact.
- RGB colour is a technology used to reproduce colour in ways that match human perception.
- The primary colours used in a colour space such as CIELAB, NCS, Adobe RGB (1998) and sRGB are the result of an extensive investigation of the relationship between visible light and human colour vision.