The form and composition of rainbows are often explained in terms of electromagnetic waves.
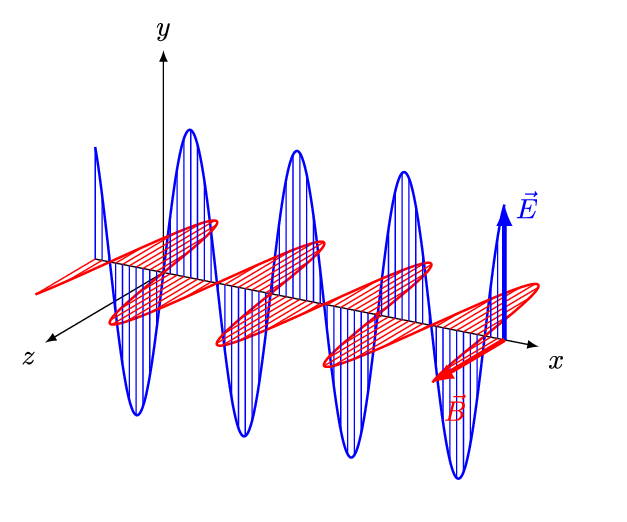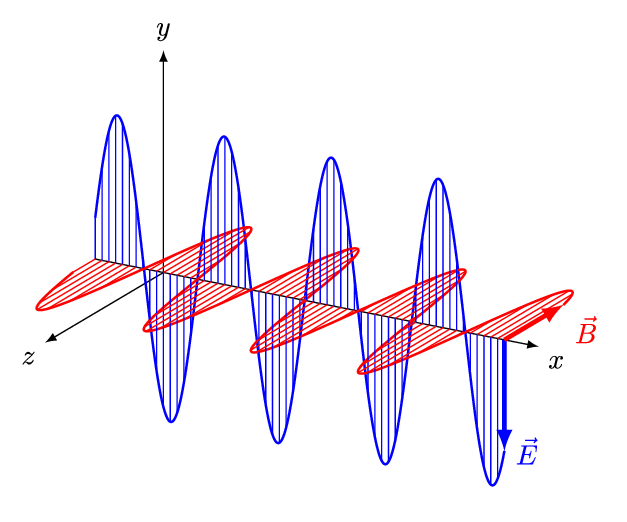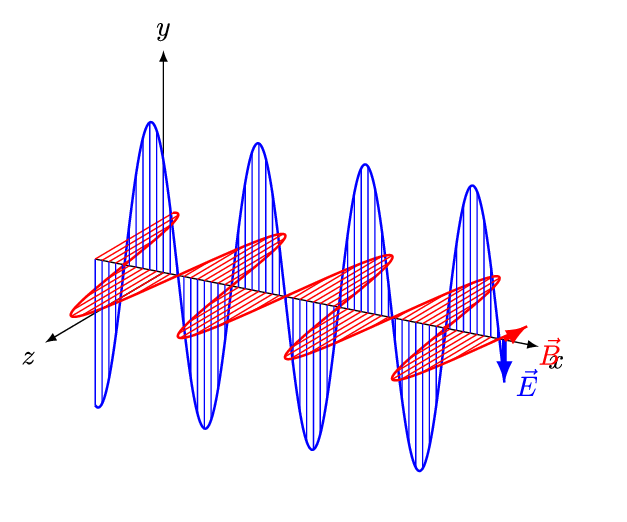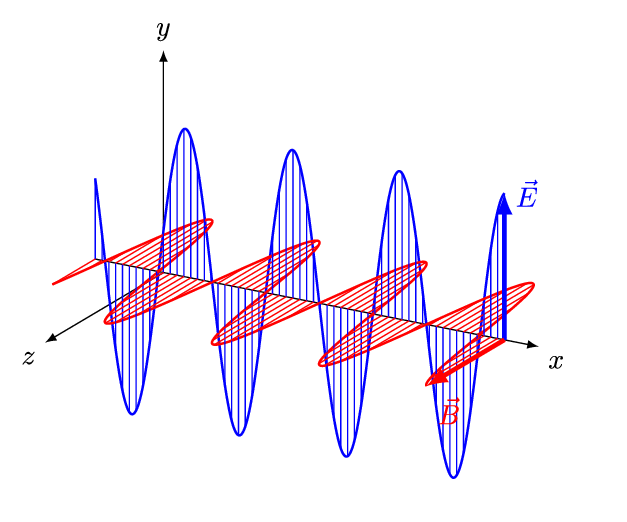
Electromagnetic waves consist of coupled oscillating electric and magnetic fields orientated at 900 to one another. (Credit: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)
- Electromagnetic waves can be imagined as oscillating electric (E) and magnetic (B) fields arranged at right angles to each other.
- In the diagram above, the coupled electric and magnetic fields follow the y-axis and z-axis and propagate along the x-axis.
- This arrangement is known as a transverse wave which means the oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of travel.
- By convention, the electric field is shown in diagrams aligned with the vertical plane and the magnetic field with the horizontal plane.
- In normal atmospheric conditions the geometric orientation of the coupled y-axis and z axis is random, so the coupled fields EB may be rotated to any angle.