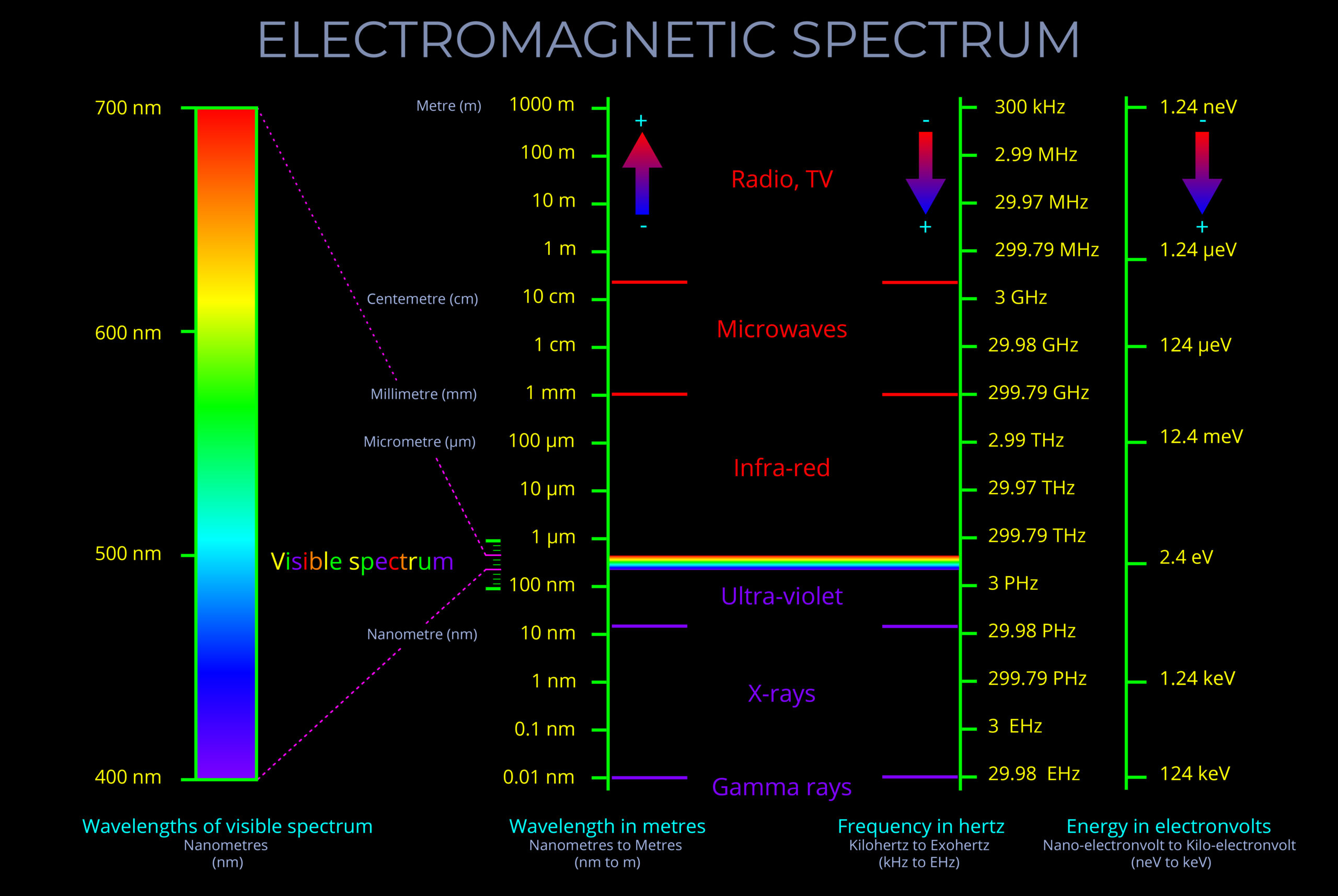
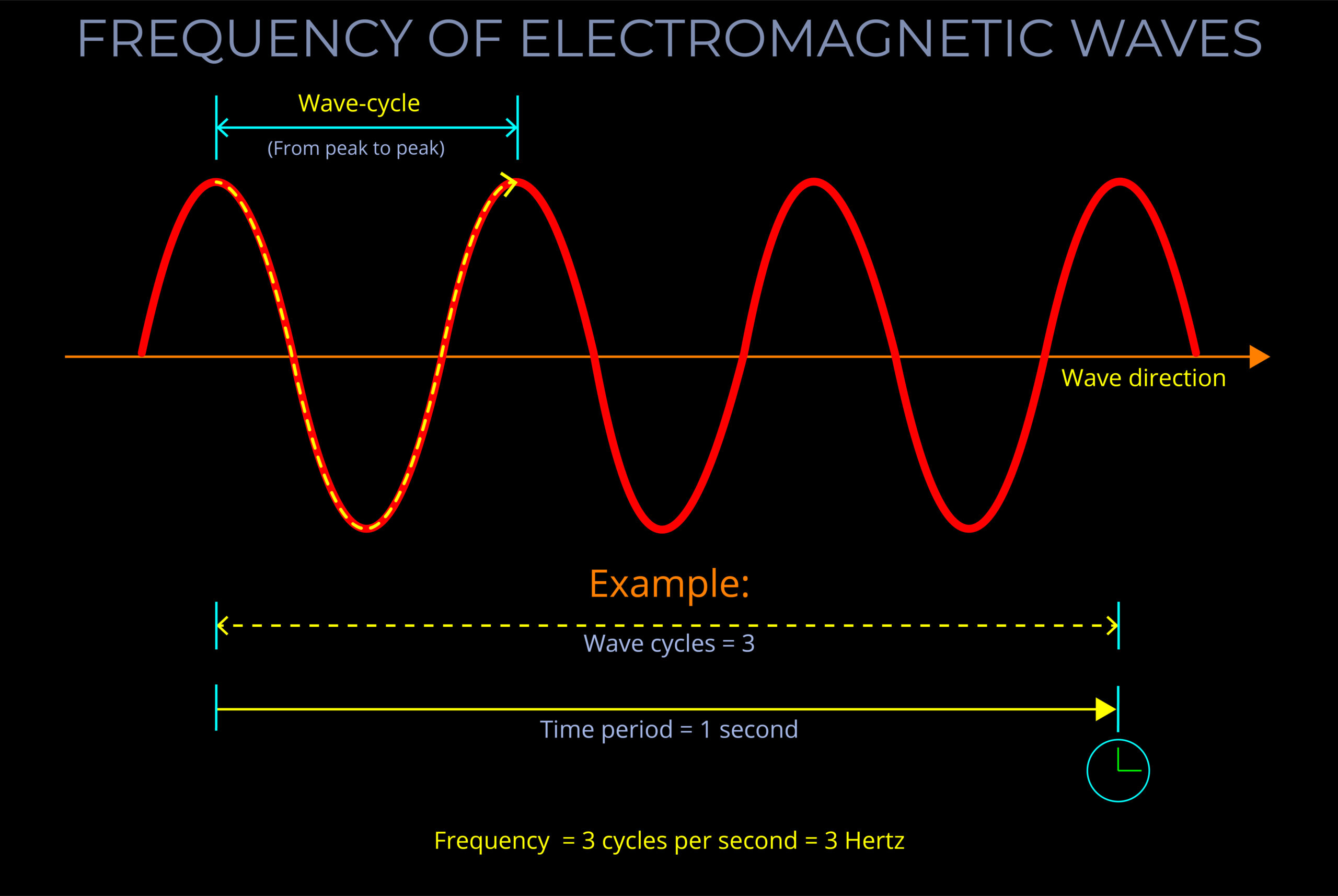
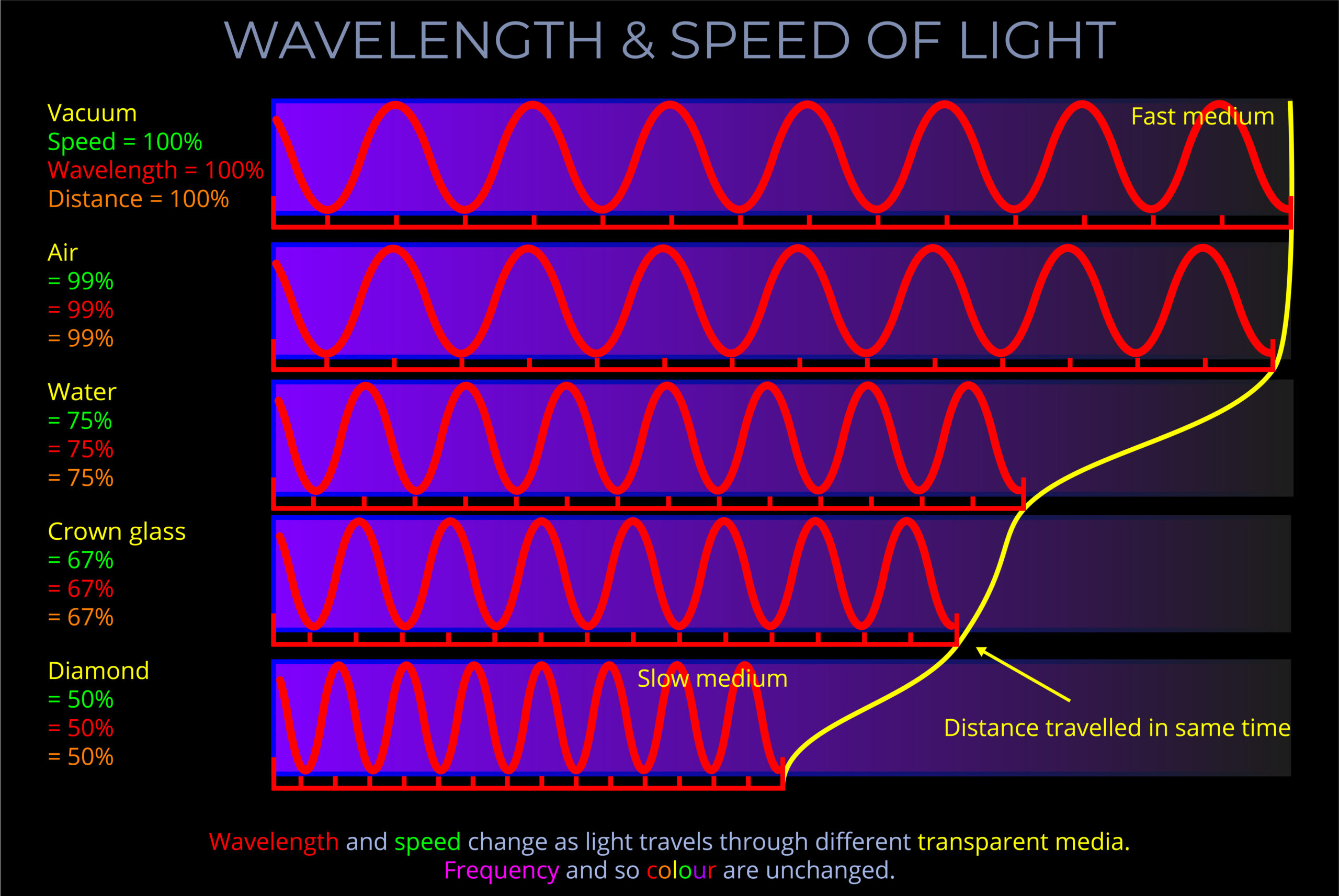
A transverse wave is a wave that oscillates up and down, left and right, or in any direction perpendicular to their direction it travels.
- A transverse wave is a type of wave in which the particles of the medium oscillate (vibrate) perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.
- Transverse waves can be observed in various phenomena, such as waves on a string, water ripples, and certain types of seismic waves.
- Note that light and other electromagnetic waves are transverse waves that can travel through a vacuum.
- Transverse waves exhibit specific properties, including wavelength, frequency, amplitude, and wave speed.
- The motion of a transverse wave can be represented graphically using a sine wave or cosine wave, illustrating the peaks and troughs of the wave.
- Transverse waves can be polarized, meaning the oscillations are confined to a particular plane or direction, which has important implications in optics and other fields.
- A transverse wave is a wave that oscillates up and down, left and right, or in any direction perpendicular to their direction it travels.
- A transverse wave is a type of wave in which the particles of the medium oscillate (vibrate) perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.
- Transverse waves can be observed in various phenomena, such as waves on a string, water ripples, and certain types of seismic waves.
- Note that light and other electromagnetic waves are transverse waves that can travel through a vacuum.
- Transverse waves exhibit specific properties, including wavelength, frequency, amplitude, and wave speed.