In the context of electromagnetic waves, velocity describes the rate of wave propagation, accounting for both its magnitude (speed) and direction. As a vector quantity, velocity provides a full description of the wave’s displacement over time, indicating how fast and in which direction it moves.
- In the context of electromagnetic waves, velocity describes the rate of wave propagation, accounting for both magnitude (speed) and direction.
- As a vector quantity, velocity provides a full description of the wave’s displacement over time, indicating how fast and in which direction it moves.
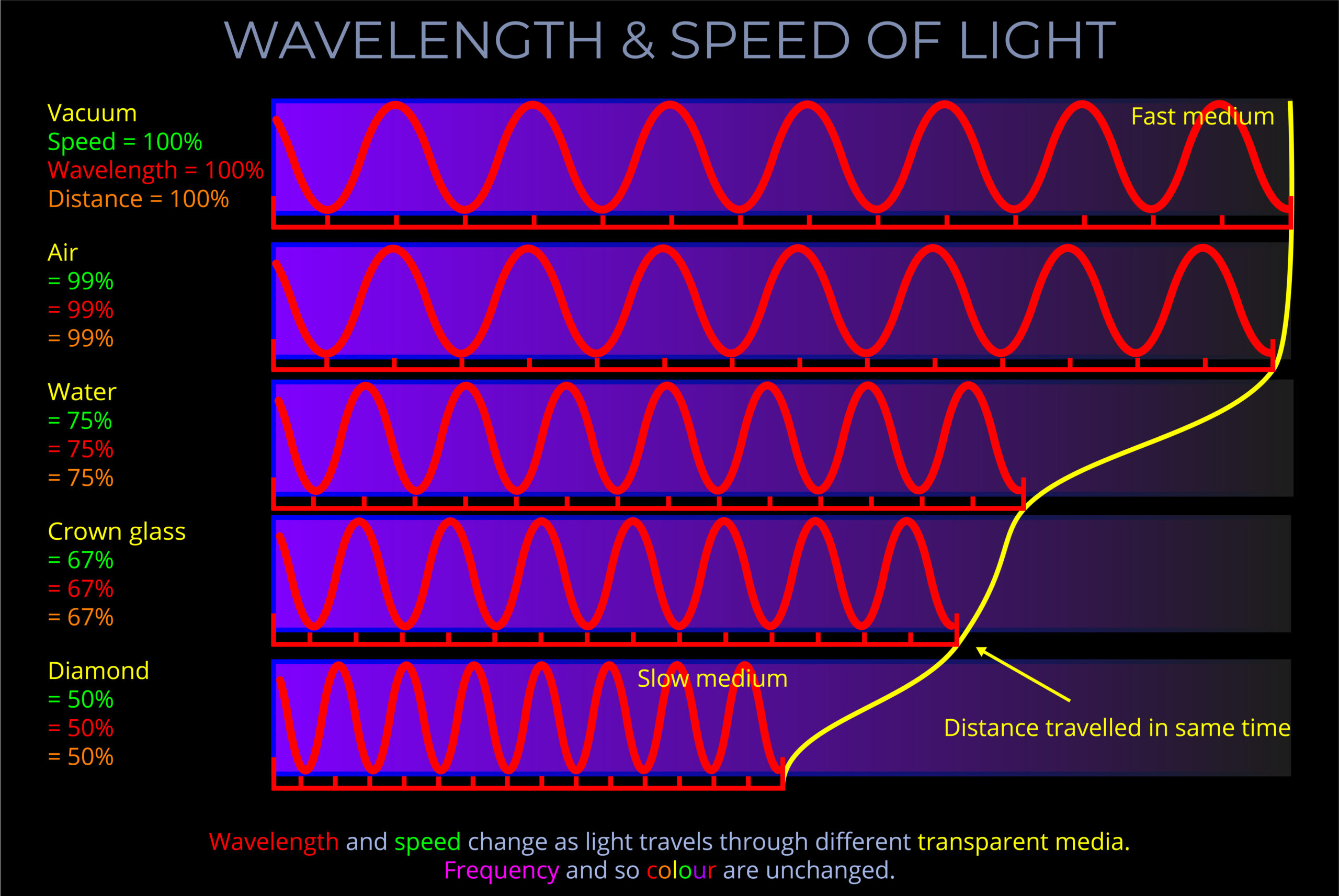
- Velocity can be positive or negative, representing motion in different directions, and is measured in units such as meters per second (m/s), kilometres per hour (km/h), or miles per hour (mph), with an indication of direction.
- In contrast, speed refers only to the magnitude of motion—how fast the wave travels—without regard to direction.
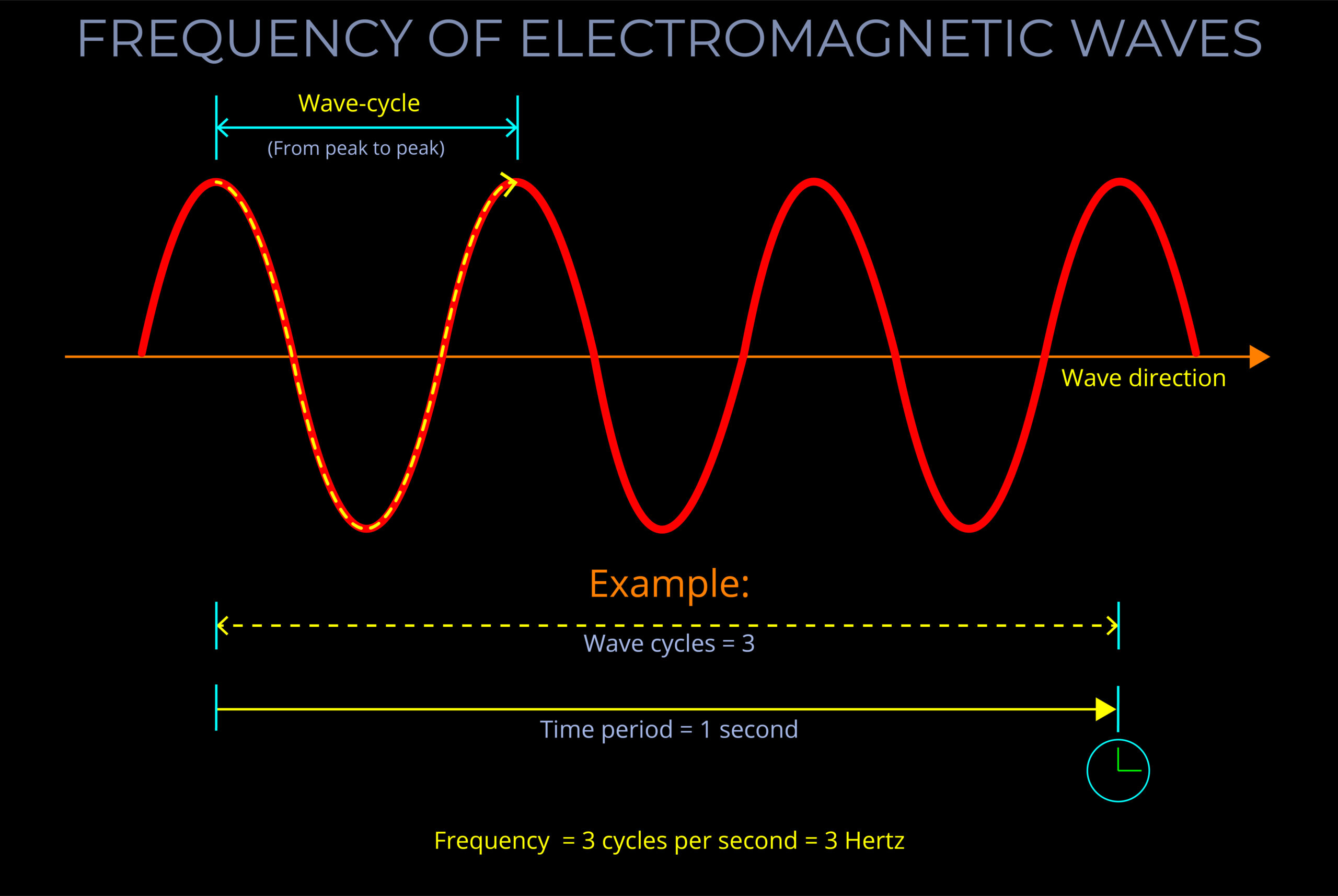
- It is the magnitude of the displacement of an object per unit of time.
- Speed does not consider the direction of motion, only the rate at which an object moves.
- Speed is always positive or zero, representing the magnitude of motion.
- Speed is measured in units such as meters per second (m/s), kilometres per hour (km/h), or miles per hour (mph).
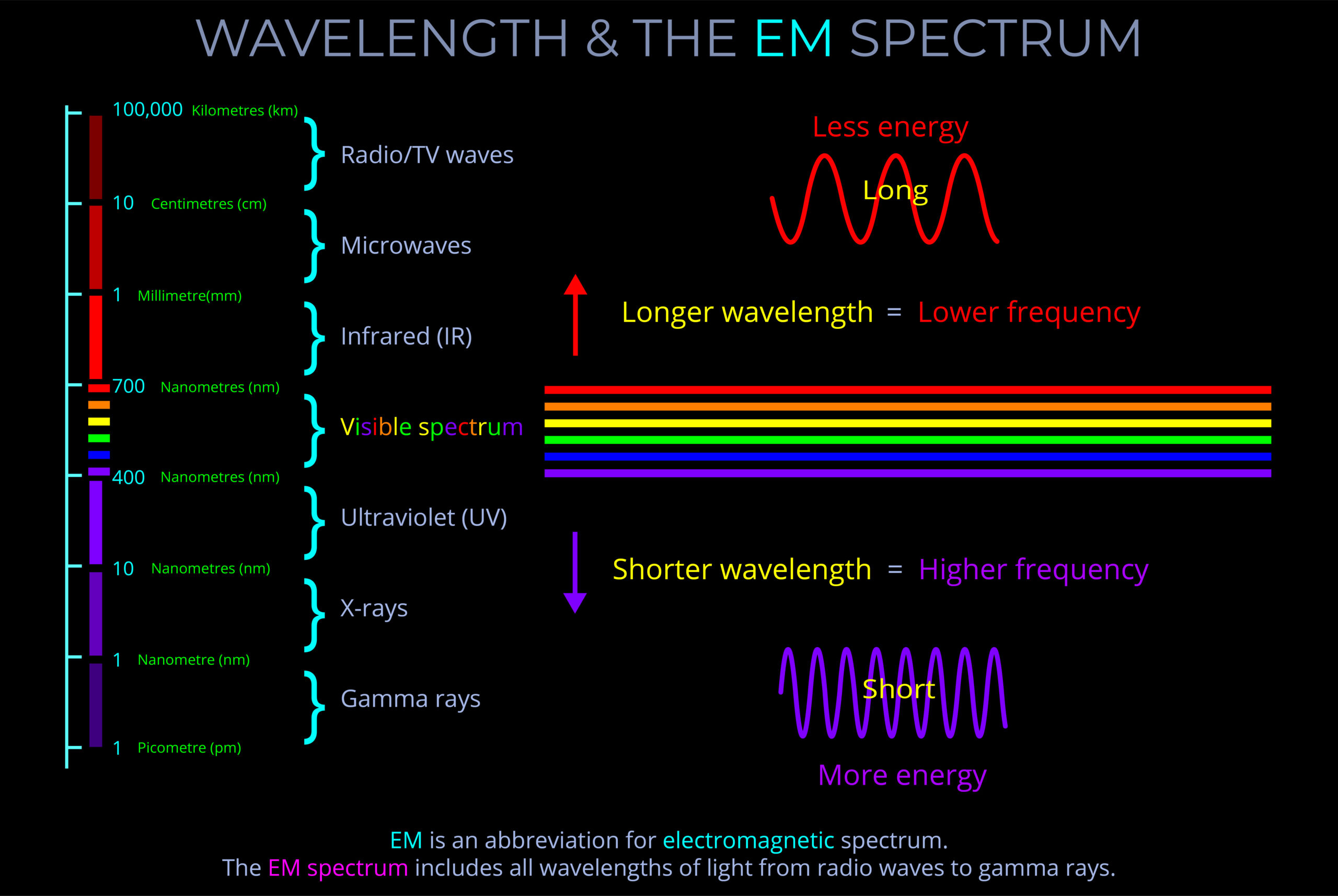
- Direction in the context of velocity is typically quantified by angles or coordinates relative to a reference point or axis.
- For electromagnetic waves, this could be described using angles (e.g., degrees or radians) from a defined direction (such as the horizontal or vertical axis in a plane) or by using a coordinate system (such as Cartesian or polar coordinates) to specify the precise direction of wave propagation.
- Positive or negative values of velocity simply indicate direction along a defined axis, with positive values often representing motion in one direction and negative values representing the opposite direction.
Velocity (General)
Velocity is a vector quantity that refers to the rate of change of an object’s position over time. It combines both speed and direction. Any change in either speed or direction results in a change in velocity.
- Speed is a scalar quantity that describes how fast an object is moving, measured as the distance covered per unit of time. It does not include direction.
- Direction is typically quantified relative to a reference point (such as along an axis or by a specific angle).