The speed of light is a measurement of how far a light wave travels in a certain amount time.
- The speed of light is typically measured in metres per second (m/s).
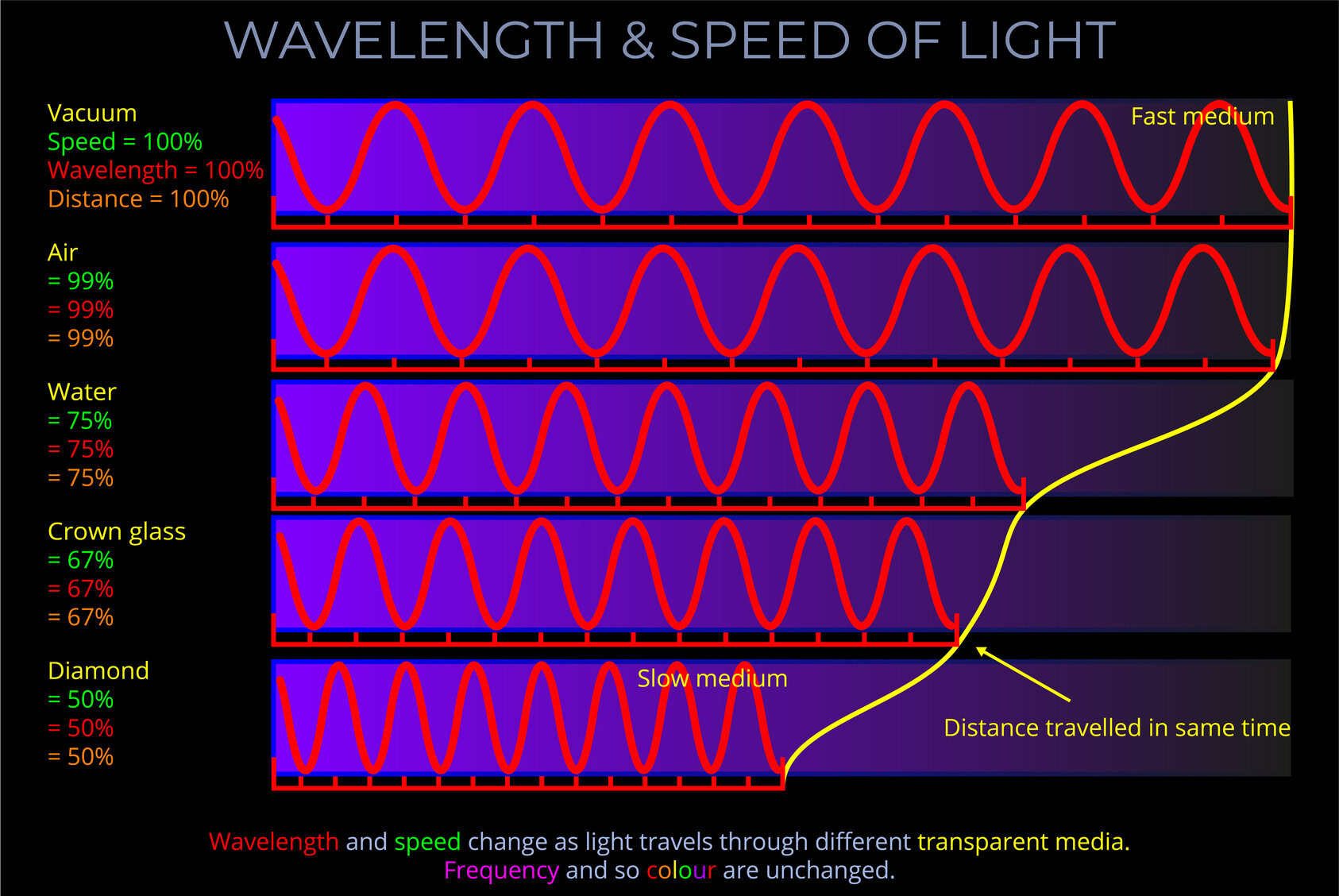
- In a vacuum, light travels at approximately 300,000 kilometres per second, or more precisely, 299,792,458 metres per second.
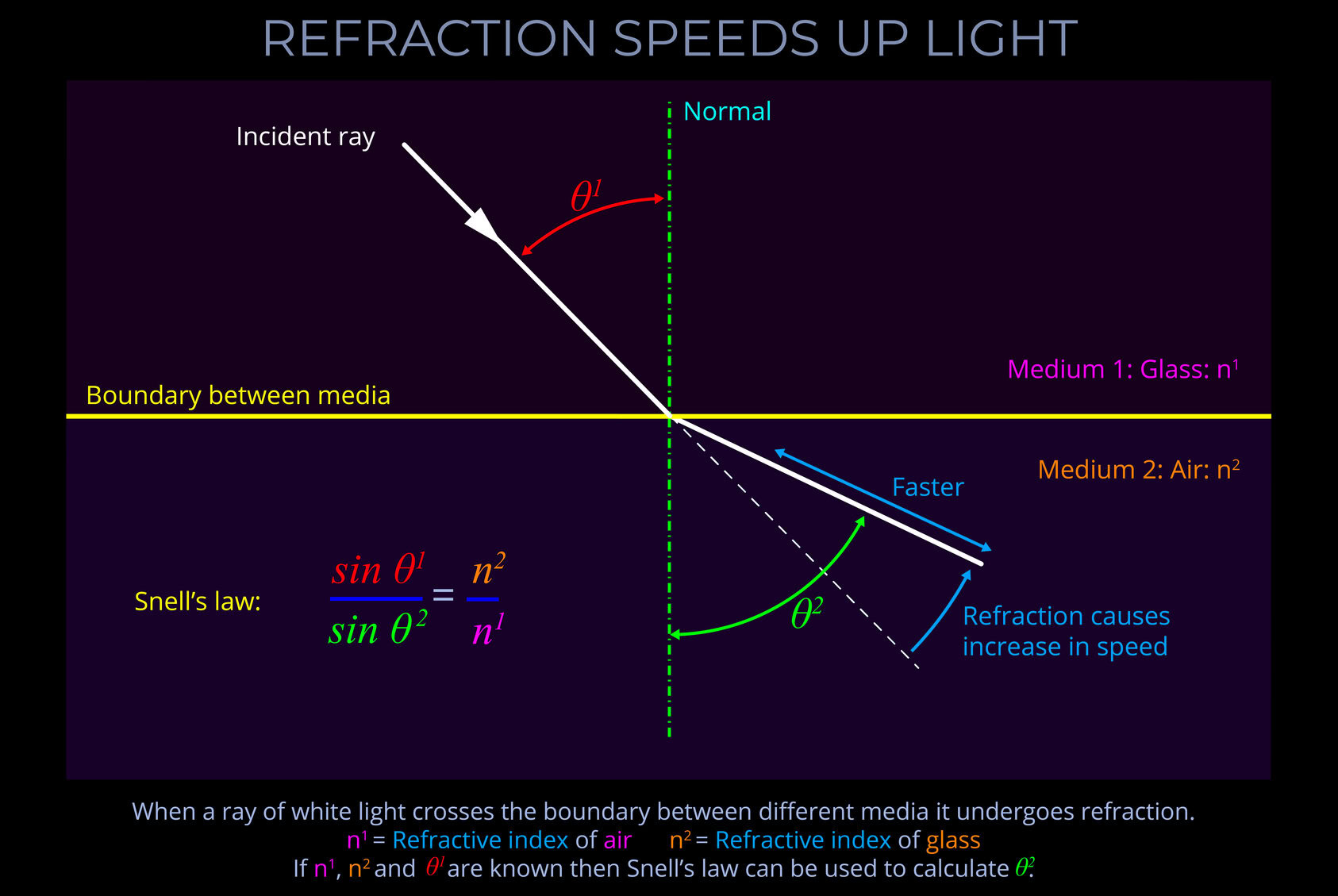
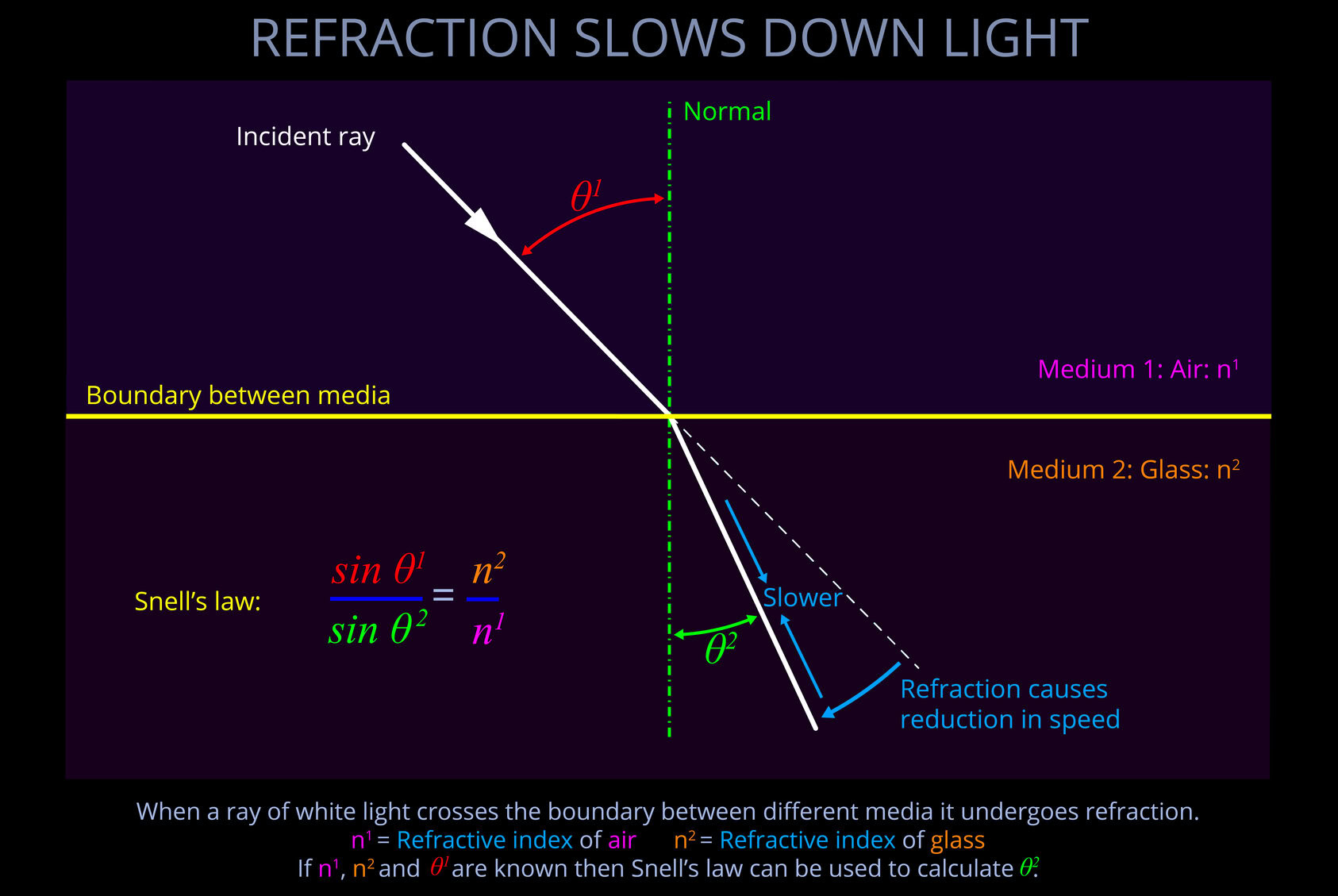
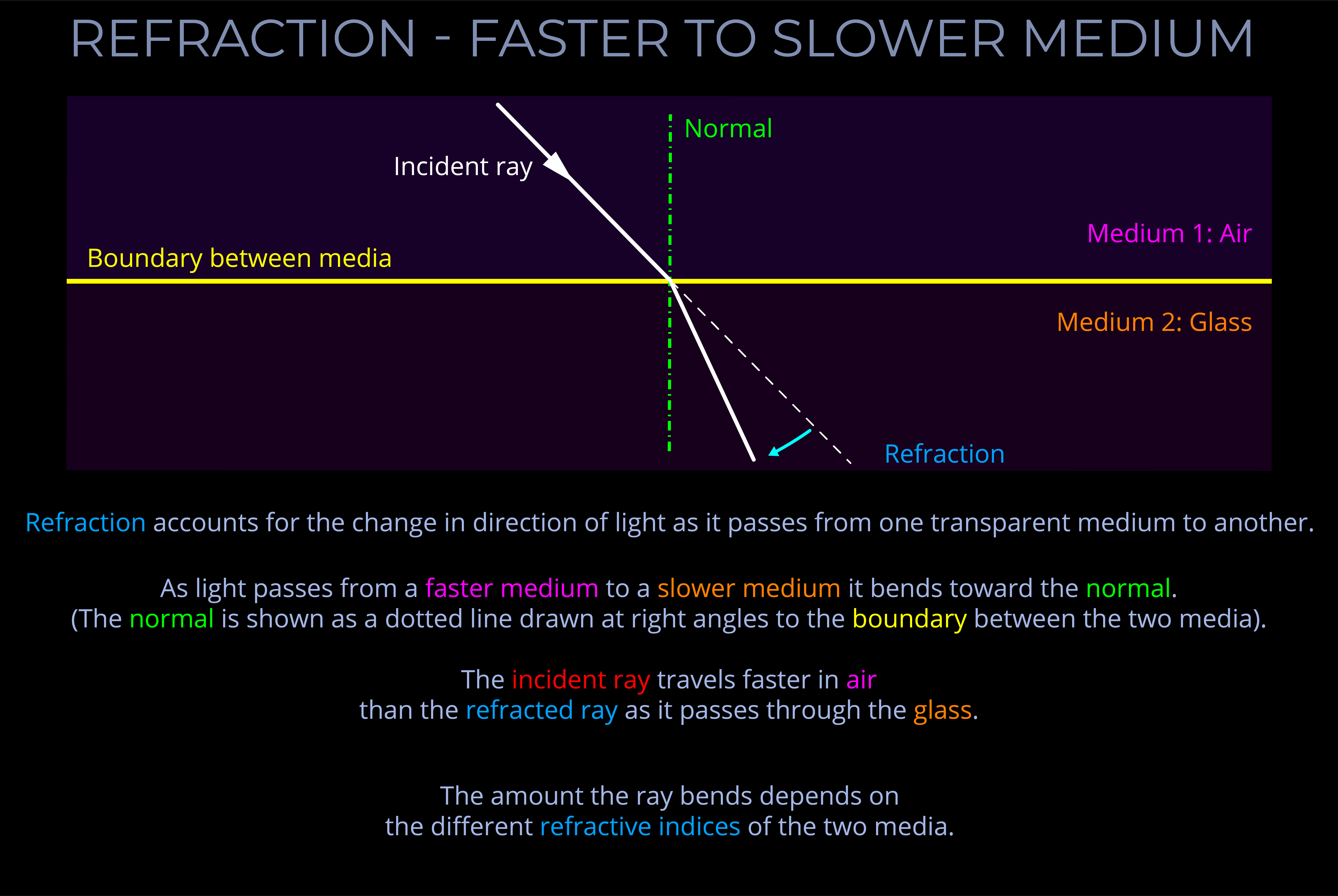
- Light moves at slower speeds when passing through different media.
- A vacuum is a region of space that contains no matter.
- Matter refers to anything that has mass and occupies space (i.e., it has volume).
- When discussing electromagnetic radiation, the term medium (plural: media) refers to anything through which light propagates, including empty space and any material such as a solid, liquid, or gas.
- In other contexts, empty space is not considered a medium because it lacks matter.
- Light itself can be described as a wave that carries energy.
- When light interacts with matter, it can behave like particles called photons.
- These photons are massless particles that travel at the speed of light. They carry energy and momentum in packets, not as continuous values.
- In science, this concept is called quantization, which means certain properties can only exist in specific amounts.
- For photons, this means their energy and momentum come in distinct, separate packets rather than a continuous range.
About speed & velocity
Speed and velocity are not the same. While they are related, there is a key difference between the two:
- Speed is a scalar quantity that refers to “how fast an object is moving.” It is the rate at which an object covers distance, without considering the direction of motion. It is expressed in units of distance per time, such as meters per second (m/s) or kilometres per hour (km/h).
- Velocity is a vector quantity that refers to “the rate at which an object changes its position.” It includes both the speed of the object and its direction of motion. It is also expressed in units of distance per time, such as meters per second (m/s) or kilometres per hour (km/h), but with a specified direction.