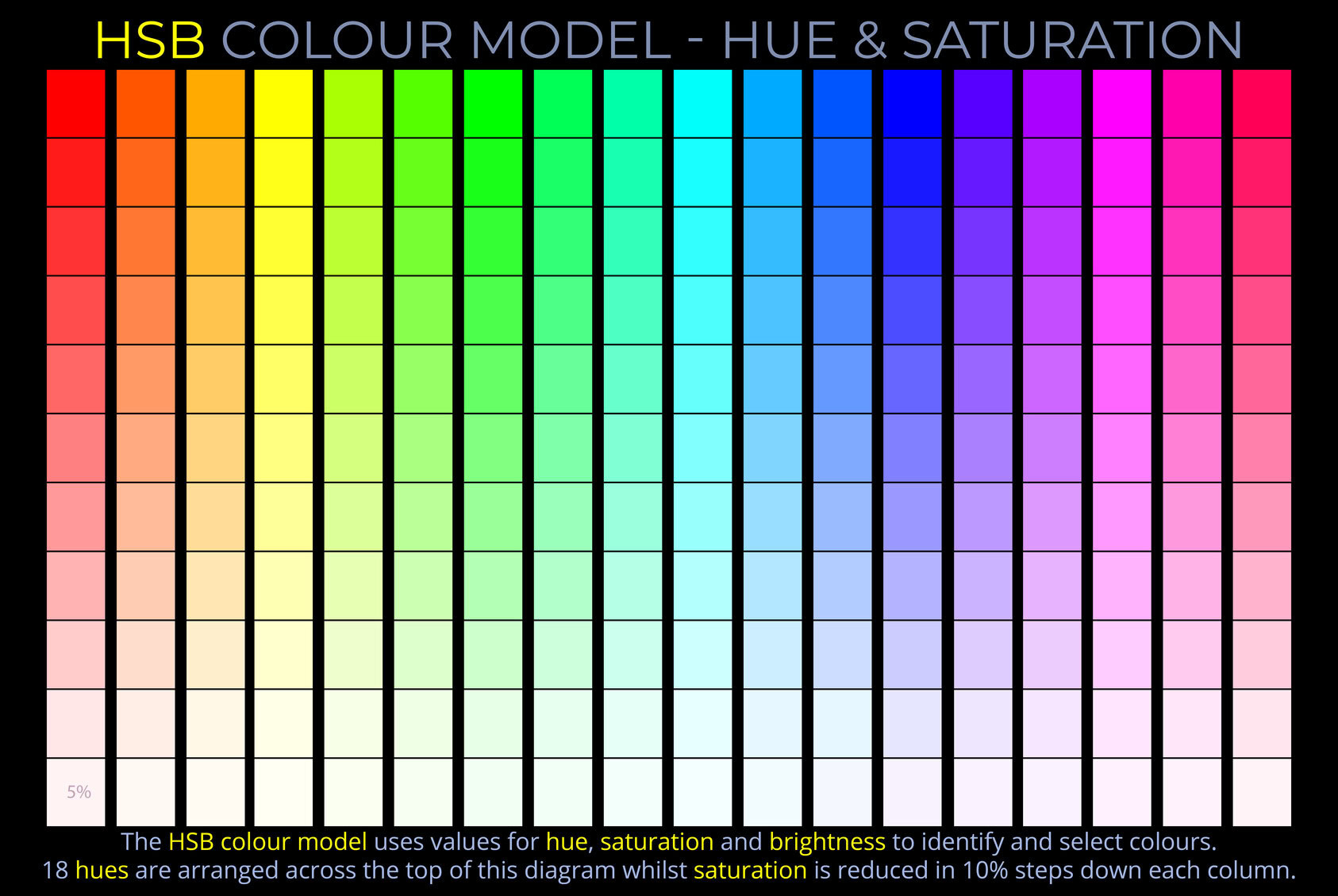
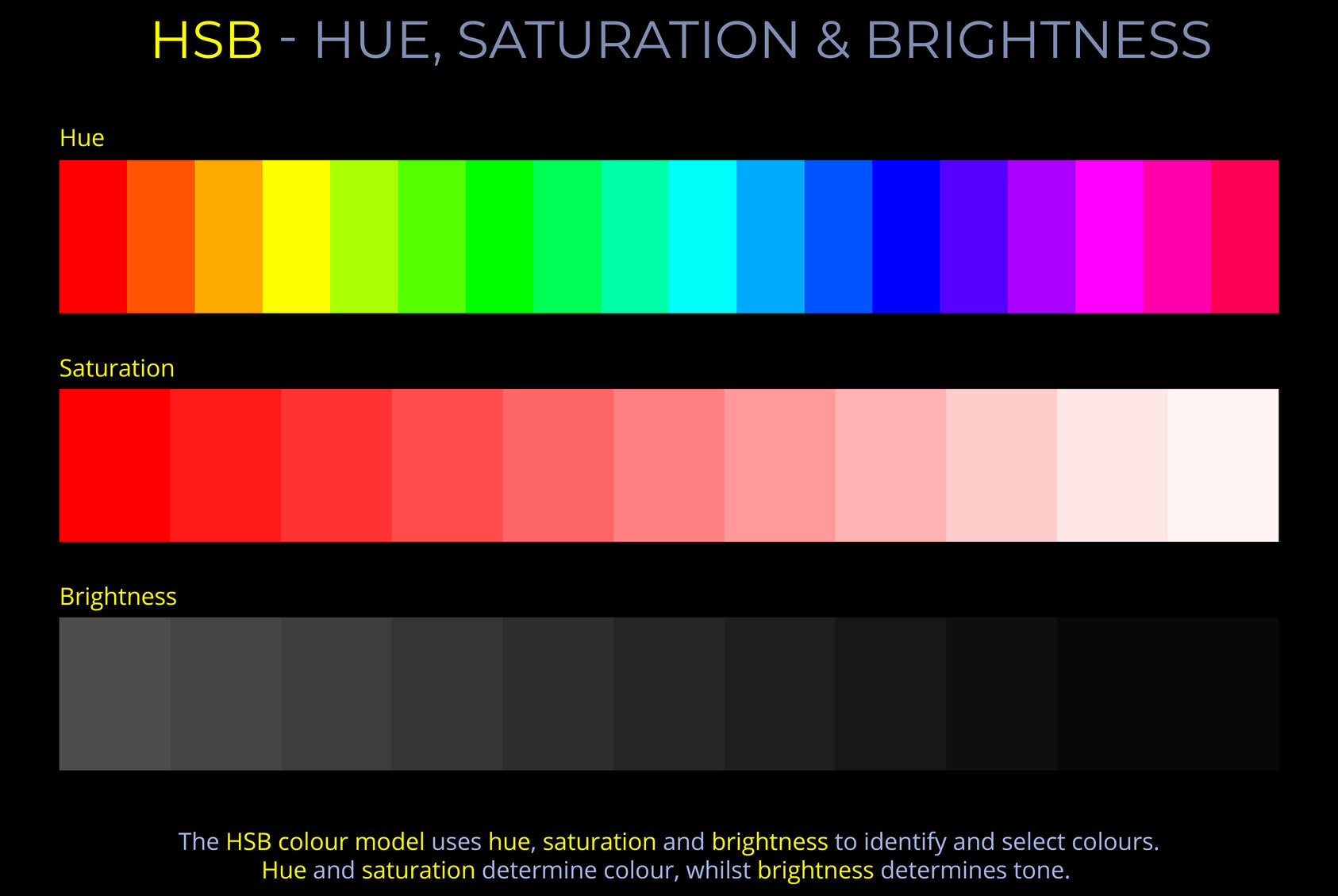
Monochromatic refers to light or electromagnetic radiation that consists of a single wavelength or frequency. In simpler terms, monochromatic light is composed of just one colour. The term comes from the Greek words mono (meaning “one”) and chroma (meaning “colour”).
- Monochromatic colours are created by using variations of a single hue, incorporating both shades (by adding black) and tints (by adding white). For example, a monochromatic colour scheme could involve a range of blues or pinks.
- It’s important not to confuse monochrome with greyscale. Monochrome refers to variations of a single hue, which can include any colour. In contrast, greyscale consists solely of shades of grey, with no colour information.
- In physics, monochromatic light refers to visible light or other electromagnetic radiation that has a single wavelength or frequency, resulting in light of a single colour.
- A surface or material is considered monochromatic if it features only one hue or a combination of tints and shades of the same colour.