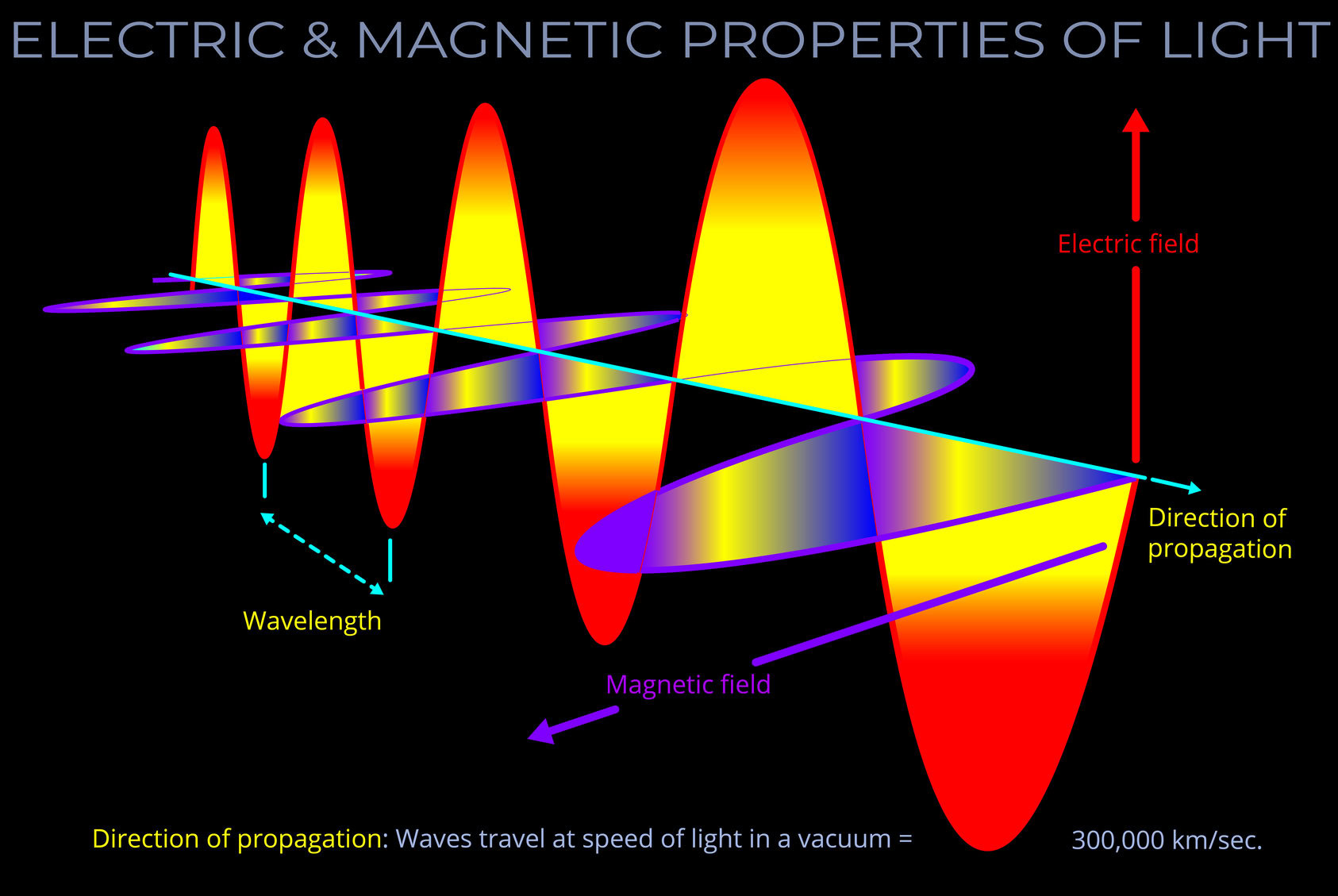
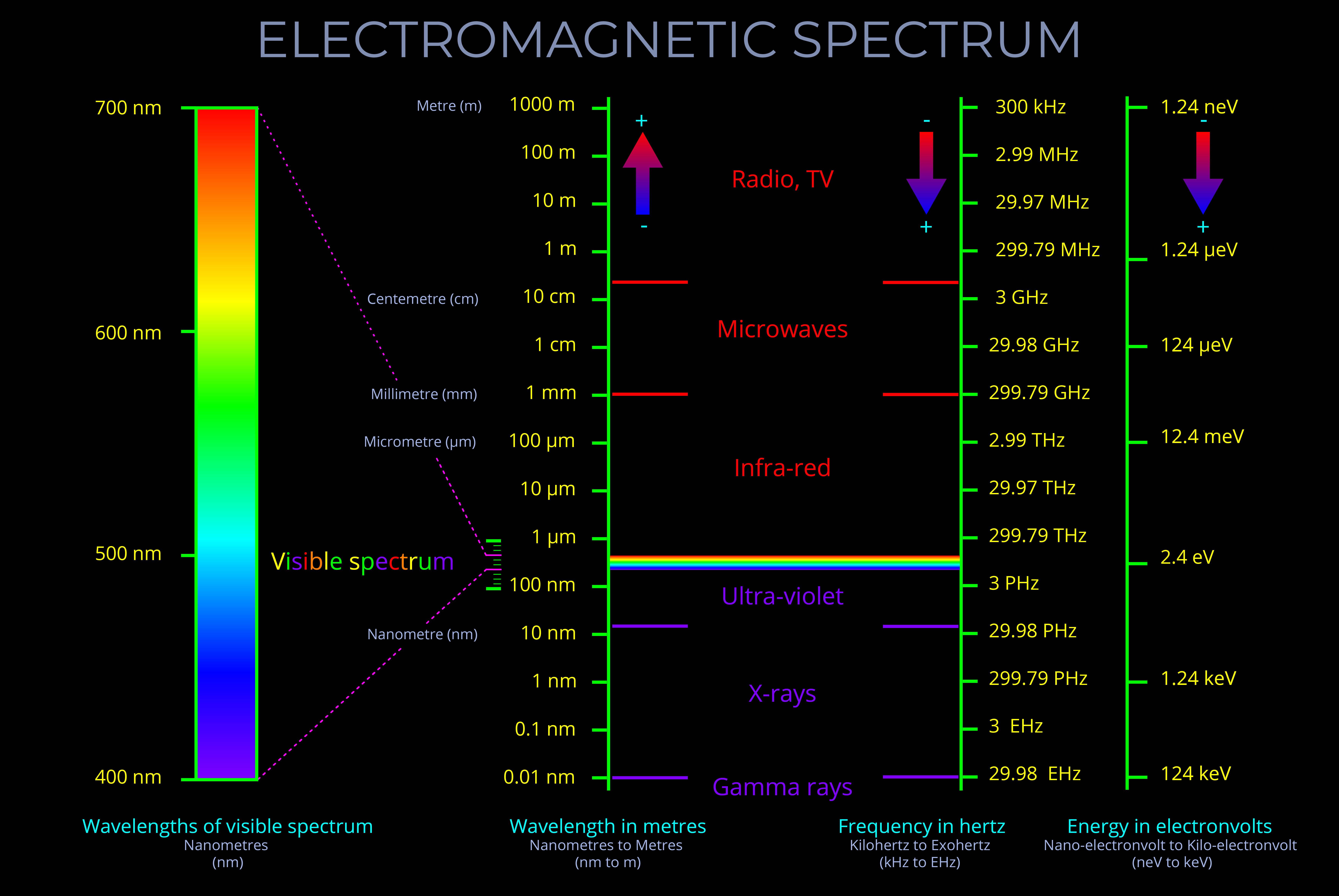
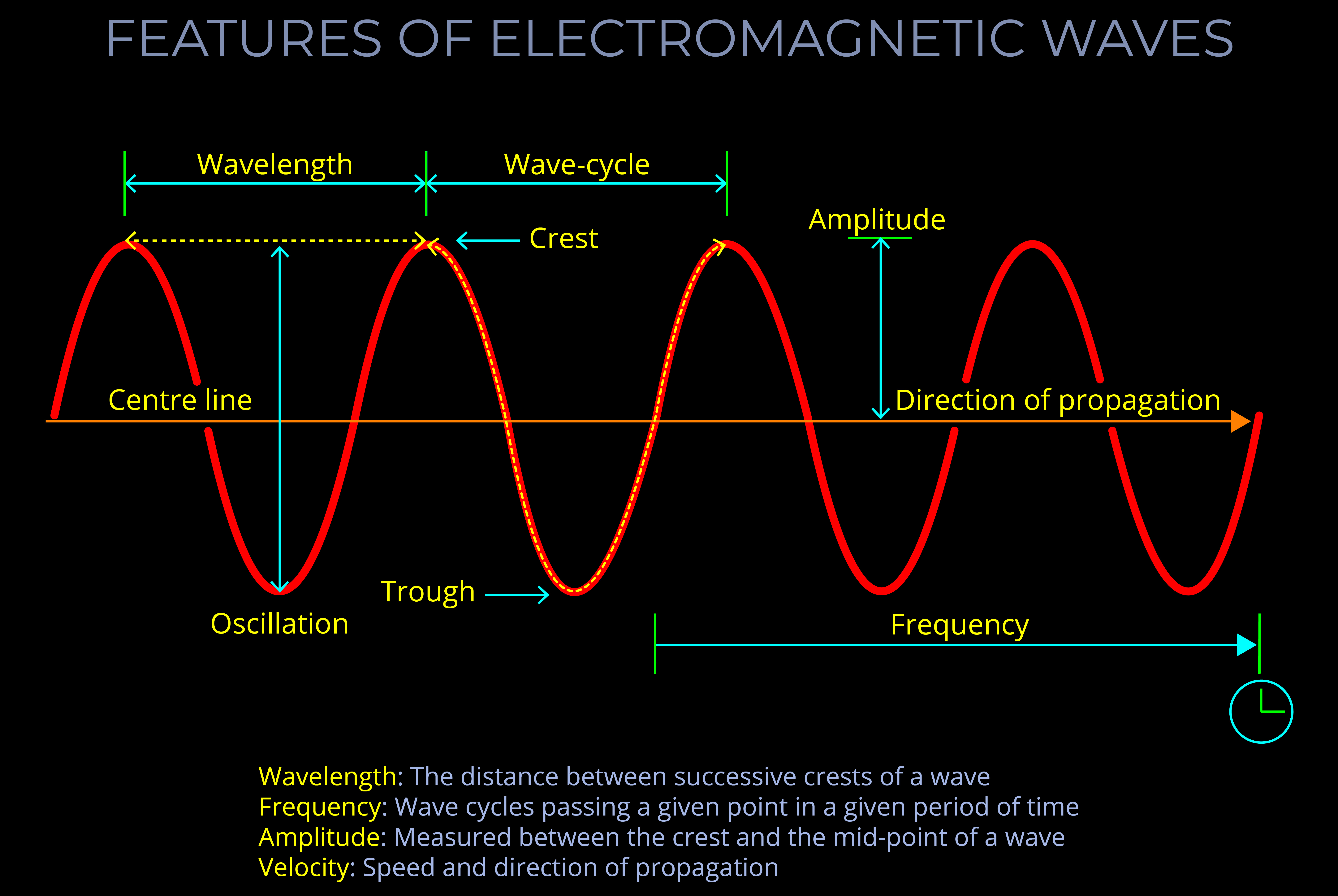
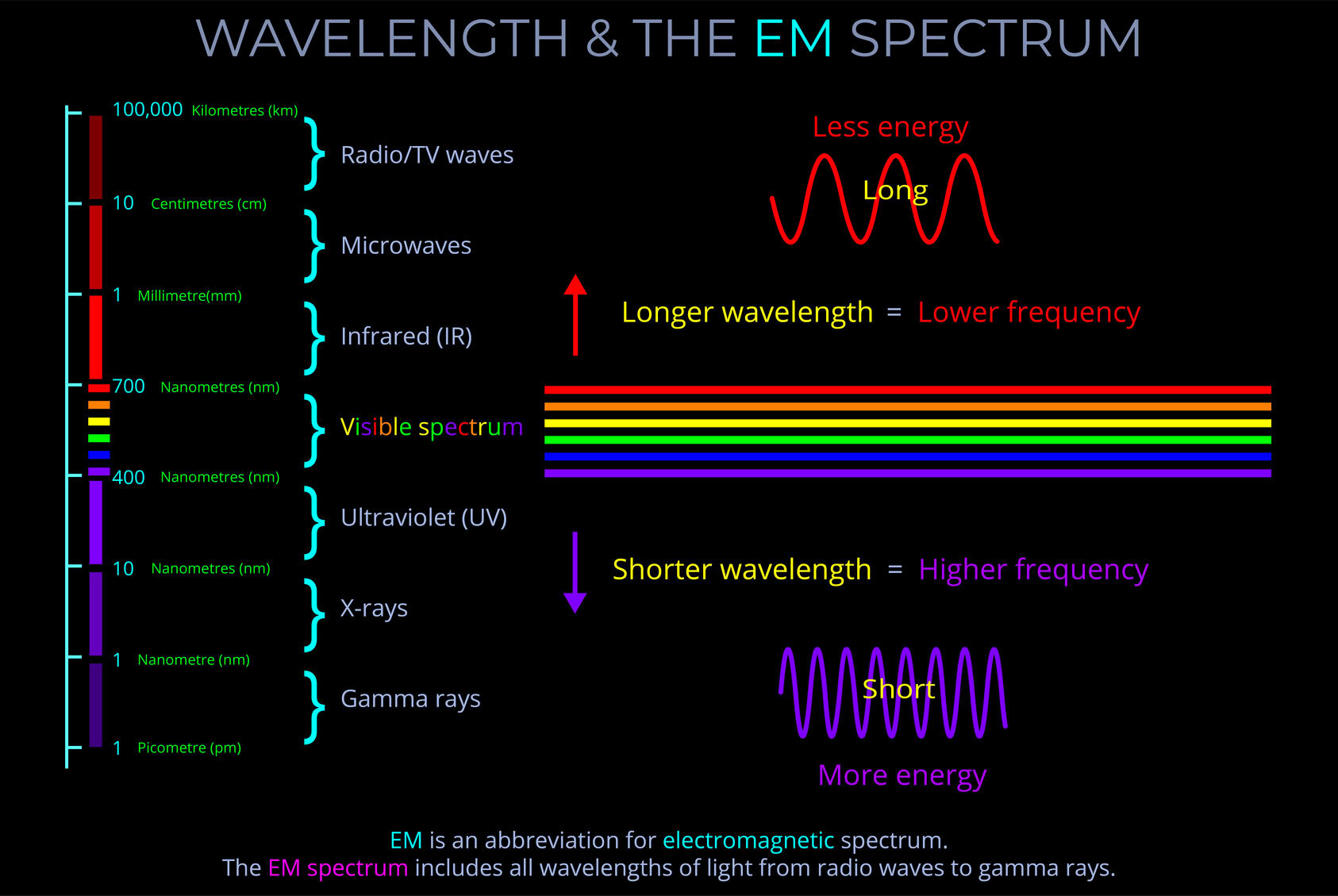
An electromagnetic field (which includes both electric and magnetic fields) is the region around an object where it can exert a force on another object without direct contact. Electric fields arise from charged objects, while magnetic fields are produced by moving charges, such as electric currents.
- Fields are fundamental in physics, playing key roles in areas like electromagnetism, quantum mechanics, and general relativity.
- Fields can be represented by lines showing the direction of the force experienced by objects within the field.
- Fields are created by a source object and influence other objects within their range.
- Electromagnetic fields combine electric and magnetic components, interconnected through electromagnetic waves.
- Electric fields are associated with positive or negative charges and exert forces on charged objects.
- Magnetic fields are generated by moving electric charges, such as currents in wires, and can affect magnetic materials and charged particles.
- Electric fields and magnetic fields together make up the electromagnetic field, which governs interactions between charged particles.
- According to quantum field theory, all particles and forces in the universe arise from interactions between underlying fields, which give rise to the properties of matter and energy.