The Adobe RGB (1998) colour space was developed by Adobe Systems. It aims to ensure the optimal range of colours available within the RGB colour model are accurately reproduced when output to a digital displays or printers.
- The general purpose of a colour space is to determine the range of colours available within a specific workflow and may be determined by a user or programmatically.
- The purpose of RGB (1998) was to improve on the gamut of colours that can be produced by the earlier sRGB colour space, primarily in the reproduction of cyan-green hues.
- It can reproduce approximately 35% more colours compared to sRGB in ideal conditions.
- It is estimated to cover approximately 50% to 70% of the colours perceived by the human eye in ideal conditions.
- In a digital environment, the aim is to ensure that a selected range of colours appears consistent throughout a workflow and that the desired range of colours is successfully reproduced at the end of the process.
About colour spaces & examples
- A colour space aims to accurately define the relationship between any selected colour within a colour model and how it will appear when it is reproduced by a specific device such as a digital display, printer or paint mixing machine.
- When an artist selects a limited number of tubes of oil paint to add to a palette, they are already working within the RYB subtractive colour model and establishing the colour space in which they plan to work.
- A colour space may aim to limit the number of colours or establish the widest possible gamut of reproducible colours.
- Digital colour spaces are commonly used to accurately set the range of colours that can be output to and then displayed by digital screens and printers.
- When a colour space is to be matched with a specific digital device such as a projector or printer, a colour profile is loaded along with the image file to ensure accurate colour reproduction.
- A colour profile is a program that enables a piece of equipment, such as a digital printer, to know how to handle and process the information it receives, ensuring it can produce the intended colour output accurately.
Examples of colour spaces include:
RGB (Red, Green, Blue) Color Space
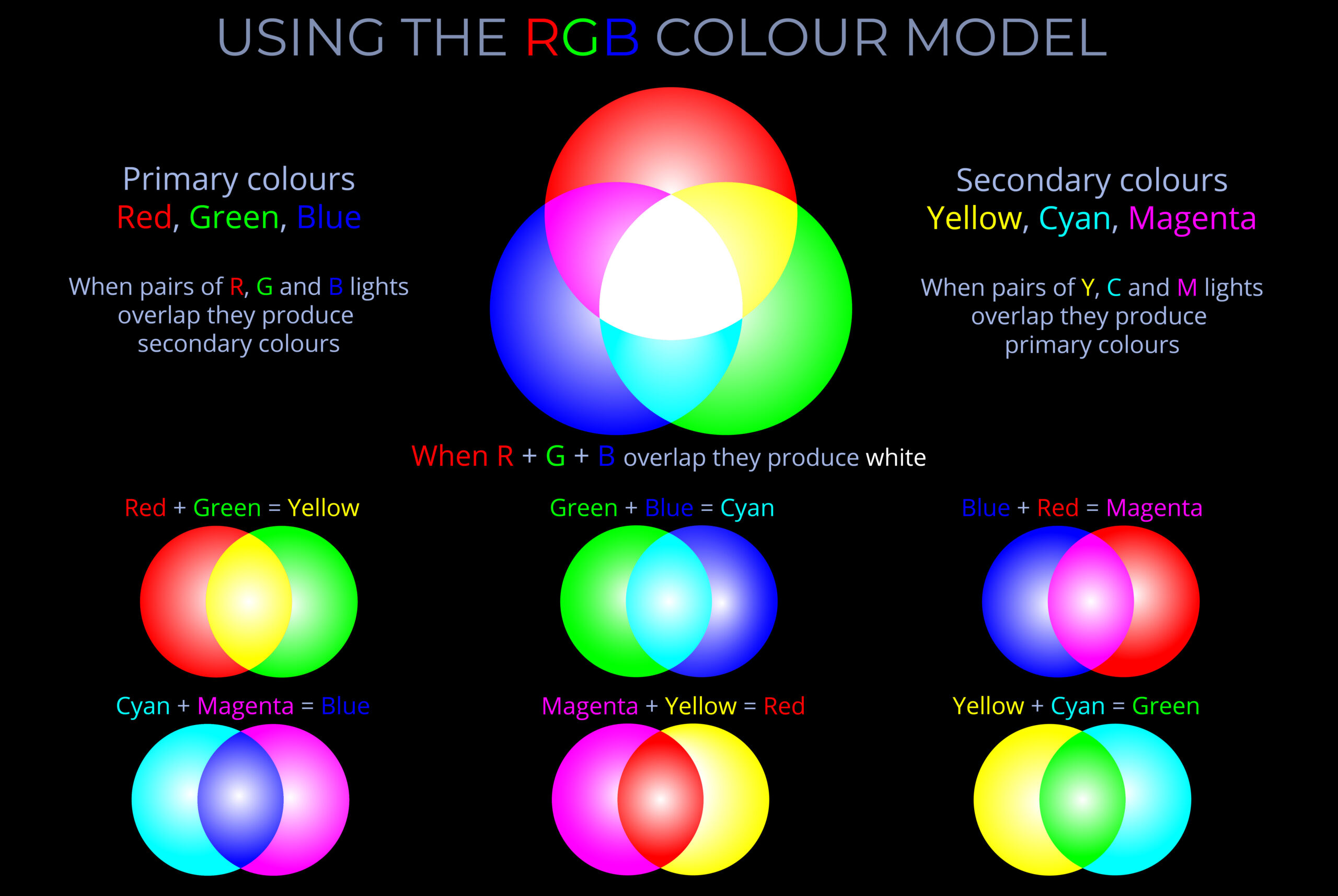
- RGB is an additive colour model used in digital displays and electronic devices. It defines colours by mixing varying intensities of red, green, and blue light. The primary colours (red, green, and blue) are combined at full intensity to produce white light.
CMYK (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Key/Black) Color Space
- CMYK is a subtractive colour model used in printing and design. It defines colours by subtracting varying amounts of cyan, magenta, yellow, and black ink from a white paper background. CMYK is used to achieve a wide range of colours on printed materials.
RYB (Red, Yellow, Blue) Color Space
- RYB is an older subtractive colour model primarily used in traditional art and paint mixing. It consists of three primary colours: red, yellow, and blue. Mixing these colours creates secondary colours, such as orange, green, and violet. RYB is not used in modern digital design.
LAB Color Space
- LAB is a device-independent colour space that represents colours in a way that is closer to human perception. It separates colour information into three channels: L (lightness), A (green to red), and B (blue to yellow). LAB is used in colour management and as an intermediate space when converting between different colour models.
HSB/HSV (Hue, Saturation, Brightness/Value) Color Space
- HSB/HSV is a cylindrical colour model that represents colours based on three parameters: hue (the type of colour), saturation (the purity of the colour), and brightness/value (the intensity of the colour). It is often used in computer graphics and design software.
XYZ Color Space
- XYZ is a CIE (Commission Internationale de l’Eclairage) standardized colour space that serves as a reference for defining other colour spaces. It is based on human vision and designed to be perceptually uniform. XYZ is used in various colour-related calculations and conversions.
Pantone Color Space
-
- The Pantone colour system is widely used in the printing and design industries. It provides a standardized set of colours represented by specific codes. Each colour swatch is carefully defined to ensure consistency in printing and reproducing colours accurately.
- The general purpose of a colour space is to determine the range of colours available within a specific workflow and may be determined by a user or programmatically.
- The Adobe RGB (1998) colour space aims to ensure the optimal range of colours available within the RGB colour model are accurately reproduced when output to a digital displays or printers.
- In a digital environment, the aim is to ensure that a selected range of colours appears consistent throughout a workflow and that the desired range of colours is successfully reproduced at the end of the process.