RGB Colour Wheels with 3 to 102 Colours
£0.00
This diagram is a new addition to the site! More information will be added ASAP 🙂
Description
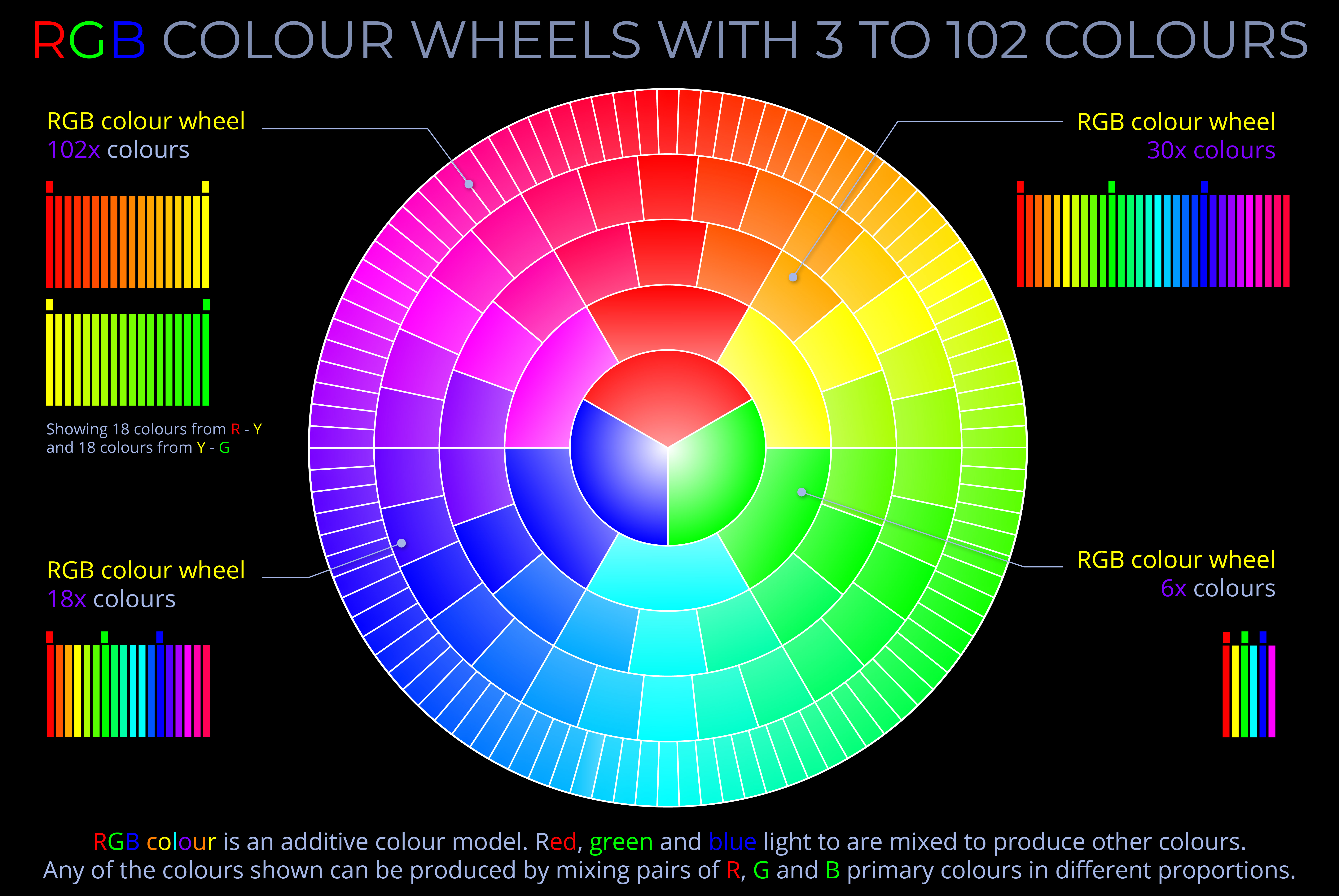
RGB Colour Wheels with 3 to 102 Colours
TRY SOME QUICK QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS TO GET STARTED
About the diagram
Some key terms
An additive colour model explains how different coloured lights (such as LEDs or beams of light) are mixed to produce other colours.
- Additive colour refers to the methods used and effects produced by combining or mixing different wavelengths of light.
- The RGB colour model and HSB colour model are examples of additive colour models.
- Additive colour models such as the RGB colour model and HSB colour model can produce vast ranges of colours by combining red, green, and blue lights in varying proportions.
- An additive approach to colour is used to achieve precise control over the appearance of colours on digital screens of TVs, computers, and phones.
Primary colours are a set of colours from which others can be produced by mixing (pigments, dyes etc.) or overlapping (coloured lights).
- The human eye, and so human perception, is tuned to the visible spectrum and so to spectral colours between red and violet. It is the sensitivity of the eye to the electromagnetic spectrum that results in the perception of colour.
- A set of primary colours is a set of pigmented media or coloured lights that can be combined in varying amounts to produce a wide range of colours.
- This process of combining colours to produce other colours is used in applications intended to cause a human observer to experience a particular range of colours when represented by electronic displays and colour printing.
- Additive and subtractive models have been developed that predict how wavelengths of visible light, pigments and media interact.
- RGB colour is a technology used to reproduce colour in ways that match human perception.
- The primary colours used in a colour space such as CIELAB, NCS, Adobe RGB (1998) and sRGB are the result of an extensive investigation of the relationship between visible light and human colour vision.
RGB colour is an additive colour model in which red, green and blue light is combined to reproduce a wide range of other colours.
- The primary colours in the RGB colour model are red, green and blue.
- In the RGB model, different combinations and intensities of red, green, and blue light are mixed to create various colours. When these three colours are combined at full intensity, they produce white light.
- Additive colour models are concerned with mixing light, not dyes, inks or pigments (these rely on subtractive colour models such as the RYB colour model and the CMY colour model).
- The RGB colour model works in practice by asking three questions of any colour: how red is it (R), how green is it (G), and how blue is it (B).
- The RGB model is popular because it can easily produce a comprehensive palette of 1530 vivid hues simply by adjusting the combination and amount of each of the three primaries it contains.
A secondary colour is created by mixing two primary colours in equal parts. The primary colours may belong to either an additive colour model, which combines wavelengths of light, or a subtractive colour model, which mixes pigments or dyes.
- In additive colour models such as the RGB colour model, which deals with the effects of mixing coloured light, a secondary colour results from overlapping the primary colours: red, green, and blue. The secondary colours produced by combining pairs of primary colours in the RGB model are cyan, magenta, and yellow.
- In subtractive colour models such as the CMY colour model, which is concerned with mixing dyes and inks, a secondary colour results from overlapping the primary colours: cyan, magenta, and yellow. The secondary colours produced by combining pairs of primary colours in the CMY model are red, green, and blue.
- A colour wheel is a circular diagram divided into segments, featuring primary colours, and used to visualize the result of colour mixing.
- Colour wheels can enhance understanding of colour relationships and assist with the accurate selection and reproduction of colours.
- A colour wheel starts with segments representing primary colours. Additional segments are added between them to explore the outcome of mixing adjacent primary colours.
- By adding more segments between existing ones, further mixing of adjacent colours can be explored.
- A colour wheel exploring the additive RGB colour model starts with red, green, and blue primary colours.
- A colour wheel exploring the subtractive CMY colour model starts with cyan, magenta, and yellow primary colours.