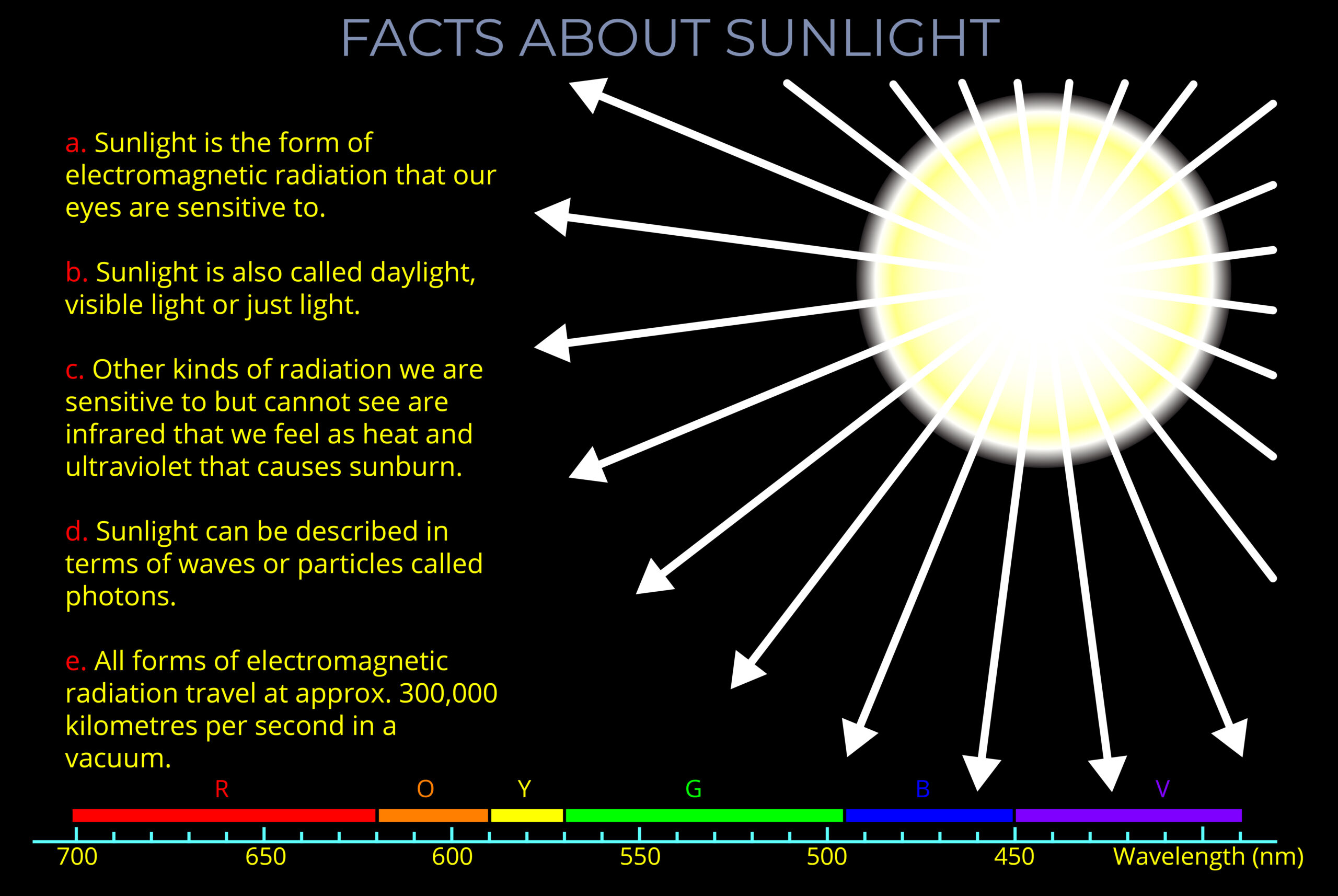
Solar radiation is the electromagnetic radiation emitted by the Sun.
- Solar means of or relating to the Sun.
- Solar radiation is the energy transferred from the Sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation. This radiation includes a wide range of wavelengths, such as ultraviolet, visible, and infrared light.
- Solar radiation includes a wide range of wavelengths, such as ultraviolet, visible, and infrared light.
- The amount of solar radiation reaching the Earth’s surface is affected by factors like atmospheric conditions, clouds, and geographical location.
- Several factors, like atmospheric conditions, clouds, and geographical location, influence how much solar radiation reaches the Earth’s surface.
- Solar radiation is essential for life on Earth, as it provides the energy needed for photosynthesis in plants and influences the Earth’s climate and weather patterns.
- Electromagnetic radiation is a type of energy that is commonly known as light. Detached from its source, it is transported by electromagnetic waves (or by their quanta, particles called photons) and propagates through space.
Solar radiation is electromagnetic radiation
- Solar radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation and includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visible) light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays.
- Not all wavelengths of solar radiation make it through the atmosphere.
- Electromagnetic radiation is sometimes called EM radiation or electromagnetic radiant energy (EMR).
- All forms of electromagnetic radiation can be described in terms of both waves or particles.
- All forms of electromagnetic radiation travel at 299,792 kilometres per second in a vacuum.