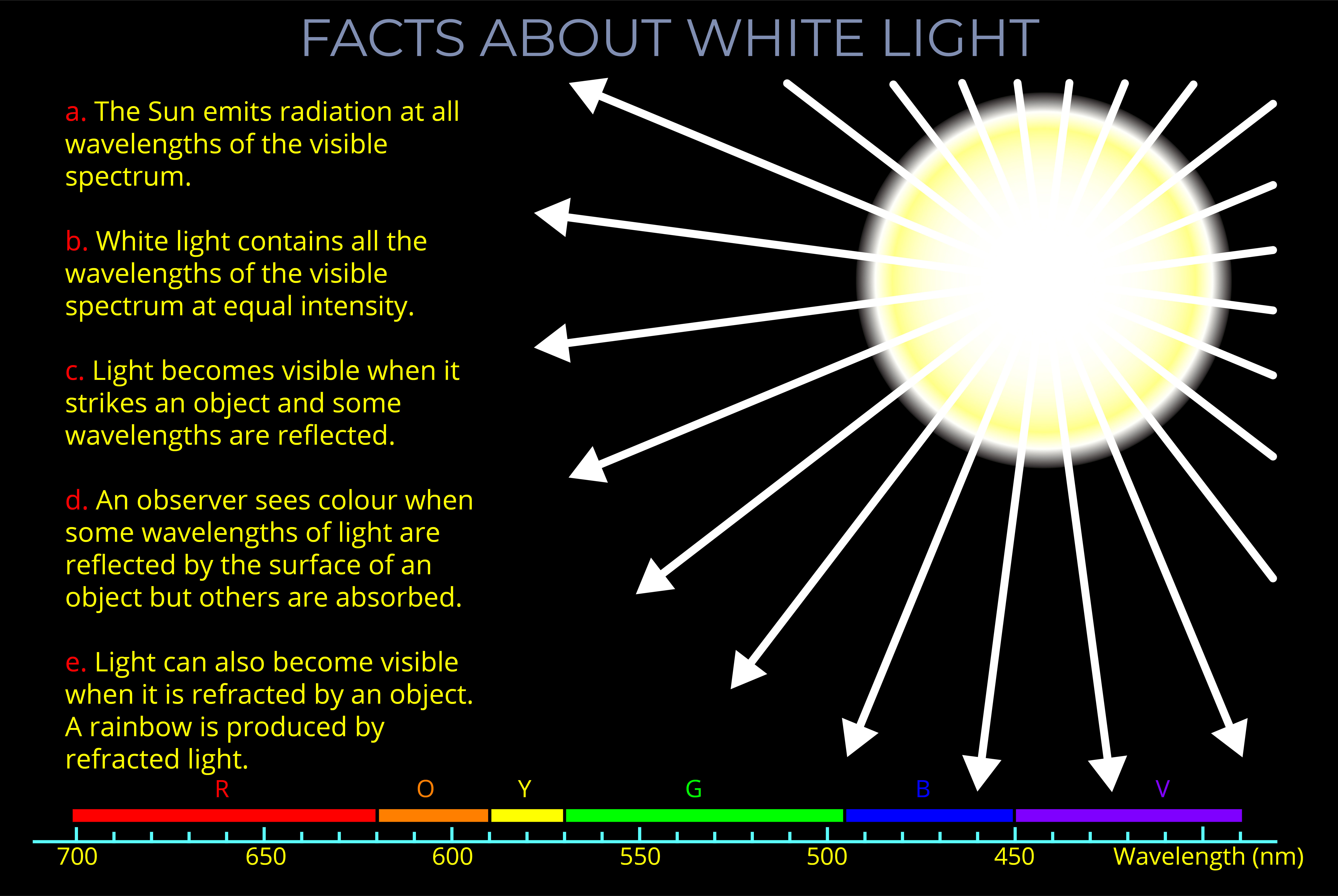
White light is the term for visible light that contains all wavelengths of the visible spectrum at equal intensities.
- The sun emits white light because sunlight contains all the wavelengths of the visible spectrum in roughly equal proportions.
- Light travelling through a vacuum or a medium is termed white light if it includes all wavelengths of visible light.
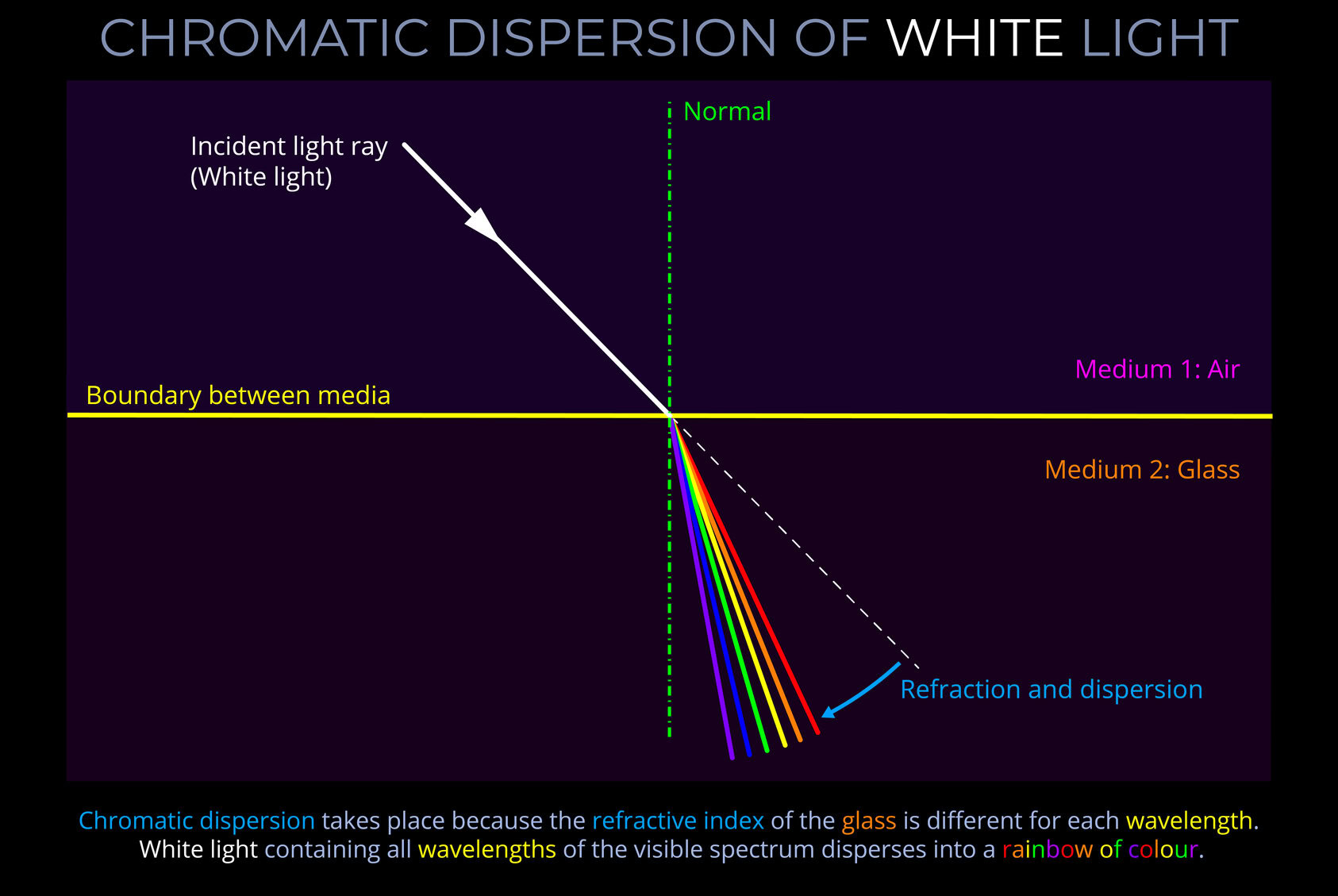
- Light travelling through a vacuum or air isn’t visible to our eyes unless it interacts with something.
- The term white light can have two meanings:
- It can refer to a combination of all wavelengths of visible light traveling through space, regardless of observation.
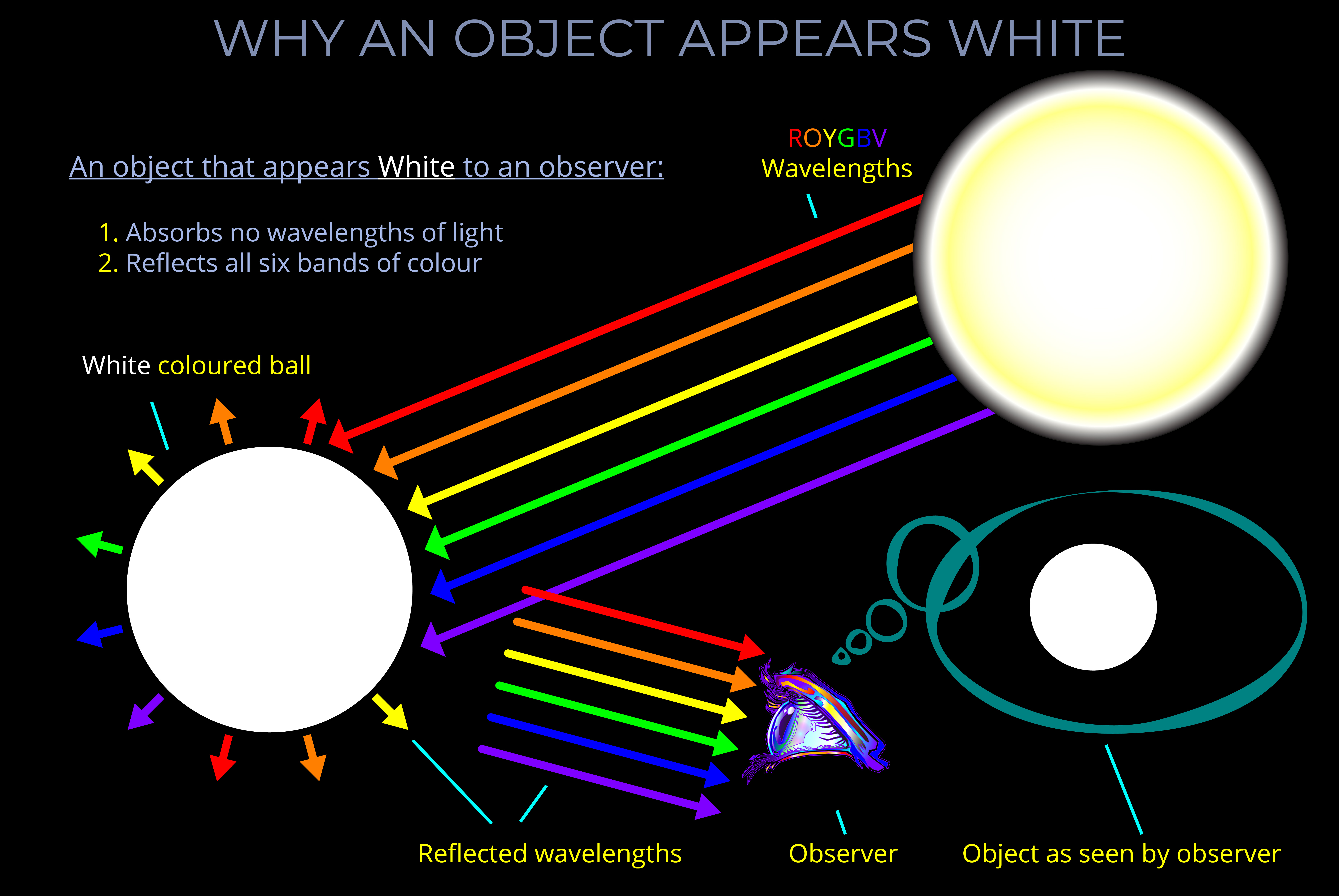
- What a person sees when all colours of the visible spectrum hit a white or neutral-coloured surface.
- The human eye sees white when the wavelengths of light associated with the three primary colours – red, green, and blue (RGB) – are projected onto an achromatic surface.
- White light appears as different colours to an observer when some wavelengths of light are reflected by an object’s surface while others are absorbed. Artificial light sources usually emit light with a varied distribution of wavelengths or intensities, so they don’t typically emit pure white light.
- While there isn’t a single, distinct definition for white light, it’s fair to say that in any given situation:
- White is the lightest possible colour.
- White is an achromatic colour, which means a colour without hue, but with maximum saturation and brightness.
- Colour constancy, the ability to perceive colours as relatively constant, even under changing lighting conditions, enables human observers to see very different whites as appearing the same.
Why do Light Bulbs Glow if Light is Invisible?
- Incandescent light bulbs work by passing an electrical current through a thin tungsten filament which has high electrical resistance.
- This resistance causes the filament’s electrons to vibrate and heat up. As the filament gets hot, it emits light.
- The yellowish-white colour we see comes primarily from the heated tungsten surface itself.
- Light bulbs, like most hot objects, also emit wavelengths of light that are outside the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum.
- These invisible wavelengths are typically infrared radiation, which we feel as heat. Additionally, a small portion of the light emitted might be ultraviolet, but these are blocked by the glass bulb.