Rainbow colours are the colours seen in rainbows and in other situations where visible light separates into its different wavelengths and the spectral colours corresponding with each wavelength become visible to the human eye.
- The rainbow colours (ROYGBV) in order of wavelength are red (longest wavelength), orange, yellow, green, blue and violet (shortest wavelength).
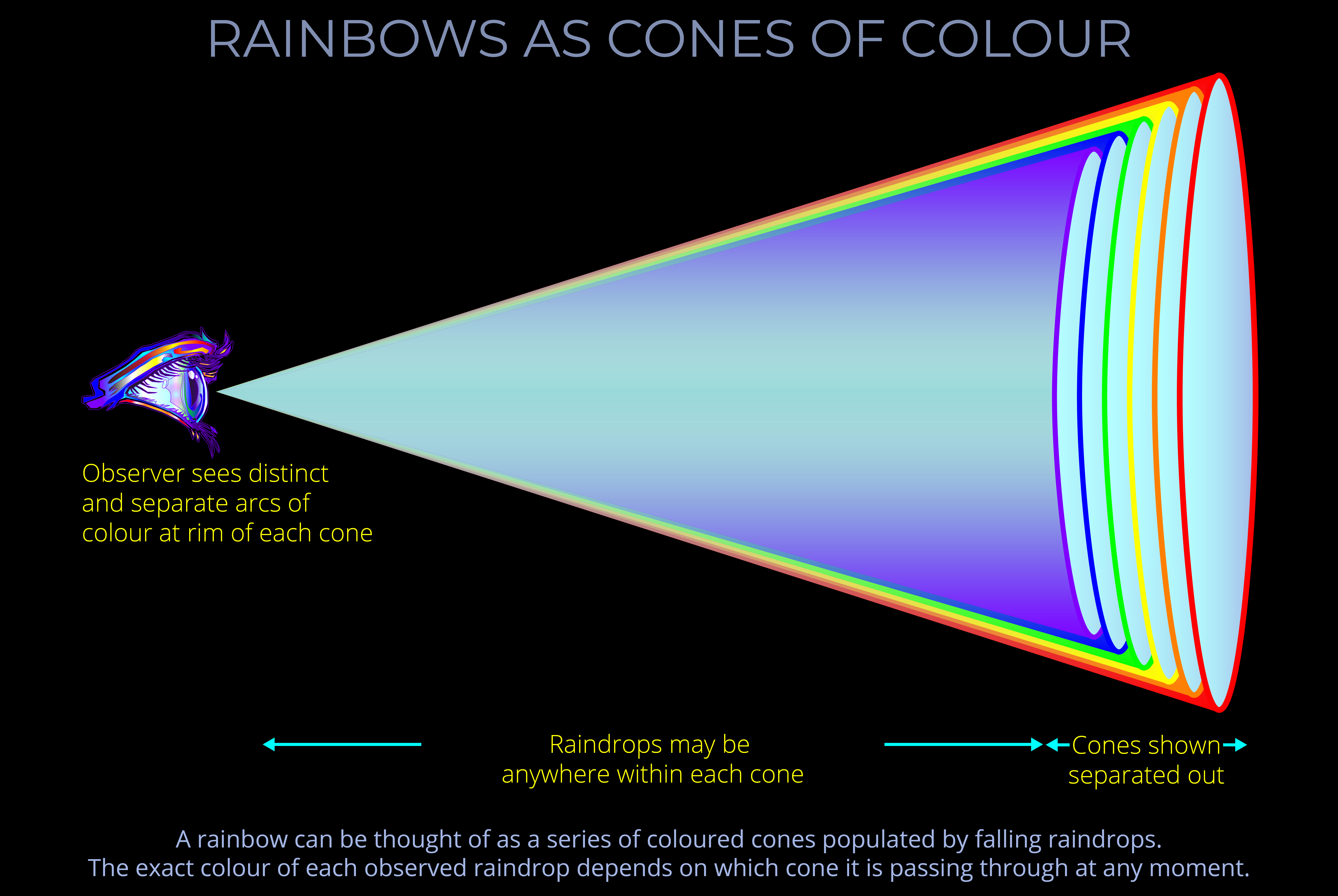
- It is the sensitivity of the human eye to this small part of the electromagnetic spectrum that results in our perception of colour.
- The names of rainbow colours is a matter more closely related to the relationship between perception and language than anything to do with physics or scientific accuracy. While the spectrum of light and the colours we see are both determined by wavelength, it’s our eyes and brains that turn these differences in light into the colours we experience.
- In the past, rainbows were sometimes portrayed as having seven colours: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet.
- Modern portrayals of rainbows reduce the number of colours to six spectral colours, ROYGBV.
- In reality, the colours of a rainbow actually form a continuous spectrum and there are no clear boundaries between one colour and the next.