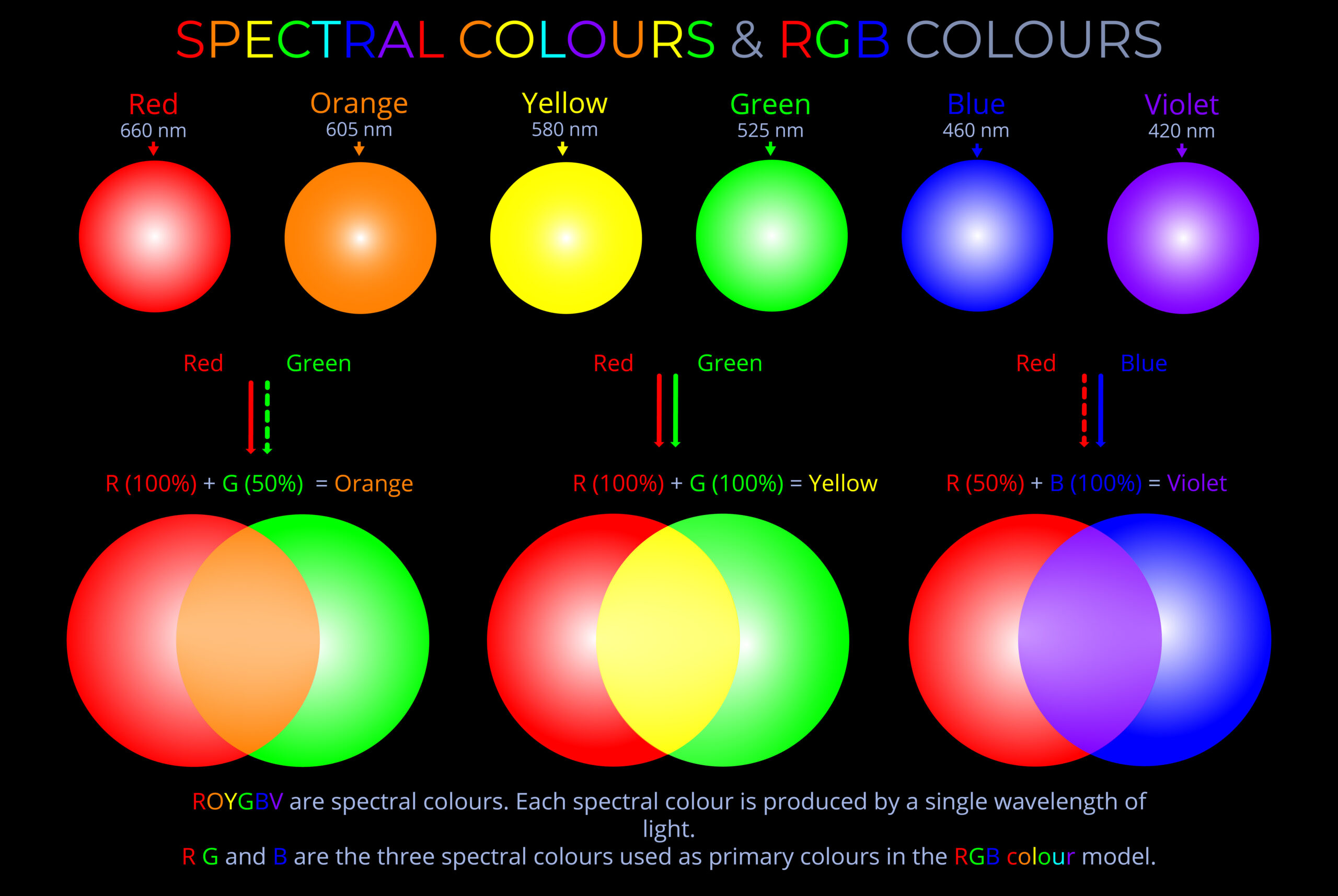
A non-spectral colour is a colour that is not present in the visible spectrum and cannot be produced by a single wavelength or narrow band of wavelengths of light.
- While spectral colours are evoked by a single wavelength of light in the visible spectrum, non-spectral colours are produced by a combination of spectral colours from different parts of the spectrum.
- Colours evoked by a single wavelength of light are often described as being produced by monochromatic light.
- Magenta, pink, cyan and brown are examples of non-spectral colours produced by combining different wavelengths of light:
- Blue and red = magenta
- Red and purple = pink
- Blue and green = cyan
- Red, yellow and blue = brown
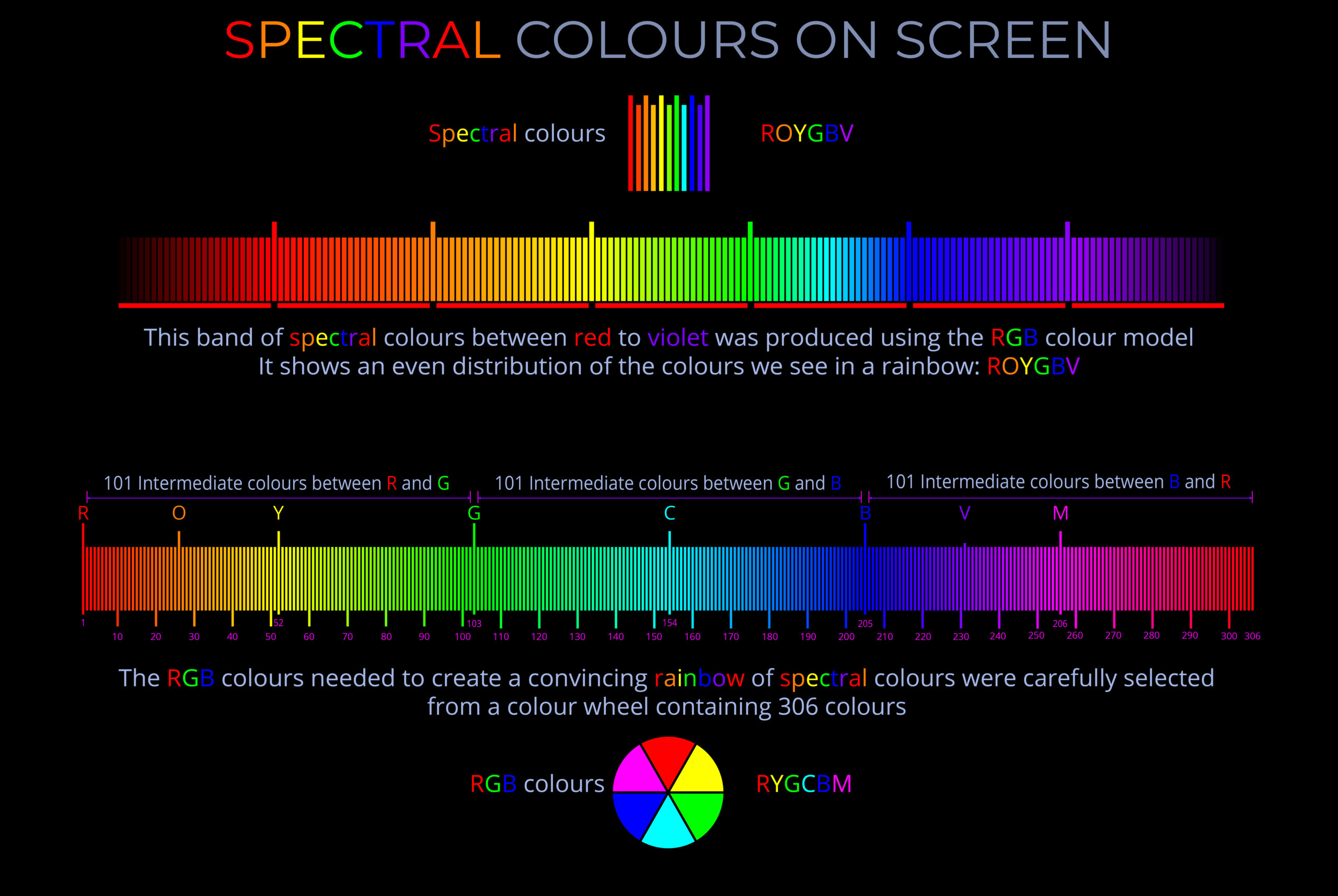
- When we look around us, the colours of things we see rarely include pure spectral colours but are more likely composed of narrow bands of contiguous wavelengths.
- Since both the RGB and CMY colour models mix primary colours from different parts of the visible spectrum, digital screens and digital printers produce non-spectral colours.
- The RGB colour model generates a complete range of colours on TVs, computers and phones by blending the primary colours (red, green and blue) in varying proportions.
- The CMY colour model produces a full spectrum of colours by blending the primary colours of cyan, magenta, and yellow in varying proportions.
How spectral colours produce non-spectral colours
- When spectral colours from different parts of the visible spectrum are combined, they stimulate multiple types of cone cells in the human eye, leading to the perception of intermediate hues that do not correspond to any single wavelength.
- For example, when red light (long wavelengths) and blue light (short wavelengths) are combined, they stimulate both the red-sensitive and blue-sensitive cones, resulting in the perception of magenta, a colour that is not present in the spectrum.
- Similarly, combining green and blue light stimulates both green-sensitive and blue-sensitive cones, resulting in the perception of cyan. The mixing of different spectral colours in varying proportions leads to the creation of a wide range of non-spectral colours, each with its own unique appearance.
- A non-spectral colour is a colour that is not present in the visible spectrum and cannot be produced by a single wavelength or narrow band of wavelengths of light.
- While spectral colours are evoked by a single wavelength of light in the visible spectrum, non-spectral colours are produced by a combination of spectral colours from different parts of the spectrum.
- Colours evoked by a single wavelength of light are often described as being produced by monochromatic light.
- Magenta, pink, cyan and brown are examples of non-spectral colours produced by combining different wavelengths of light:
- Blue and red = magenta
- Red and purple = pink
- Blue and green = cyan
- Red, yellow and blue = brown