- The greyscale colour model is used for:
- Converting colour images to black-and-white.
- Creating black-and-white images by cameras, scanners, and other input devices.
- Three algorithms, the lightness method, weighted average method and luminosity method, are used for greyscale conversion.
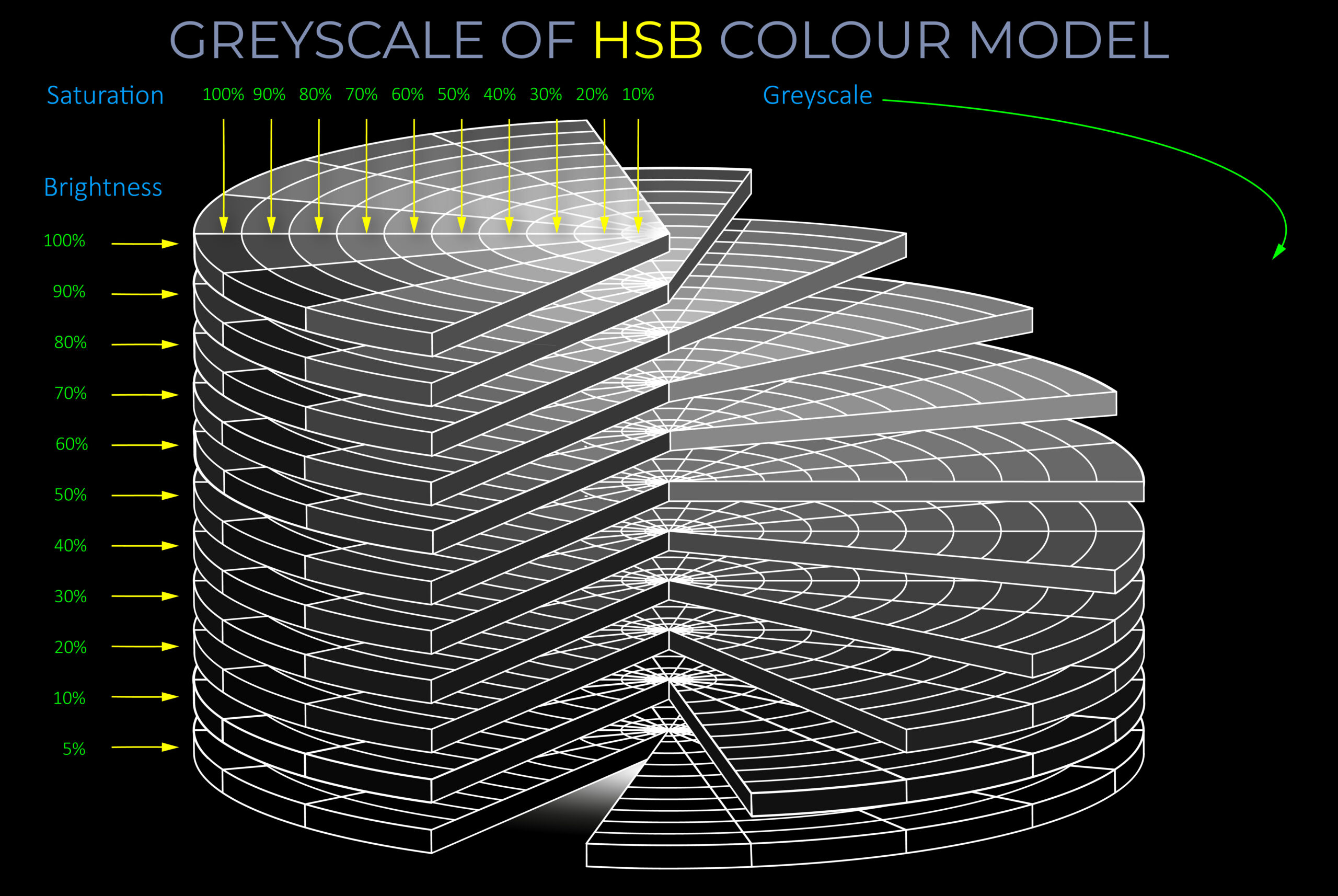
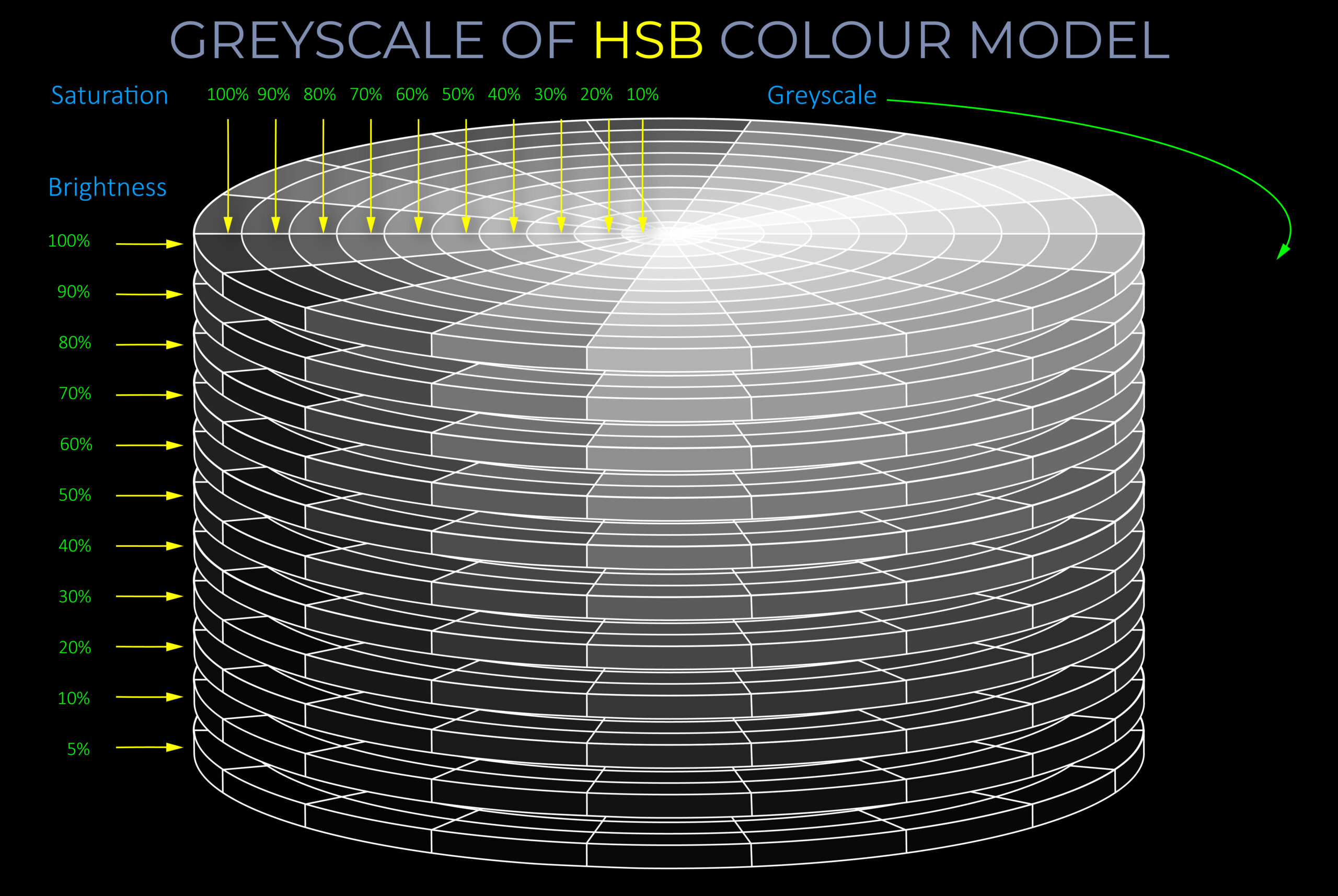
- A greyscale colour model is not a linear scale from black to white but a way of converting colour brightness to show tonal relationships.
- Converting digital images to greyscale involves assigning every pixel the correct level of brightness.
- When fully saturated spectral colours are converted to greyscale, their brightness is usually between 11% and 89%. So:
- Red = 70%
- Orange = 40.38%
- Yellow = 11%
- Green = 41%
- Blue = 89%
- Violet = 74.06%
- Any RGB decimal colour value can be converted to greyscale, so the decimal colour value corresponding with cyan is 178, 178, 178.
- Any HSB colour value can be converted to greyscale, with the HSB value for pure yellow being Hue = 0, Saturation = 0, Brightness = 11.00%.
References
- In the context of images, a greyscale model represents a picture using only shades of grey, from pure black to pure white. There’s no colour information included. This is commonly used in black and white photography or to convert colour images into black and white.
- The greyscale colour model is used for:
- Converting colour images to black-and-white.
- Creating black-and-white images by cameras, scanners, and other input devices.
- Three algorithms, the lightness method, weighted average method and luminosity method, are used for greyscale conversion.
- A greyscale colour model is not a linear scale from black to white but a way of converting colour brightness to show tonal relationships.
- Converting digital images to greyscale involves assigning every pixel the correct level of brightness.
- When fully saturated spectral colours are converted to greyscale, their brightness is usually between 11% and 89%.