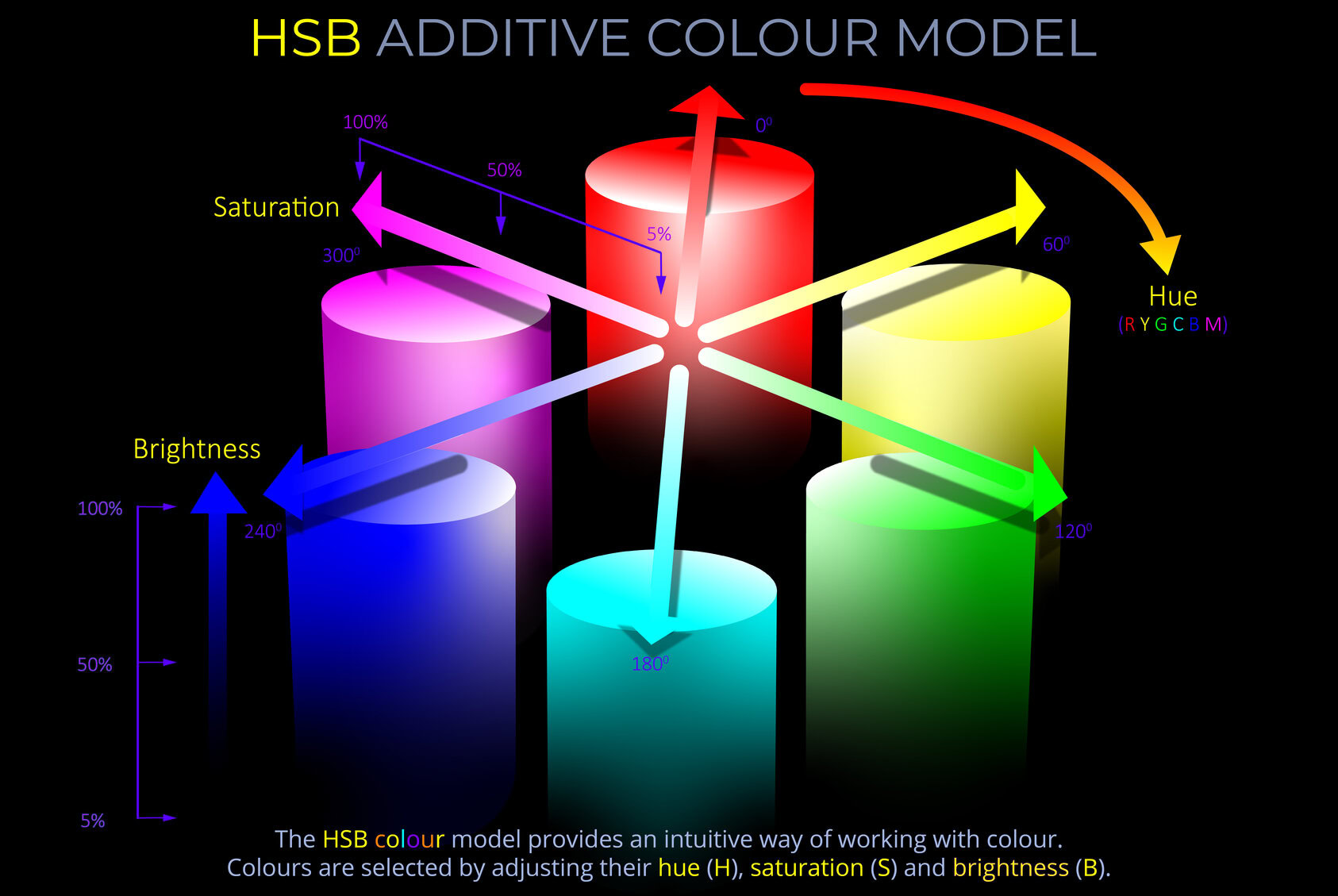
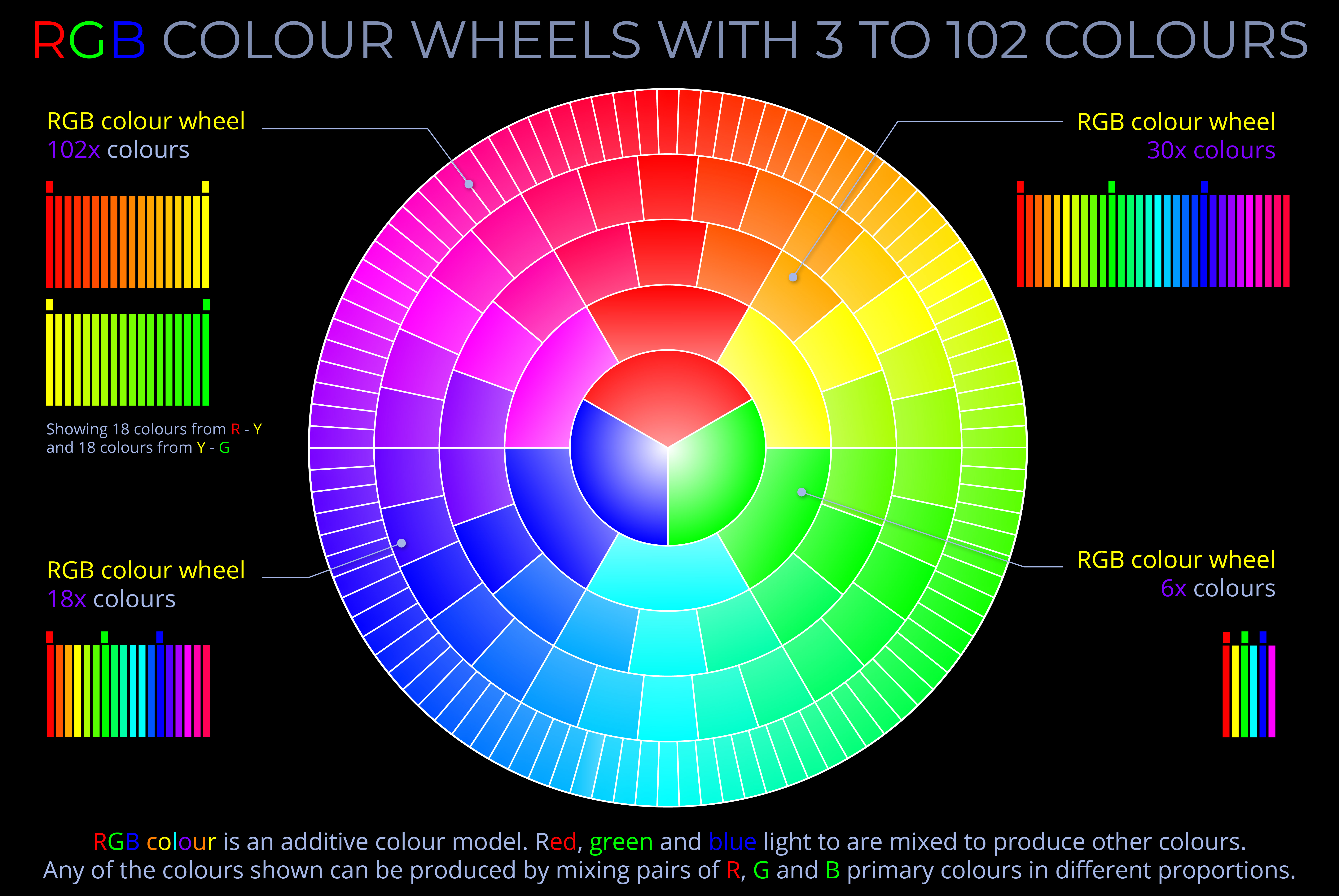
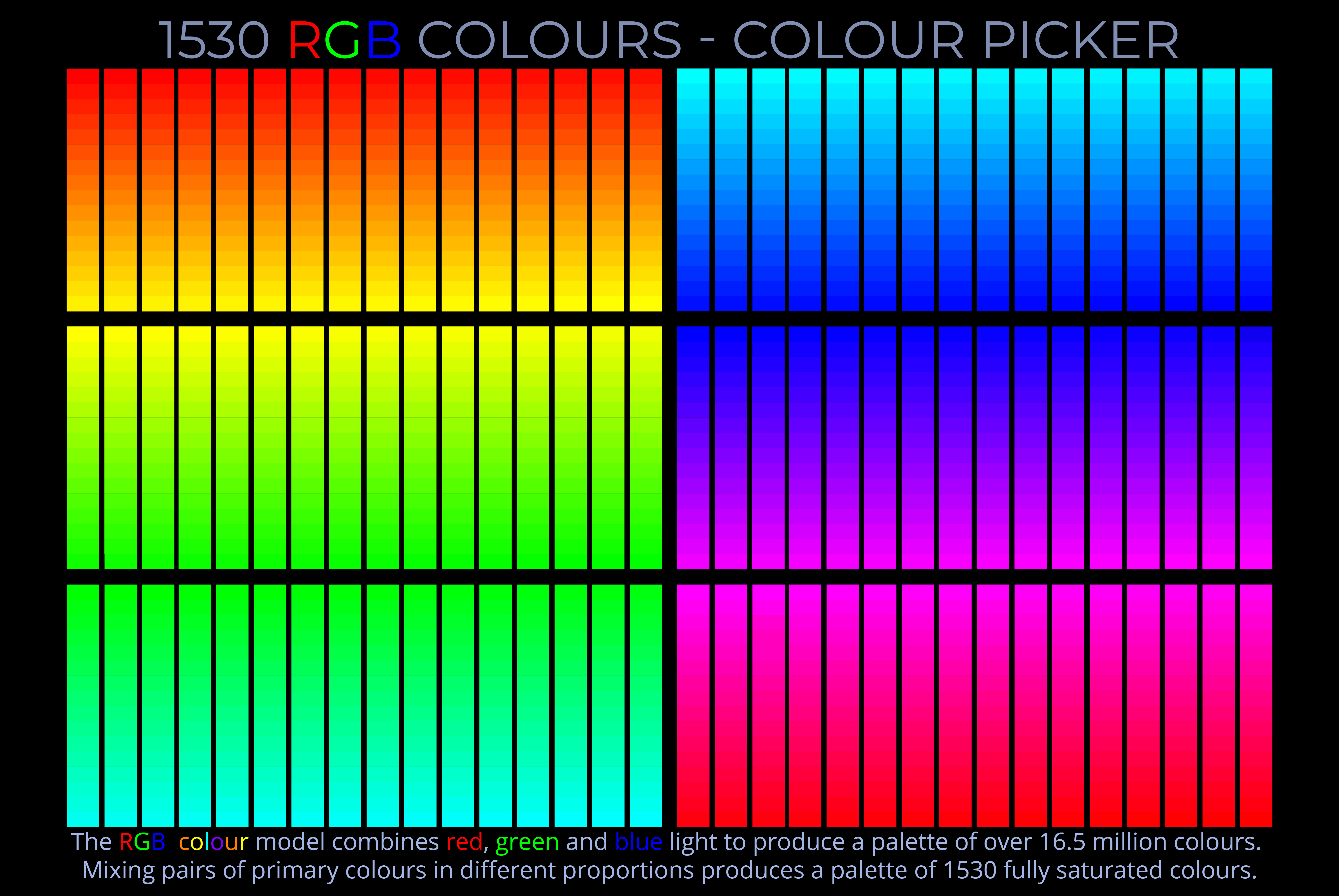
An additive colour model explains how different coloured lights (such as LEDs or beams of light) are mixed to produce other colours. The RGB colour model and HSB colour model are examples of additive colour models.
- Additive colour refers to the methods used and effects produced by combining or mixing different wavelengths of light.
- Additive colour models such as the RGB colour model and HSB colour model can produce vast ranges of colours by combining red, green, and blue lights in varying proportions.
- An additive approach to colour is used to achieve precise control over the appearance of colours on the digital screens of TVs, computers, and phones.
- Subtractive colour models such as the CMY colour model provide methods for mixing pigments such as dyes, inks, or paints to produce different colours.
- Both additive and subtractive colour models rely on mixing primary colours in different proportions:
- CMY refers to the primary colours cyan (C), magenta (M) and yellow (Y).
- CMYK refers to the primary colours cyan, magenta and yellow plus black (K).
- RYB refers to the primary colours red (R), yellow (Y) and blue (B).
- Both additive and subtractive colour models can be studied and understood by exploring colour wheels.
No posts found.