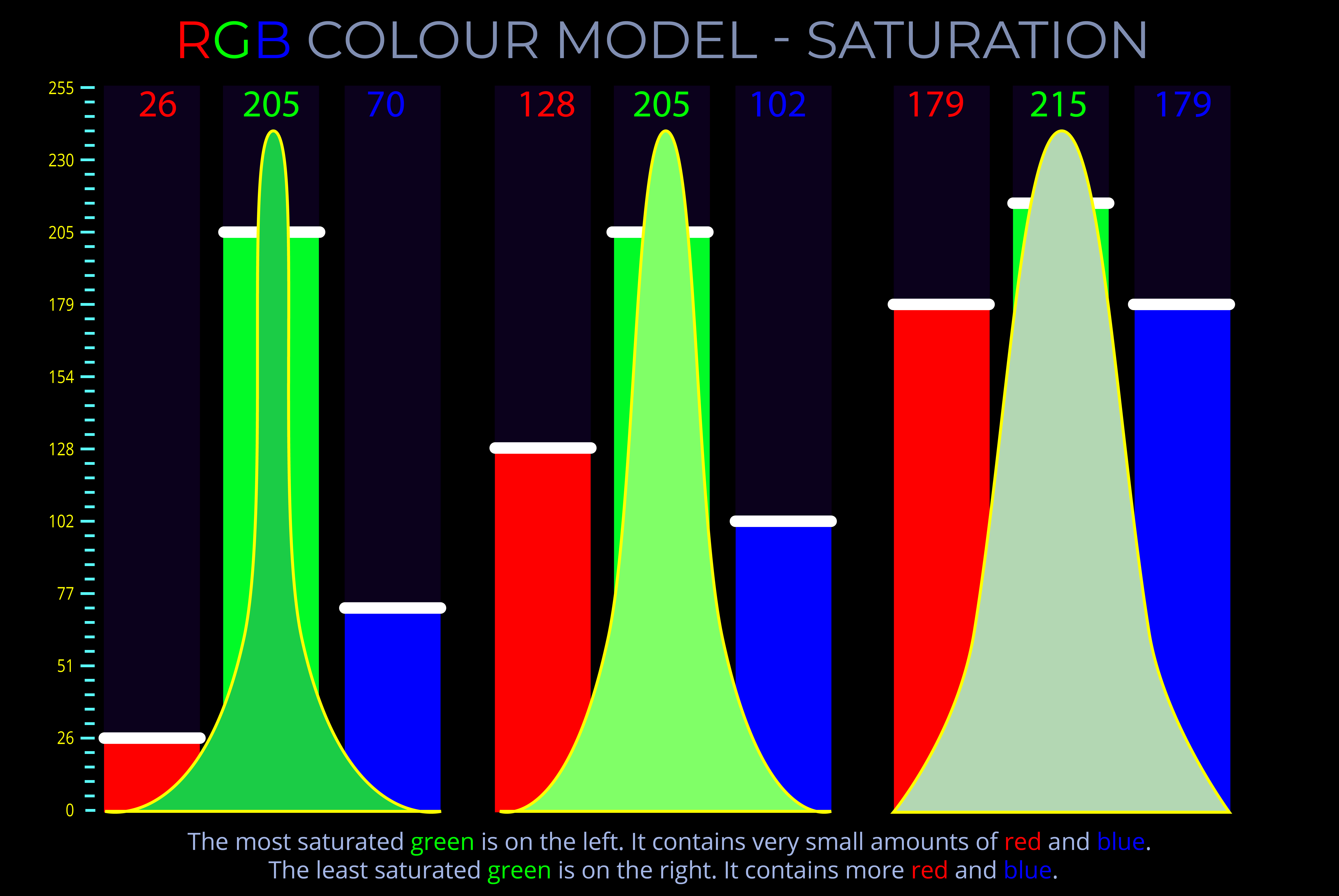
RGB Colour Model – Saturation
£0.00
This diagram is a new addition to the site! More information will be added ASAP 🙂
Description
RGB Colour Model - Saturation
TRY SOME QUICK QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS TO GET STARTED
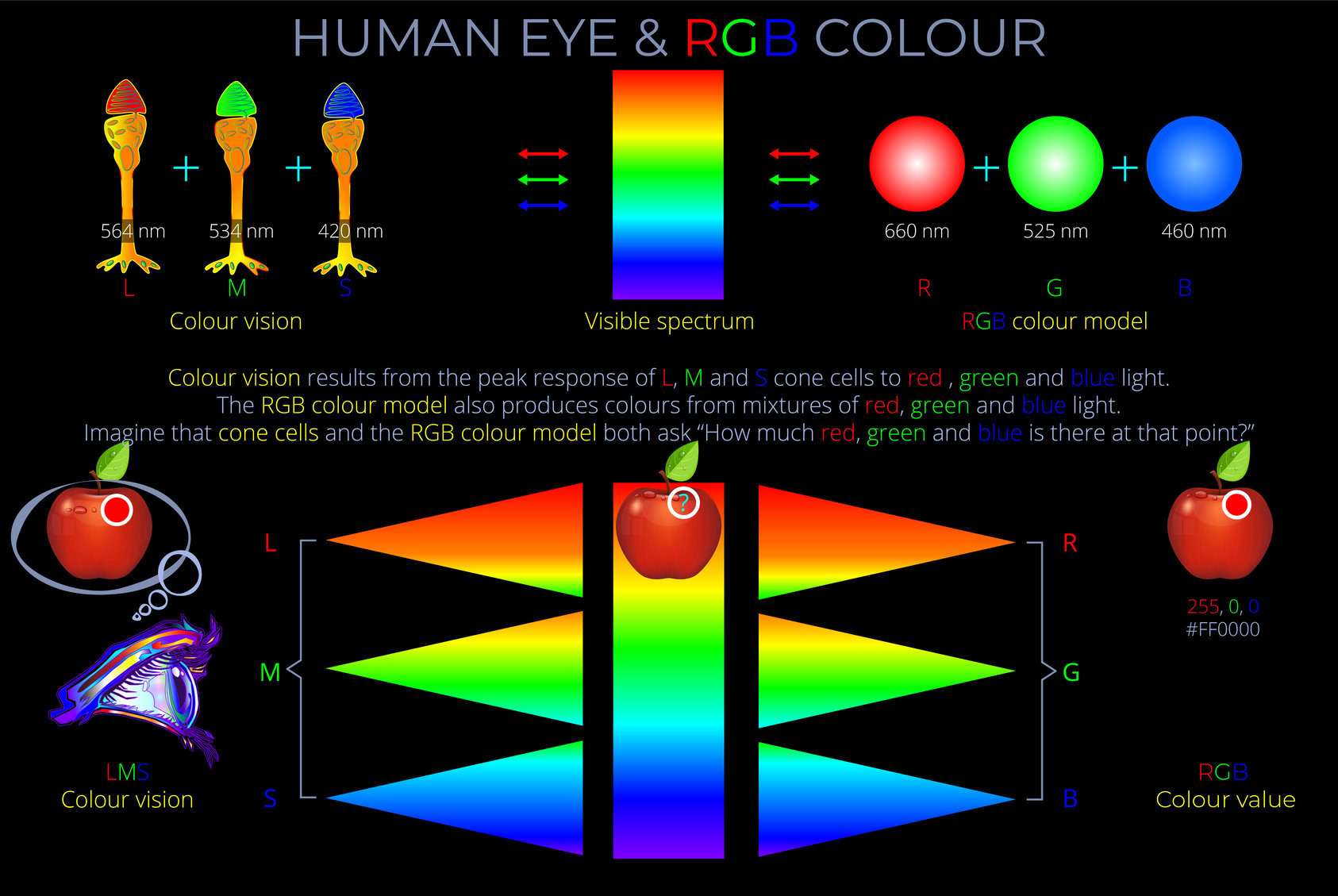
RGB refers to the colours red, green and blue. These are the primary colours used by the RGB colour model to mix wavelengths of light to produce a palette of as many as 16 million colours.
The RGB colour model uses colour values that identify how much red, green and blue light is present in a colour. The HSB colour model uses colour values to identify the hue and the level of saturation and brightness.
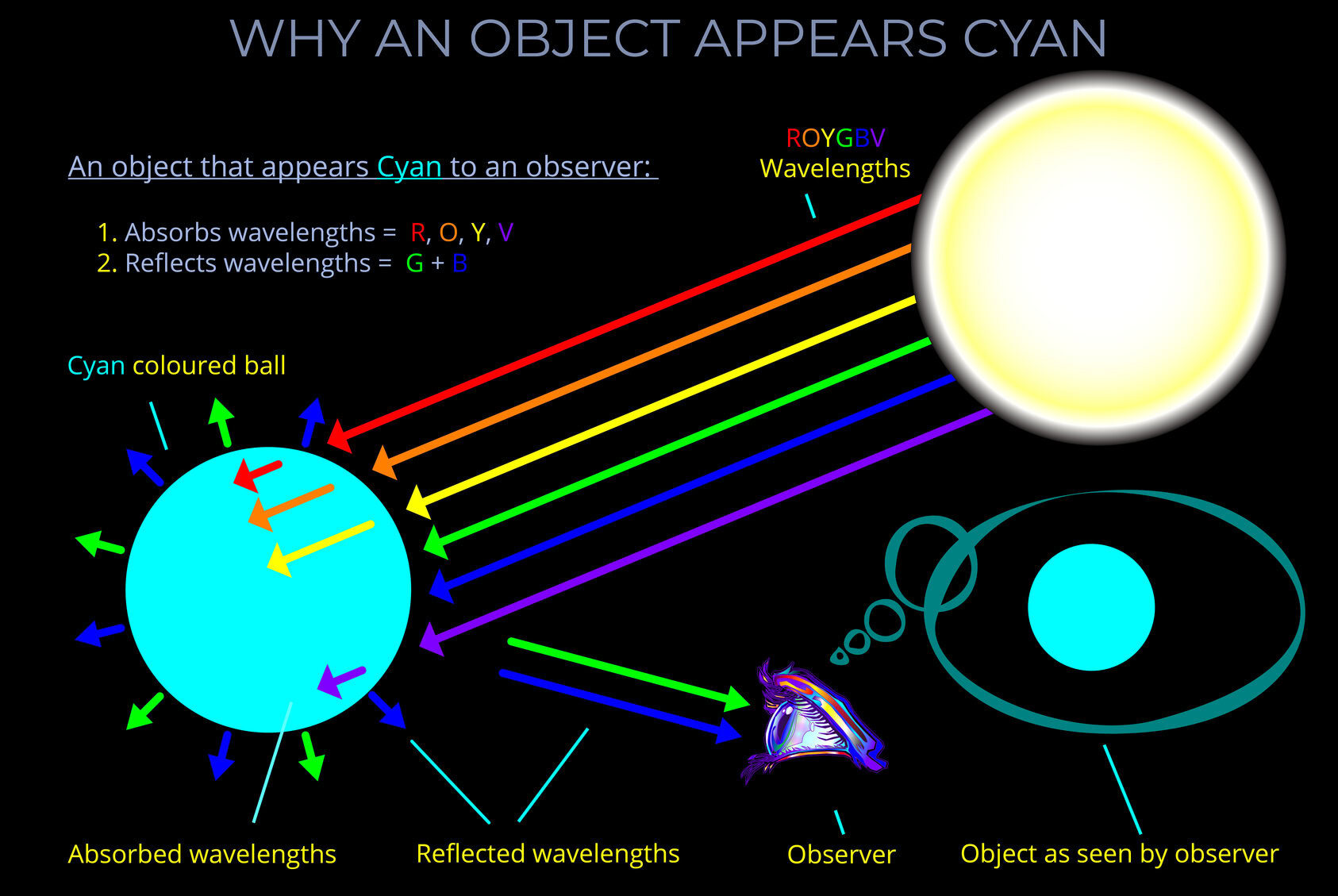
In the RGB colour model green and blue are the two primary colours that together make cyan!
RGB is a colour model used to produce a full palette of colours by mixing red, green and blue light sources in different proportions.
Red, green and blue are the three primary colours in the RGB colour model.
About the diagram
Some key terms
RGB colour is an additive colour model in which red, green and blue light is combined to reproduce a wide range of other colours.
- The primary colours in the RGB colour model are red, green and blue.
- In the RGB model, different combinations and intensities of red, green, and blue light are mixed to create various colours. When these three colours are combined at full intensity, they produce white light.
- Additive colour models are concerned with mixing light, not dyes, inks or pigments (these rely on subtractive colour models such as the RYB colour model and the CMY colour model).
- The RGB colour model works in practice by asking three questions of any colour: how red is it (R), how green is it (G), and how blue is it (B).
- The RGB model is popular because it can easily produce a comprehensive palette of 1530 vivid hues simply by adjusting the combination and amount of each of the three primaries it contains.
Saturation refers to the perceived difference between one colour and another in terms of its purity and vividness.
- A fully saturated colour appears bright and vibrant because it has a single strong dominant hue.
- A freshly cut tomato is a good example of a saturated colour with a strong red hue.
- A saturated colour is a unique spectral colour produced by a single wavelength (or a narrow band of wavelengths) of light.
- A fully saturated colour (100%) is the purest version of a hue.
- Unsaturated colours (0-10%) can appear:
- Misty or milky the nearer they are to white.
- Dull and washed out as their hue disappears leaving achromatic grey tones.
- The hue of a vivid colour appears to be at full strength and can leave an after-image of its complementary colour as an observer looks away.