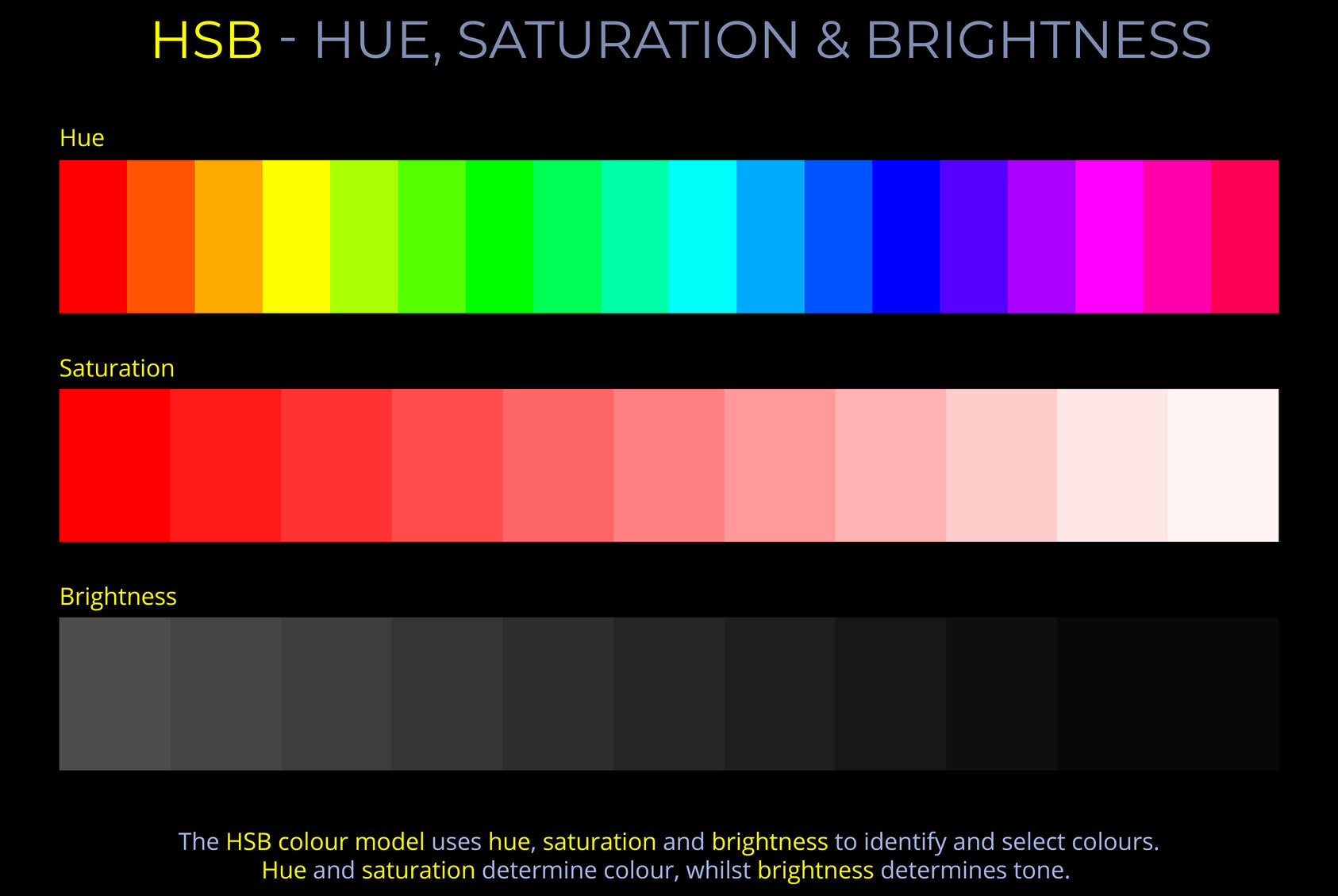
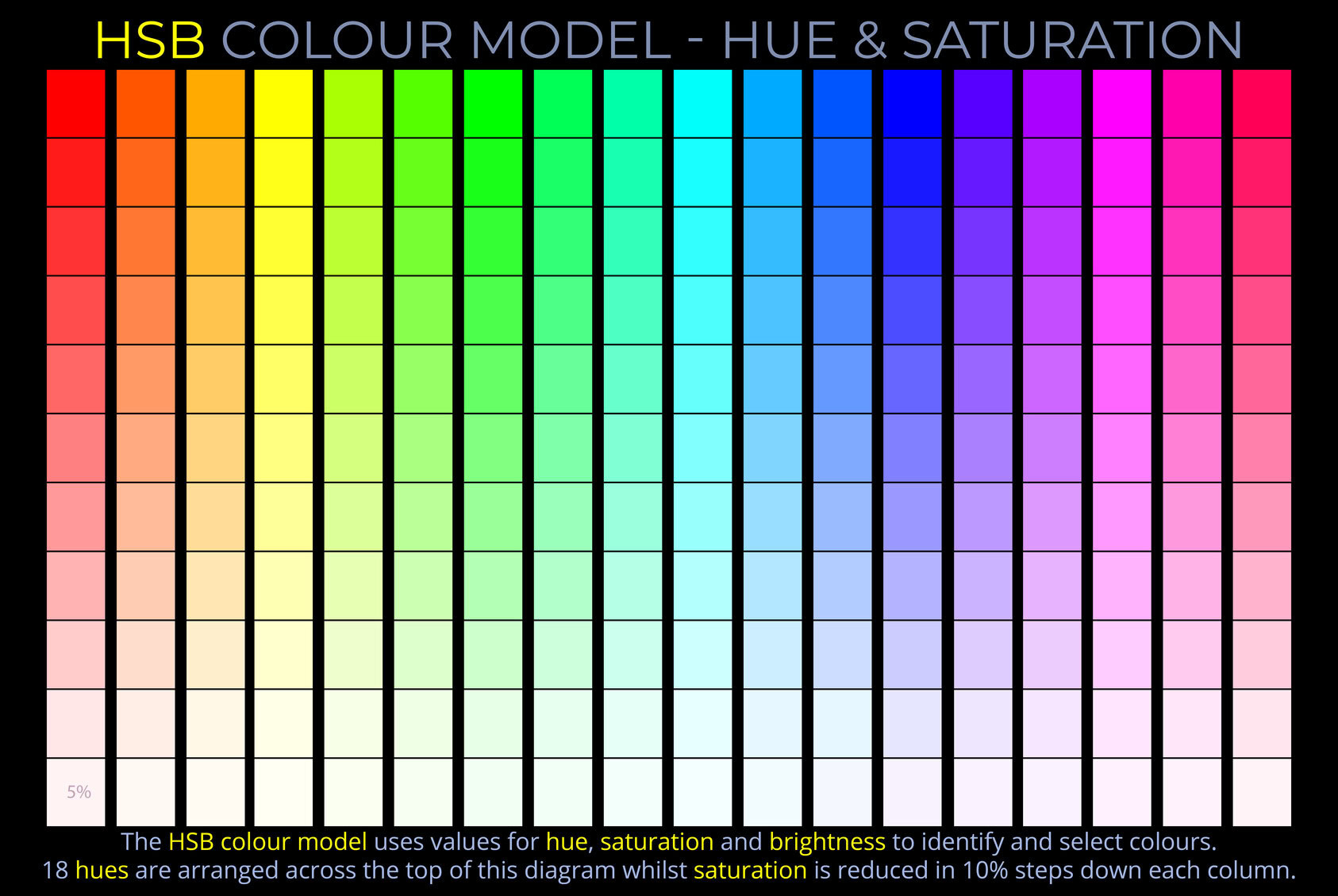
In colour theory, tone refers to a colour’s relative lightness or darkness, independent of its hue (colour) or saturation (intensity). A darker tone of a hue can be produced by reducing its brightness in additive colour models (like RGB or HSB) or by adding black or a darker colour in subtractive models (like CMY or RYB). The result is a desaturated, muted version of the original colour.
- In the context of additive colour models such as RGB or HSB, a darker tone of a hue is produced by reducing its colour brightness. The result is a desaturated, muted version of the original colour.
- In the context of subtractive colour models such as CMY and RYB, A darker tone (or shade) of a colour is achieved by adding black or a darker colour to it. The result is a desaturated, muted version of the original colour.
- In photography, tone refers to the different shades of grey that can be produced, ranging from pure white to pure black.
- Here, tone describes the relative darkness or lightness of a specific shade of grey.
- A greyscale image is created by discarding hue information from a range of colours. The resulting shades of grey reflect the original colours’ luminance (light intensity) but may not perfectly match their perceived brightness.
- Whilst yellow appears to have a very light tone when converted to greyscale, blue appears to have a very dark tone.
- In the context of a greyscale, tone is used to describe the relative darkness or lightness of a specific shade of grey.
- A greyscale is the result of removing hue from a range of colours leaving their saturation and brightness unaffected.
- More sophisticated methods of producing a greyscale use specific algorithms to create images that better represent the perceived brightness of the original colours.
- Tone and value are closely related concepts. Tone describes the perceived lightness or darkness within a colour context, while value refers to the objective amount of light reflected or emitted, independent of colour.
- To clarify this difference, think of value as a light meter reading that measures the amount of light reflecting off a surface. This reading would be a numerical value, independent of any colour information.
- In colour theory, tone refers to a colour’s relative lightness or darkness, independent of its hue (colour) or saturation (intensity). A darker tone of a hue can be produced by reducing its brightness in additive colour models (like RGB or HSB) or by adding black or a darker colour in subtractive models (like CMY or RYB). The result is a desaturated, muted version of the original colour.
- In the context of additive colour models such as RGB or HSB, a darker tone of a hue is produced by reducing its colour brightness. The result is a desaturated, muted version of the original colour.
- In the context of subtractive colour models such as CMY and RYB, A darker tone (or shade) of a colour is achieved by adding black or a darker colour to it. The result is a desaturated, muted version of the original colour.
- In photography, tone refers to the different shades of grey that can be produced, ranging from pure white to pure black.