A digital screen (or digital display) is an output device for the presentation of visual information. RGB digital screens are used in TVs, computers, phones and projectors.
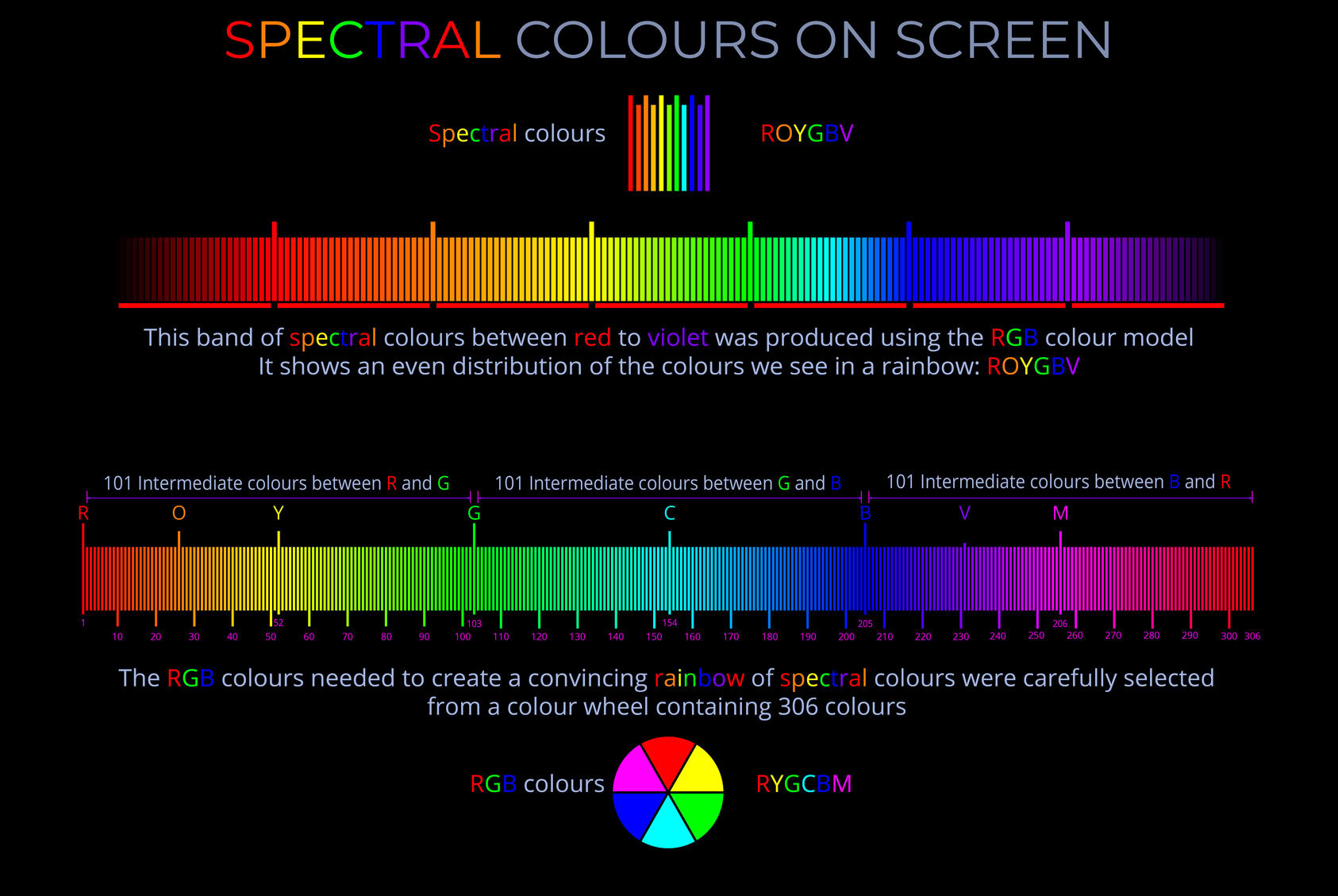
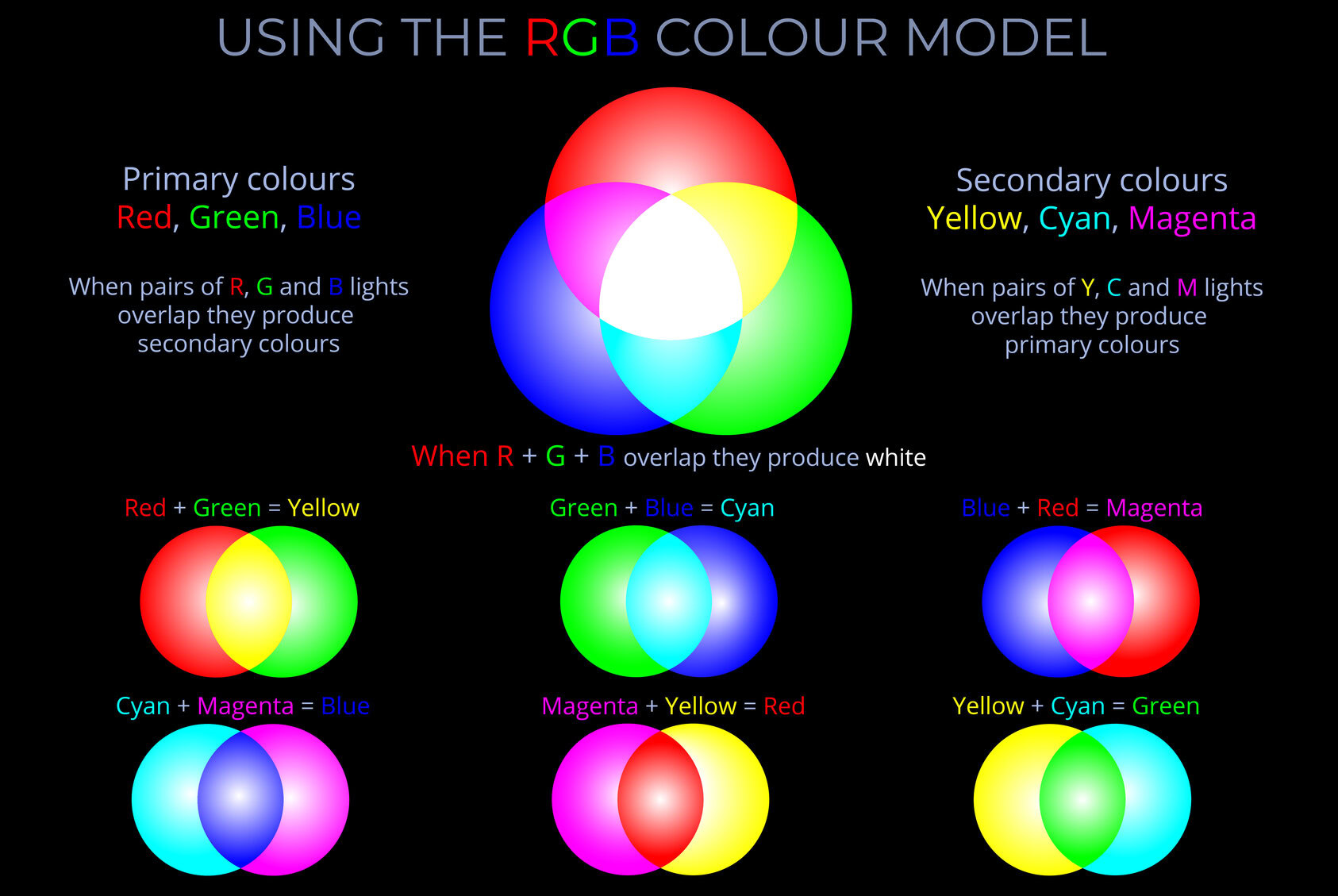
- Digital screens use the RGB (red, green, blue) colour model to represent and display information.
- The range of colours that different types of screen can display depends on their technology and specifications.
- Many RGB digital screens include light-emitting diodes (LEDs) that are able to directly or indirectly adjust the intensity of red, green and blue light within each addressable component of the screen to produce pixels of colour that together produce an image.
- LEDs are typically used to backlight LCD (liquid crystal display )screens. Different colours are created by colour filters and by adjusting the amount and the polarization of light that is allowed to pass through the crystal sub-pixels that make up each pixel on the screen.
- In an OLED displays, each pixel provides its own illumination. The organic materials in the OLED emit light when an electric current is applied. Because each pixel can be turned on or off individually, OLED displays are able to achieve deeper blacks (by completely turning off pixels) and a higher contrast ratio compared to LED-backlit LCD screens.
- Fully saturated hues (colours) are produced when pixels in an area of the screen are at maximum intensity (brightness).
- Darker tones of any hue are produced by decreasing the intensity of light produced by each pixel.
- Some digital screens use technologies other than RGB to create images. For example, some E-ink screens used in e-readers can only display shades of grey.