The HSB colour model is similar to the RGB colour model insofar as it is an additive model based on RGB primary colours.
The strength of the HSB colour model is that it provides a more intuitive way than the RGB colour model to select and adjust colours in software applications used for graphic design, web development and photography.
Both RGB and HSB are additive colour models with red, green and blue primary colours. But whilst RGB relies on directly adjusting the amount of red, green and blue light needed to produce other colours the HSB colour model relies on adjusting hue, saturation and brightness.
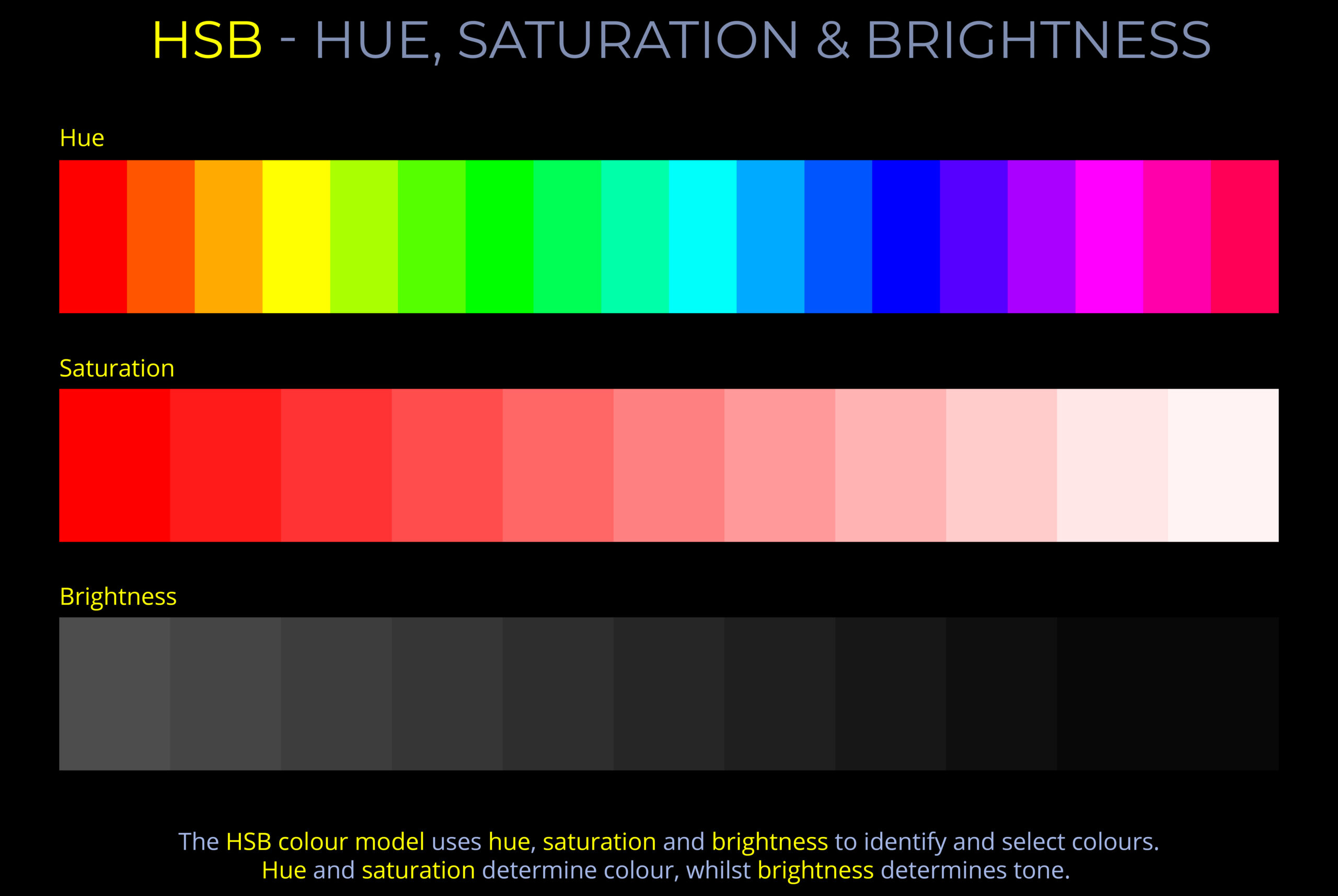
- Hue refers to the perceived difference between colours and is usually described using names such as red, yellow, green, or blue.
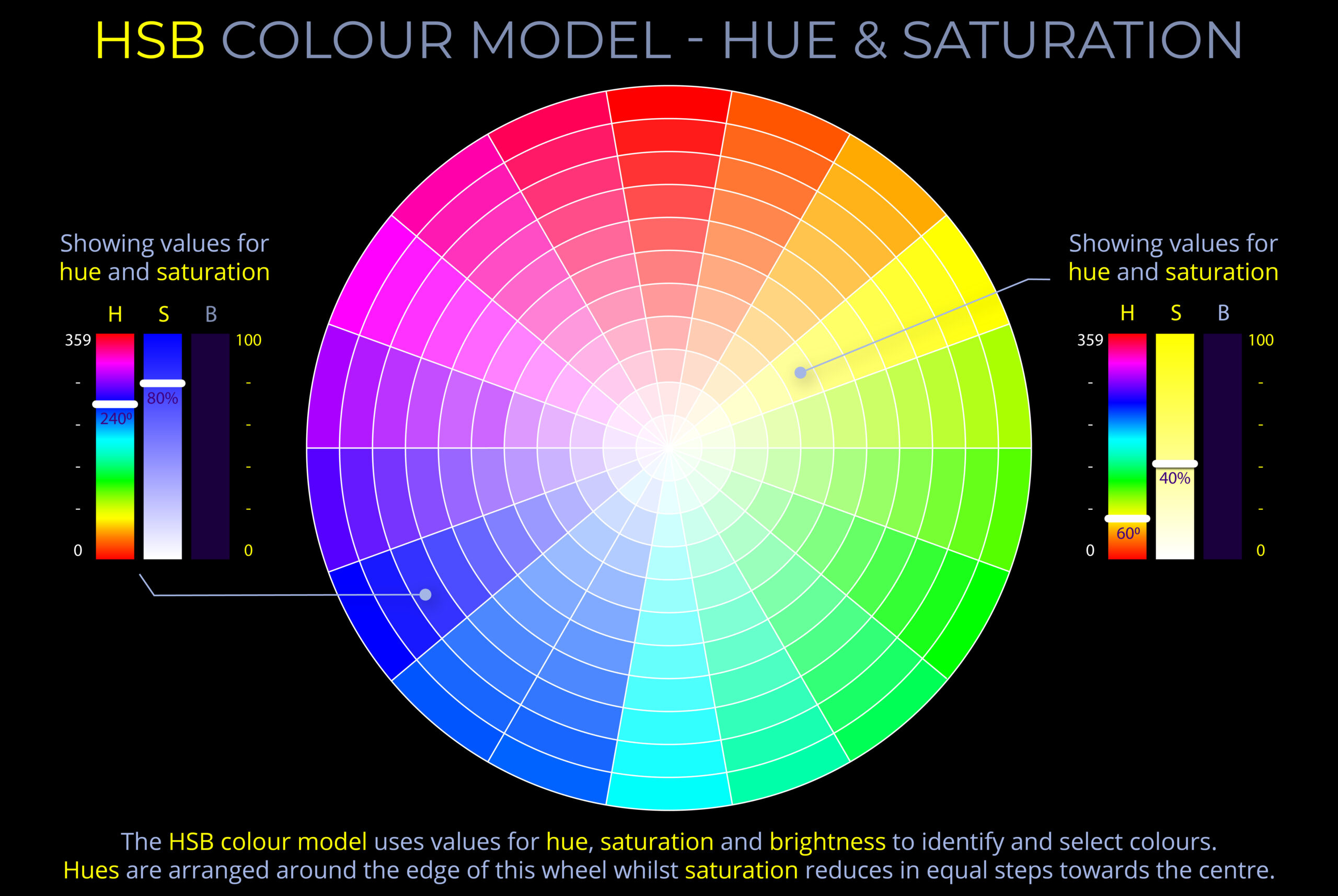
- Hue can be measured as a location on an HSB colour wheel and expressed as a degree between 0 and 360.
- Saturation refers to the vividness of a colour compared to an unsaturated colour.
- Saturation is measured between a fully saturated colour (100%) and an unsaturated colour (0%)that appears either:
- Dull and washed out until all colour disappears, leaving only a monochromatic grey tone (0%).
- Misty or milky the nearer they are to white.
- On many HSB colour wheels, saturation decreases from the edge to the centre.
- Saturation is measured between a fully saturated colour (100%) and an unsaturated colour (0%)that appears either:
- Brightness refers to the perceived difference in the appearance of colours under ideal sunlit conditions compared to poor lighting conditions where a hue’s vitality is lost.
- Brightness can be measured as a percentage from 100% to 0%.
- As the brightness of a fully saturated hue decreases, it appears progressively darker and achromatic.
HSB colour model in practice
In the implementation of the HSB colour model used in Adobe Illustrator CC:
- The HSB colour model can be accessed in the Colour Panel.
- If the Colour Panel is not visible, find it in the Windows menu.
- To switch from the default RGB setting to HSB, click on the hamburger menu (icon with three horizontal lines) in the top right of the panel.
- Hue, saturation, and brightness can all be adjusted using the sliders or by clicking anywhere on the HSB Spectrum.
- To enter an HSB colour using hexadecimal notation, switch back to the RGB colour model using the hamburger menu and enter the code in the provided window.
- HSB notation typically appears as follows:
- H = 00, S = 100%, B = 100% produce a fully saturated primary red hue with maximum brightness.
- H = 00, S = 100%, B = 50% produce a fully saturated primary red hue that has lost some of its brightness so appears much darker in colour.
- H = 00, S = 50%, B = 100% produce a bright but less saturated primary red hue.
- The HSB colour model is similar to the RGB colour model insofar as it is an additive model based on RGB primary colours.
- The strength of the HSB colour model is that it provides a more intuitive way than the RGB colour model to select and adjust colours in software applications used for graphic design, web development and photography.
- Both RGB and HSB are additive colour models with red, green and blue primary colours. But whilst RGB relies on directly adjusting the amount of red, green and blue light needed to produce other colours the HSB colour model relies on adjusting hue, saturation and brightness.
- Hue refers to the perceived difference between colours and is usually described using names such as red, yellow, green, or blue.
- Hue can be measured as a location on an HSB colour wheel and expressed as a degree between 0 and 360.
- Saturation refers to the vividness of a colour compared to an unsaturated colour.
- Saturation is measured between a fully saturated colour (100%) and an unsaturated colour (0%)that appears either:
- Dull and washed out until all colour disappears, leaving only a monochromatic grey tone (0%).
- Misty or milky the nearer they are to white.
- On many HSB colour wheels, saturation decreases from the edge to the centre.
- Saturation is measured between a fully saturated colour (100%) and an unsaturated colour (0%)that appears either:
- Brightness refers to the perceived difference in the appearance of colours under ideal sunlit conditions compared to poor lighting conditions where a hue’s vitality is lost.
- Brightness can be measured as a percentage from 100% to 0%.
- As the brightness of a fully saturated hue decreases, it appears progressively darker and achromatic.